Unit Test (Solutions): Reproduction in Plants | Science Class 7 (Old NCERT) PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
Maximum Marks: 30
Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question numbers 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1: Which of the following is an example of vegetative reproduction by stems? (1 Mark)
(a) Rose
(b) Mango
(c) Papaya
(d) Coconut
Ans: (a) Rose
Vegetative propagation in rose occurs through stem cutting.
Q2: What is the male reproductive part of a flower? (1 Mark)
Ans: Stamen
The stamen consists of anther and filament and produces pollen grains.
Q3: Which type of flower has both male and female reproductive parts? (1 Mark)
(a) Unisexual flower
(b) Bisexual flower
(c) Incomplete flower
(d) None of these
Ans: (b) Bisexual flower
Bisexual flowers like hibiscus and mustard contain both stamen and pistil.
Q4: Name a plant that reproduces asexually through leaves. (1 Mark)
Ans: Bryophyllum
The leaves of Bryophyllum have buds on their edges, which develop into new plants.
Q5: What is the function of pollen grains in reproduction? (1 Mark)
Ans: Pollen grains contain the male gametes, which fertilize the female gametes (ovules) in the ovary.
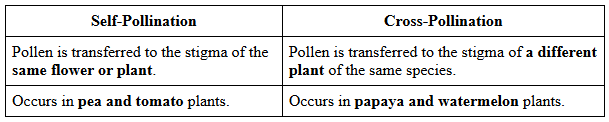
Q6: Differentiate between self-pollination and cross-pollination. (2 Marks)
Ans:
 Q7: What is the role of spores in reproduction? (2 Marks)
Q7: What is the role of spores in reproduction? (2 Marks)
Ans:
- Spores are reproductive structures found in fungi and some plants.
- They have a protective covering, allowing them to survive harsh conditions.
- When favorable conditions return, spores germinate and grow into new organisms.
Q8: How does fragmentation help in plant reproduction? Give an example. (2 Marks)
Ans:
- In fragmentation, the plant body breaks into pieces, and each piece grows into a new plant.
- Example: Spirogyra (algae) reproduces by breaking into fragments, which later grow into complete plants.
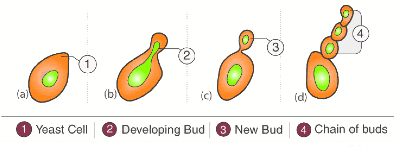
Q9: Explain the process of budding in yeast with a diagram. (3 Marks)
Ans:
- Budding is a form of asexual reproduction in yeast.
- A small outgrowth (bud) appears on the parent yeast cell.
- The bud enlarges, receives cytoplasm, and eventually detaches to become a new yeast cell.
Q10: Describe three different methods of seed dispersal with examples. (3 Marks)
Ans:
- By Wind: Light seeds with wing-like structuresfloat in the air.
- Example: Drumstick, Maple.
- By Water: Seeds with fibrous husksfloat and travel through water.
- Example: Coconut.
- By Animals: Spiny seeds attach to animal furand get carried away.
- Example: Xanthium, Urena.
Q11: How does a seed develop into a new plant? (3 Marks)
Ans:
- The seed absorbs water, softens, and swells.
- The radicle (root) emerges first, growing into the soil.
- The plumule (shoot) grows upwards towards the light.
- The stored food in the seed helps the young plant grow until it can perform photosynthesis.
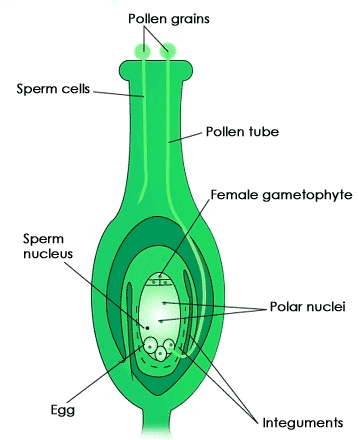
Q12: Explain the steps of fertilization in flowering plants with a diagram. (5 Marks)
Ans:
- Pollination: Pollen is transferred from the anther to the stigma.
- Pollen tube formation: The pollen grain develops a tube that grows towards the ovule.
- Fusion of gametes: The male gamete (from pollen) fuses with the female gamete (egg cell) inside the ovule.
- Zygote formation: The fertilized egg develops into a zygote, which later forms an embryo.
- Seed and fruit formation: The ovule develops into a seed, and the ovary becomes a fruit.
Q13: Describe vegetative reproduction by stem, root, and leaves with examples. (5 Marks)
Ans:
- Stem Cutting:
- A cut stem piece of a plant is planted in soil, which develops roots and shoots.
- Example: Rose, Sugarcane.
- Root Tubers:
- Thickened roots store food and develop shoot buds that grow into new plants.
- Example: Dahlia, Sweet Potato.
- Leaf Buds:
- Some plants have buds on their leaf margins that grow into new plants.
- Example: Bryophyllum.
|
111 videos|435 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): Reproduction in Plants - Science Class 7 (Old NCERT)
| 1. What are the main types of reproduction in plants? |  |
| 2. How do flowering plants reproduce? |  |
| 3. What is the role of pollinators in plant reproduction? |  |
| 4. What is asexual reproduction in plants, and what are some methods? |  |
| 5. Why is genetic diversity important in plant reproduction? |  |
















