Unit Test (Solutions): Energy — How Things Work | Our Wondrous World Class 5 - New NCERT PDF Download
Time: 45 Minutes
M.M.: 20
Attempt all questions.
Question numbers 1 to 6 carry 1 mark each.
Question numbers 7 to 9 carry 3 marks each.
Question number 10 carries 5 marks.
Q1. Which is a clean source of energy?
(a) Coal
(b) Diesel
(c) Solar energy
(d) Kerosene
Ans: (c) Solar energy
Q2. Fill in the blanks:
Energy makes things ______, produce ______, give ______, and change temperature.
Ans: move, sound, light
Q3. True or False:
Wind can make a pinwheel rotate, and water can turn a water wheel.
Ans: True
Q4. Which fuel commonly used at home for cooking is cleaner than coal or wood?
Ans: LPG (cooking gas)
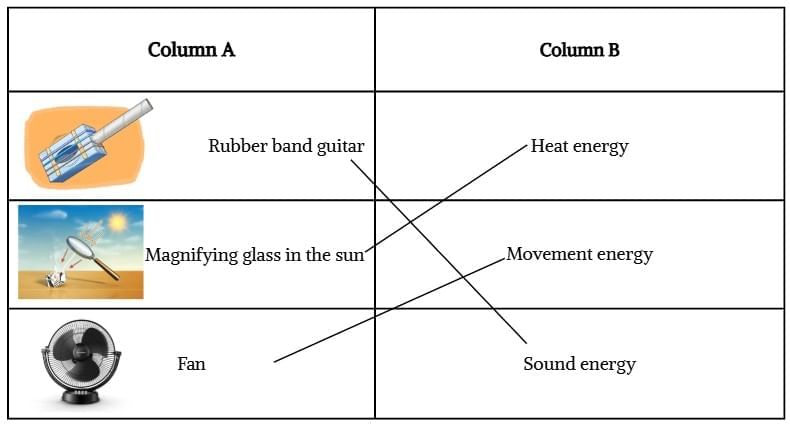
Q5. Match the following:
Ans:
Q6. Which airport is known for being entirely powered by solar energy?
(a) Mumbai
(b) Delhi
(c) Cochin
(d) Chennai
Ans: (c) Cochin
Q7. Give three examples from daily life where electricity is used for different purposes.
Ans: 1. Bulb/tube light for light.
2. Fan for movement/air circulation.
3. Heater/iron for heat.
Q8. Why is energy efficiency important? List three actions to save energy at home/school.
Ans: 1. Saves resources and reduces pollution.
2. Use LED bulbs, turn off devices when not in use.
3. Use natural light/ventilation instead of lights/AC.
Q9. Give three reasons why wind, solar, and water are called clean sources of energy.
Ans: 1. Produce electricity without smoke.
2. Reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
3. Use naturally replenished resources.
Q10. Draw a simple “Energy Flow” for any one device and explain:
(a) Source of energy,
(b) Type of energy used/converted,
(c) Useful output.
Ans:
Solar lamp(a) Source: Sunlight captured by solar panel.
(b) Conversion: Light energy to electrical energy stored in a battery.
(c) Output: Light for studying at night.
(Other valid examples: Water wheel → movement to mechanical work; Windmill → movement to electricity.)
|
11 videos|224 docs|10 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): Energy — How Things Work - Our Wondrous World Class 5 - New NCERT
| 1. What is energy and why is it important in our daily lives? |  |
| 2. What are the different forms of energy? |  |
| 3. How is energy transformed from one form to another? |  |
| 4. Can energy be created or destroyed? |  |
| 5. How do we measure energy? |  |