Unit Test (Solutions): Electricity and Its Effects | Science Class 7 (Old NCERT) PDF Download
Time: 1 hour
Maximum Marks: 30
Attempt all questions.
- Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each.
- Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
- Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
- Question numbers 12 & 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1: Which of the following is an electrical component used in a circuit? (1 Mark)
(a) Bulb
(b) Wire
(c) Battery
(d) All of the above
Ans: (d) All of the above
These components help in the functioning of an electric circuit.
Q2: What does an electric fuse do in a circuit? (1 Mark)
Ans: An electric fuse protects the circuit by breaking the connection when excessive current flows through it.
Q3: Which of the following devices does not work based on the heating effect of electric current? (1 Mark)
(a) Electric iron
(b) Refrigerator
(c) Immersion heater
(d) Toaster
Ans: (b) Refrigerator
A refrigerator works on cooling mechanisms, while the others generate heat using electric current.
Q4: What is an electromagnet? (1 Mark)
Ans: An electromagnet is a temporary magnet created when electric current flows through a coil of wire wound around an iron core.
Q5: Name one safety device other than a fuse that prevents excessive current from damaging electrical appliances. (1 Mark)
Ans: Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB)
MCBs automatically switch off the circuit when the current exceeds a safe limit.
Q6: Differentiate between open circuit and closed circuit. (2 Marks)
Ans: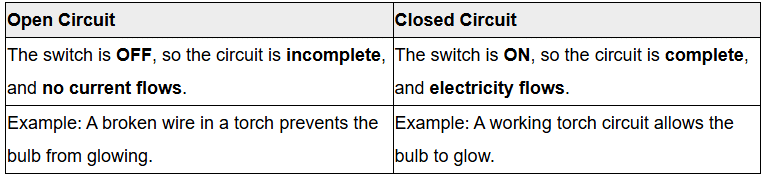
Q7: Explain how overloading can cause damage to electrical circuits. (2 Marks)
Ans:
- Overloading happens when too many electrical appliances are connected to a single socket.
- The excessive flow of current generates excess heat, which can damage appliances and cause fires.
Q8: Why do CFLs consume less electricity than ordinary bulbs? (2 Marks)
Ans:
- Ordinary bulbs use the heating effect of current to produce light, wasting energy as heat.
- CFLs use a fluorescent coating and electrodes to generate light efficiently, consuming less energy.
Q9. Explain how an electric fuse works. (3 Marks)
Ans:
- A fuse is a thin wire that melts when excessive current flows through it.
- This breaks the circuit, preventing damage to electrical appliances.
- Example: If a sudden voltage surge occurs, the fuse blows, stopping the current flow and preventing fires.
Q10: Describe how electromagnets are used in daily life. (3 Marks)
Ans:
- In Cranes: Used to lift heavy metal objects in scrapyards.
- In Electric Bells: Creates magnetic attraction to produce sound.
- In MRI Machines: Used in hospitals for medical imaging.
- In Maglev Trains: Uses magnetic levitation to reduce friction.
Q11: How does a Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) work? (3 Marks)
Ans:
- MCBs automatically turn off when excessive current flows in a circuit.
- Unlike fuses, MCBs do not burn out and can be reset manually.
- They help prevent electric shocks and fires in households and industries.
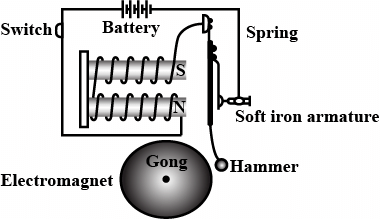
Q12: Explain the construction and working of an electric bell with a diagram. (5 Marks)
Ans:
Construction:
- Electromagnet: A coil wound around an iron core.
- Armature: A piece of iron that moves when attracted by the magnet.
- Hammer: Attached to the armature, strikes the gong.
- Spring: Returns the armature to its original position.
- Gong: Produces sound when struck by the hammer.
Working:
- When the switch is pressed, current flows through the electromagnet, creating a magnetic field.
- The electromagnet attracts the armature, making the hammer strike the gong.
- This breaks the circuit, turning off the electromagnet.
- The spring pulls the armature back, reconnecting the circuit.
- The process repeats rapidly, producing a ringing sound.
Q13: How does the magnetic effect of electric current help in making an electromagnet? Explain its applications. (5 Marks)
Ans:
How an Electromagnet is Made:
- A coil of insulated copper wire is wound around an iron core.
- When electric current flows, the iron core behaves like a magnet.
- The magnetism lasts only as long as the current flows.
- When the current is switched off, the iron core loses its magnetism.
Applications of Electromagnets:
- Lifting Heavy Metals: Used in cranes for lifting scrap iron.
- MRI Scanners: Used in hospitals for medical imaging.
- Loudspeakers & Microphones: Convert electrical signals into sound waves.
- Electric Motors: Convert electricity into mechanical motion in fans and washing machines.
- Maglev Trains: Use powerful electromagnets for fast, frictionless movement.
|
111 videos|435 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): Electricity and Its Effects - Science Class 7 (Old NCERT)
| 1. What are the basic principles of electricity that are covered in the unit test? |  |
| 2. How do you calculate electrical resistance using Ohm's law? |  |
| 3. What are some common applications of electricity in daily life? |  |
| 4. What safety measures should be taken when working with electricity? |  |
| 5. Can you explain the effects of electric current on materials? |  |
















