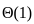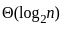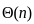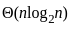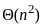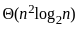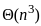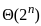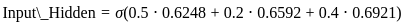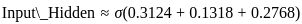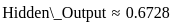UGC NET Past Year Question Paper II: Computer Science (7 Dec 2023 Shift I) | UGC NET Past Year Papers PDF Download
Q1: Given below are two statements:
Statement (I): In datagram networks - routers hold state information about connections
Statement (II): In virtual circuit network- each virtual circuit requires router table space per connection
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Statement (I): In datagram networks - routers hold state information about connections.
- In a datagram network, each packet is routed independently from all others. When a packet is to be forwarded, a router does not take into consideration any other packets even if they arrived from the same source or are destined to the same output port.
- Datagram networks are connection-less because they do not establish a physical or virtual path before the start of data transmission. An example of a datagram network is the Internet.
- Here, routers do not keep any state information about connections because they, conceptually, have no connections to keep states for. Each packet is its own independent unit of information, unrelated to any other packet.
Statement (II): In virtual circuit network- each virtual circuit requires router table space per connection
- Virtual circuit networks, on the other hand, establish a defined path between endpoints before data is transmitted. This is called a 'virtual circuit'. This circuit is a logical concept, in that the network provides the appearance of a dedicated physical circuit to the connected devices, but it may be shared by other circuits.
- Information packets sent between the same source and destination will follow the same path. The router must maintain state information, e.g., the path of each established circuit, in order to ensure all packets of the same connection follow the same path. This requires router table space for each connection.
- This is why an ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode) network or a Frame Relay network, for example, which are virtual circuit networks, need to maintain a table of all established virtual circuits.
So, the Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q2: An Address in main memory is called :
(a) Virtual address
(b) Memory address
(c) Logical address
(d) Physical address
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is Physical address
Physical address:
- This is the actual address in the computer's memory. Each byte of memory in a computer can be identified by a unique physical address.
- Whereas a virtual (or logical) address specifies a location in the virtual address space set up by a system using virtual memory, the MMU translates this into a physical address to access the actual data.
- The physical address directly corresponds to a specific location of a byte in the system's RAM.
Other Related Points
- Virtual address: This term is used in a system that uses virtual memory, where the memory management unit (MMU) and the operating system work together to give each process the illusion that it is the only process running on the computer. Each process has its own set of virtual address spaces, which the MMU translates into actual physical addresses. Virtual addresses help in the abstraction of the memory implementation, making programming easier.
- Memory address: This is a more general term that refers to the identifier for a particular memory location where a data byte or a group of data bytes is stored. It can represent either a virtual or a physical address, depending on the context.
- Logical address: This is another term for virtual address. It's the address that a process uses to reference a memory location, unaware of the actual physical address of the data in memory. The MMU translates these logical addresses into physical addresses.
Q3: If universe of disclosure are all real numbers, then which of the following are true?
(A) ∃x ∀y (x + y = y)
(B) ∀x ∀y (((x ≥ 0) ∧ (y < 0) → (x - y > 0))
(C) ∃x ∃y (((x ≤ 0) ∧ (y ≤ 0) ∧ (x - y > 0))
(D) ∀x ∀y ((x ≠ 0) ∧ (y ≠ 0) ↔ (xy ≠ 0))
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) and (B) Only
(b) (C) and (D) Only
(c) (A), (B) and (D) Only
(d) (A), (B), (C) and (D) Only
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (B), (C) and (D) Only
(A) ∃x ∀y (x + y = y):
- This says there exists some real number x such that for all real numbers y, x + y = y. This statement is true for x = 0. So, (A) is true.
(B) ∀x ∀y (((x ≥ 0) ∧ (y < 0) → (x - y > 0)):
- This says for all real x, y that if x is positive (or zero) and y is negative then x - y is positive. This is indeed true because if x is positive and y is negative, subtracting y from x will increase x and thus will be positive. Therefore, (B) is true.
(C) ∃x ∃y (((x ≤ 0) ∧ (y ≤ 0) ∧ (x - y > 0)):
- The statement means there are some real numbers x and y such that both x and y are negative (or zero) and the difference x - y > 0. This condition will be satisfied when y is more negative than x. So, (C) is also true.
(D) ∀x ∀y ((x ≠ 0) ∧ (y ≠ 0) ↔ (xy ≠ 0)):
- This condition means that for all x and y, x and y can't be zero if and only if their product xy isn't zero. This condition is always true because in the real numbers, the product of two non-zero numbers is never zero. So, (D) is also true.
All options from (A) to (D) are true, so the correct answer is: (A), (B), (C) and (D) Only.
Q4: What is the generic structure of Multi Agent System (MAS) ?
(a) Single agent with multiple objectives
(b) Multiagents with a single objectives
(c) Multiagents with diverse objectives and communication abilities
(d) Multiagent with two objectives
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Multiagents with diverse objectives and communication abilities
A Multi-Agent System (MAS) is generally structured based on your third description, "Multi-agents with diverse objectives and communication abilities."
In more depth, the generic structure of MAS involves the following main components:
- Agents: At the core of a MAS, there are multiple autonomous agents. Each agent in the system has the ability to perform tasks individually.
- Objectives: Each agent can have diverse objectives. Their goals do not necessarily have to align and can be either cooperative (sharing a goal), or competitive (having conflicting goals).
- Communication: Agents in a MAS have the ability to communicate with one another. This can be through a variety of means, such as direct communication (e.g., message passing) or indirect communication (e.g., stigmergy).
- Tasks: The tasks assigned to agents can vary, including problem solving, information retrieval, negotiation, cooperation, competition, etc.
- Environment: MAS also involves the Environment where the agents operate - their world, essentially. This includes anything that the agents can interact with.
The other structures mentioned (single agent with multiple objectives, multiagents with a single objective, multiagent with two objectives) do not fully encapsulate the complexity and capability of a full-fledged Multi-Agent System, although they represent certain aspects or cases of an MAS.
Q5: What is the result of evaluating the postfix expression “43*25* + 8 -” ?
(a) 8
(b) 14
(c) 10
(d) 5
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 14
- Scan the expression from left to right.
- When you encounter a number, push it onto the stack.
- When you encounter an operator, pop the required number of operands from the stack, perform the operation, and push the result back onto the stack.
step by step:
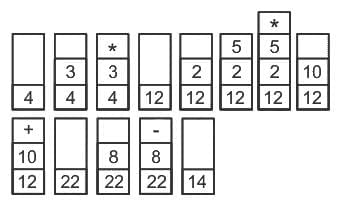
Evaluate “4325 + 8 -”:
4, 3, *: Push 4, 3; pop 3, 4; compute 4 * 3 = 12; push 12.
2, 5, *: Push 2, 5; pop 5, 2; compute 2 * 5 = 10; push 10.
+: Pop 10, 12; compute 12 + 10 = 22; push 22.
8, -: Push 8; pop 8, 22; compute 22 - 8 = 14; push 14.
Result: 14.
The answer (b) is correct.
Q6: Given below are two statements:
Statement (I) : In Reuse Oriented Model, Modification of the old system parts appropriate to the new requirements.
Statement (II): In Reuse Oriented Model, Integration of the modified parts are not possible into the new systems.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
Statement (I): "In Reuse Oriented Model, Modification of the old system parts appropriate to the new requirements."
- This statement suggests that in a Reuse Oriented Model, it is possible to modify old system parts to meet new requirements. This aligns with the concept of reusability, where existing components or modules are adapted or modified to fulfill the needs of a new system. Therefore, Statement I is correct.
Statement (II): "In Reuse Oriented Model, Integration of the modified parts is not possible into the new systems."
- This statement implies that once parts are modified in a Reuse Oriented Model, they cannot be integrated into the new systems. However, this contradicts the essence of reusability. In a Reuse Oriented Model, the goal is to modify and reuse existing components, making integration into new systems a key aspect. Therefore, Statement II is incorrect.
So, Statement I is correct, but Statement II is incorrect.
Q7: The statement P(x): "x=x2". If the universe of disclosure consists of integers, what are the following have truth values:
(A) P(0)
(B) P(1)
(C) P(2)
(D) ∃x P(x)
(E) ∀x P(x)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B) and (E) Only
(b) (A), (B) and (C) Only
(c) (A), (B) and (D) Only
(d) (B), (C) and (D) Only
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (B) and (D) Only
(A) P(0):
- 0 = 02 is true, so (A) is true.
(B) P(1):
- 1 = 12 is true, so (B) is true.
(C) P(2):
- 2 ≠ 22 is false, so (C) is false.
(D) ∃x P(x):
- There exists an x such that x = x2. From the previous evaluations, we can see that x = 0 and x = 1 satisfy this condition. So, (D) is true.
(E) ∀x P(x):
- For all x, x = x2. This is not true for all integers, as we saw with x = 2. So, (E) is false.
Therefore, the correct answer is option:(A), (B) and (D) Only
Q8: One of the purposes of using intermediate code in compilers is to :
(a) make parsing and semantic analysis simpler
(b) improve error recovery and error reporting
(c) increase the chances of reusing the machine independent code optimizer in other compilers
(d) improve the register allocation
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is increase the chances of reusing the machine independent code optimizer in other compilers
- The intermediate code is a lower level representation of the source code that can be used to bring some level of platform independence to the compilation process.
- By defining an intermediate representation, we can design the first part of the compiler (called the front end), which translates high-level source code into intermediate code, to work with multiple languages.
- The second part of the compiler (called the back end), which translates intermediate code into machine-specific code, can be made to work with multiple target architectures.
- Therefore, the intermediate code can increase the chances of reusing the machine-independent code optimizer in other compilers, making the process more efficient.
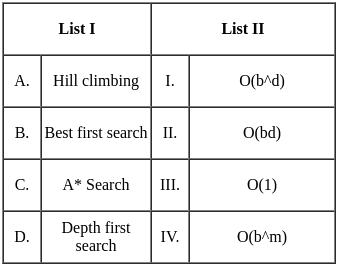
Q9: Match List-I with List-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(b) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
(c) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
(d) A - I, B - III, C - II, D - IV
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
A. Hill Climbing - III. O(1)
- Hill climbing is a local search algorithm that focuses on finding a solution in the immediate neighborhood of the current state. The time complexity is often constant (O(1)) because it explores only one path at a time.
B. Best First Search - I. O(bd)
- Best-first search is a graph search algorithm that uses a heuristic to determine the most promising path to explore first. The time complexity is generally exponential, O(bd), where b is the branching factor and d is the depth of the shallowest goal.
C. A* Search - IV. O(bm)
- A* search is an informed search algorithm that uses a heuristic to guide the search process. The time complexity is typically exponential but is often more efficient than a naive best-first search. O(bm) represents the complexity, where b is the branching factor, and m is the maximum depth of the search.
D. Depth First Search - II. O(bd)
- The time complexity of depth-first search is O(bd) where b is the branching factor (2 for the binary trees below) and m is the maximum depth of the tree. Its space complexity is only bd.
So, the correct match is A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II.
Q10: Which of the following circuit is used to store one bit of data ?
(a) Encoder
(b) Decoder
(c) Flip-flop
(d) Register
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Flip-flop
Flip-flop:
- A flip-flop is a bistable multivibrator, a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store binary information (0 or 1).
- It is the fundamental building block of digital memory elements and is widely used for storing a single bit of data.
Other Related Points
Encoder:
- An encoder is a combinational circuit that converts a set of input signals into a coded output representing the input.
- It is commonly used in communication systems and data transmission.
Decoder:
- A decoder is a combinational circuit that performs the opposite function of an encoder. It converts coded input into a set of output signals.
- Decoders are often used in digital systems to select a particular output based on the input code.
Register:
- A register is a group of flip-flops that are used to store multiple bits of data.
- It can be used for various purposes, including data storage, temporary storage during processing, or as part of a CPU to store operands and results of operations.
Q11: Consider a triangle PQR with coordinates as P(0,0), Q(2,2) and R(10,4). If this triangle is to be magnified to four times its size while keeping R(10, 4) fixed, then the coordinates of the magnified triangle are :
(a) (-20, -12), Q(-20, -4) and R(10, 4)
(b) (-30, -12), Q(-22, -4) and R(10, 4)
(c) (-25, -10), Q(22, -4) and R(10, 4)
(d) (30,-12), Q(-22, 4) and R(10, 4)
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is (-30, -12), Q(-22, -4) and R(10, 4)
To magnify a shape, we can use the principle of scalings in transformations. We keep the point R(10,4) fixed and magnify everything with a factor of 4 from that point.
Start with thepoint P(0,0).
- The vector from R to P is P - R = (0,0) - (10,4) = (-10, -4). Now, we multiply this vector by 4 (our scale factor) to get (-40, -16). Then, we add this to our fixed point R, to get the new position for P: R + 4*(P - R) = (10,4) + (-40, -16) = (-30, -12).
Similarly, for point Q(2,2).
- The vector from R to Q is Q - R = (2,2) - (10,4) = (-8, -2). Again, we multiply this vector by our scale factor 4, to get (-32, -8). Adding this to R, we find the new position for Q: R + 4*(Q - R) = (10,4) + (-32, -8) = (-22, -4).
- The coordinates of the magnified triangle are thus P'(-30, -12), Q'(-22, -4) and R(10, 4).
So, option 2) (-30, -12), Q(-22, -4) and R(10, 4) is the correct one.
Q12: Which of the following are example of CSMA channel sensing methods?
(A) 1-persistent
(B) 2-persistent
(C) p-persistent
(D) non-persistent CSMA
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B) and (D) Only
(b) (A), (C) and (D) Only
(c) (B), (C) and (D) Only
(d) (A), (B) and (C) Only
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (C) and (D) Only
The CSMA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access) channel sensing methods are:
- 1-persistent CSMA: The station continuously senses the carrier, and if the channel is idle, it sends the frame immediately with a probability of 1 (i.e., persistence value of 1). If the channel is busy, the station waits until it becomes idle.
- p-persistent CSMA: The station senses the channel, and if it is idle, it sends the frame with a probability p (0 < p ≤ 1). If the channel is busy or the frame is not sent, it waits for a certain period and tries again.
- 0-persistent CSMA: The station senses the channel, and if it is idle, it sends the frame immediately with a probability of 0. This means it does not persistently check the channel if busy but waits a random period before retrying.
Therefore, the correct answer is (A), (C), and (D) Only.
Q13: Arrange the following steps in the correct sequence for applying an unsupervised learning technique such as K-means clustering is to a data set:
(A) Randomly initialize cluster centroids
(B) Assign each data point to nearest cluster centroid
(C) Update the cluster centroids based on the mean of data points assigned to each cluster
(D) Specify the number of clusters (K) to partation the data into
(E) Repeat steps B and C until convergence criteria are met
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (D), (A), (B), (C), (E)
(b) (A), (B), (C), (D), (E)
(c) (C), (B), (A), (D), (E)
(d) (D), (C), (A), (B), (E)
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is (D), (A), (B), (C), (E)
Specify the number of clusters (K) to partition the data into (D).
- The first step in K-means clustering is deciding how many clusters you want to end up with. This is typically determined based on your understanding of the data and the specific objectives of your analysis.
Randomly initialize cluster centroids (A).
- After deciding on the number of clusters, initialize their centers or "centroids". This is often done randomly, though there are various strategies for choosing initial centroids.
Assign each data point to the nearest cluster centroid (B).
- This step involves measuring the distance between each data point and each of the centroids, and then assigning each data point to the nearest one. The distance is usually calculated using a method like the Euclidean distance.
Update the cluster centroids based on the mean of data points assigned to each cluster (C).
- Once all data points have been assigned to clusters, we can re-calculate the center of each cluster. This is generally done by taking the mean of all the data points currently assigned to the cluster.
Repeat steps B and C until convergence criteria are met (E).
- The process of assigning data points to clusters and updating the centroids is repeated multiple times. Each repetition refines the cluster assignments and centroids. The algorithm continues to iterate until a stopping condition or convergence criteria is met. This could be a fixed number of iterations, or stopping when the change in centroids falls below a set threshold (i.e., the centroids have stabilized).
So in summary, we start by deciding on the number of clusters, initialize their centers, assign data points to the nearest centers, and then keep updating the centers and re-assigning data points until the centers stop moving significantly. This is how K-means clustering works.
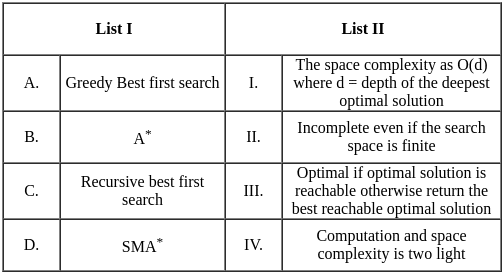
Q14: Match List-I with List-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
(b) A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV
(c) A - III, B - II, C - IV, D - I
(d) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
A. Greedy Best-First Search (List I: A, List II: II)
- Greedy Best-First Search uses heuristic information to select the most promising path. It evaluates nodes based on a heuristic function without considering the entire path cost. Incomplete even if the search space is finite.
B. A* (List I: B, List II: IV)
- A* is a search algorithm that uses both the cost to reach a node and an estimate of the remaining cost to the goal (heuristic). It is optimal if the heuristic is admissible (never overestimates the true cost) and consistent. Computation and space complexity is too high.
C. Recursive Best-First Search (List I: C, List II: I)
- Recursive Best-First Search is a variation of Best-First Search that uses recursion. The space complexity as O(d) where d = depth of the deepest optimal solution
D. SMA* (List I: D, List II: III)
- SMA* (Simplified Memory-Bounded A*) is a variant of A* that limits its memory usage. It returns the best reachable solution within the memory constraints. Optimal if optimal solution is reachable otherwise return the best reachable optimal solution
So, the correct match is: A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III (Option 1)
Q15: Which of the following symbol table implementation is best suited if access time is to be minimum ?
(a) Linear list
(b) Search tree
(c) Hash Table
(d) Self organisation list
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Hash Table
- All of the data structures you listed can be used to implement a symbol table, but they offer different trade-offs between operation times (like insertion, deletion, access).
- Our primary concern is minimizing access time, then use Hash Table.
- A Hash Table can provide constant time O(1) average case complexity for lookup operations, assuming a good hash function and well-distributed data.
- This means that, on average, lookup time remains constant regardless of the number of elements in the table. Potential downside is that in worst case scenario (all keys collide), it can degrade to O(n).
Q16: Which of the following(s) are main memory?
(A) Virtual memory
(B) Cache memory
(C) RAM
(D) SSD
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) and (C) Only
(b) (B) and (C) Only
(c) (C) and (D) Only
(d) (A), (B) and (C) Only
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is (B) and (C) Only
(B) Cache Memory:
- Cache memory is a type of computer memory that is very fast compared to regular RAM and is situated on the processor chip.
- After the processor reads from the main memory for the first time, it stores a copy of the data in the cache. If the same data is needed again, it can be rapidly accessed from the cache. This improves the performance and speed of the computer.
(C) RAM (Random Access Memory):
- RAM is a type of computer memory that can be accessed randomly; that is, any byte of memory can be accessed without touching the preceding bytes.
- RAM serves as the computer's "working" memory. It provides space for your computer to read and write data to be accessed by the CPU (central processing unit). When you shut your computer off, everything stored in RAM is lost.
Other Related Points
(A) Virtual Memory:
- Virtual memory is a memory management capability of an operating system (OS) that uses hardware and software to allow a computer to compensate for physical memory shortages by temporarily transferring data from random access memory (RAM) to disk storage. This process is done automatically and is completely transparent to the user.
(D) SSD (Solid State Drive):
- An SSD is a type of mass storage device, not a type of RAM. This non-volatile storage medium uses solid-state memory to store data persistently.
- It has no moving parts, as data in an SSD is stored in microchips. This differs from the traditional hard drive, which has a motor and moving head, making it slower than an SSD.
- SSDs are used for secondary storage, long-term storage, or for holding data when the system is powered off. They are not part of the main memory system.
Q17: The microoperation which divides a signed binary number by 2 is :
(a) Circular shift
(b) Logical shift
(c) Arithmetic shift right
(d) Arithmetic shift left
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Arithmetic Shift Right
Arithmetic Shift Right:
- An arithmetic right shift operation moves bits one position to the right, similar to logical shift.
- However, in this case, the leftmost bit (sign bit) stays the same to preserve the number's sign. T
- his means a positive number remains positive, and a negative number remains negative, so an arithmetic right shift can correctly divide signed binary numbers by 2.
Other Related Points
- Circular Shift:
- In a circular shift operation, the bits are moved one position to the left or right in a way that the bit at one end does not get lost but instead moves to the other end.
- If a bit is shifted out from the right end, it inserts at the left end, and vice versa. This maintains the number of bits in the data.
Logical Shift:
- Logical shifts are used for unsigned binary numbers. In a logical right shift, the bits are moved one position to the right, and a '0' is added at the left-most bit.
- This is equivalent to division by 2 for unsigned binary numbers but doesn't work for signed numbers (where the left-most bit is a sign bit) because it changes the sign of the number.
Arithmetic Shift Left:
- In an arithmetic left shift, bits are moved one position to the left, and a '0' is added in the least significant bit (rightmost bit), doubling the number.
- The sign bit (the leftmost bit) remains the same, so signed numbers stay positive or negative. This operation is similar to multiplying a signed binary number by 2.
Q18: The Hue of a colour is related to its :
(a) Luminance
(b) Saturation
(c) Incandescence
(d) Wavelength
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is Wavelength
Wavelength:
- This is the distance between two successive crests or troughs in a wave— in this context, a light wave.
- The wavelength of light determines its color, or hue. Different colors of light have different wavelengths.
- For instance, violet light has a short wavelength, while red light has a long wavelength. So this is the term most closely connected with the hue of a color.
Other Related Points
Luminance:
- This is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light traveling in a given direction.
- It describes the amount of light that passes through or is emitted from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle. It's often used in the context of the emission or reflection of light from flat, diffused surfaces.
Saturation:
- In color theory, saturation refers to the intensity of a color. It's the degree to which a color is different from a gray of the same brightness or lightness.
- A highly saturated color is vivid, while an unsaturated color appears washed out or muted.
Incandescence:
- This is the emission of light from a hot body as a result of its temperature. The color of incandescent light varies with the temperature of the light-emitting body.
- This term is often used to describe the light emitted by traditional light bulbs, which work by heating a filament until it glows. Incandescence mainly connects to temperature.
Q19: Let L={ab, aa, baa}. Which of the following strings are not in L*.
(a) abaabaaabaa
(b) aaaabaaaa
(c) baaaaabaaaab
(d) baaaaabaa
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer isbaaaaabaaaab
The closure of a language L is denoted L* and represents the set of those strings that can be formed by taking any number of strings from L, possibly with repetitions (i.e., the same string may be selected more than once) and concatenating all of them. pairs.
Given the language L = { ab, aa, baa}
- Option 1: abaabaaabaa
- True, L* has "abaabaaabaa" is a correct combination. "ab aa baa ab aa".
- Option 2: aaaabaaaa
- True, L* has "aaaabaaaa" is a correct combination. "aa aa baa aa".
- Option 3: baaaaabaaaab
- False , L* can not accept "baaaaabaaaab" combination. "baa aa ab aa aa b". It is ending with "b" can not accept the given automata.
- Option 4: baaaabaa
- True, L* has "baaaabaa" is a correct combination. "baa aa baa".
L* includes concatenations of ab, aa, baa, all ending in ‘a’.
(c) baaaaabaaaab ends in ‘b’, so it’s not in L*.
Hence the correct answer is baaaaabaaaab.
Q20: Identify the code sequence :
1010
1011
1001
1000
(a) BCD
(b) Excess-3
(c) Gray
(d) Excess-3 gray
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Gray
Gray Code: Gray code is a binary numeral system where two consecutive numbers differ by only one bit. The given sequence does not exhibit this characteristic, as the difference between consecutive numbers is not consistently one bit.
- MSB = Most significant bit
- 2MSB = Second Most significant bit
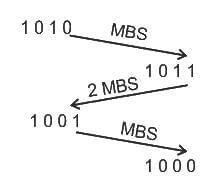
So the correct answer is Gray Code
Other Related Points
- BCD (Binary-Coded Decimal): BCD is a binary-encoded representation of decimal numbers. In BCD, each decimal digit is represented by its 4-bit binary equivalent. The given sequence does not follow the typical BCD pattern, as the difference between consecutive numbers is not consistent with BCD.
- Excess-3: Excess-3 (XS-3) is a binary-coded decimal (BCD) code in which each decimal digit is represented by its corresponding 4-bit binary representation, and the code for each decimal digit is obtained by adding 3 to the binary representation of the decimal digit.
- Excess-3 Gray: There is no widely recognized coding system known as "Excess-3 Gray." Excess-3 and Gray code are different coding systems. Excess-3 is a BCD code, whereas Gray code is a binary code where two consecutive numbers differ by only one bit.
Q21: The head of a moving head disk with 200 tracks, numbered 0 to 199, has just finished a request at track 125, and currently serving a request at track 143. The queue of requests is given in the FIFO order as 86, 147, 91, 177, 94, 150, 102, 175, 130. What will be the total number of head movements required to satisfy these requests for SCAN algorithm ?
(a) 259 cylinders
(b) 169 cylinders
(c) 154 cylinders
(d) 264 cylinders
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 169 cylinders
In the SCAN algorithm (also known as the elevator algorithm), the disk arm starts from one end of the disk and moves towards the other end, servicing requests until it gets to the other end. After reaching the other end, it reverses its direction and again services the requests coming in its path.
In this case, the head is currently at track 143 and moving towards higher-numbered tracks (because it just serviced a request at track 125 and is now at track 143).
Given the queue of requests: 86, 147, 91, 177, 94, 150, 102, 175, 130.
We first sort the queue in ascending order but consider only those, which are in the direction of the head movement: 147, 150, 175, 177.
Then, it reverses its direction and services the remaining requests.
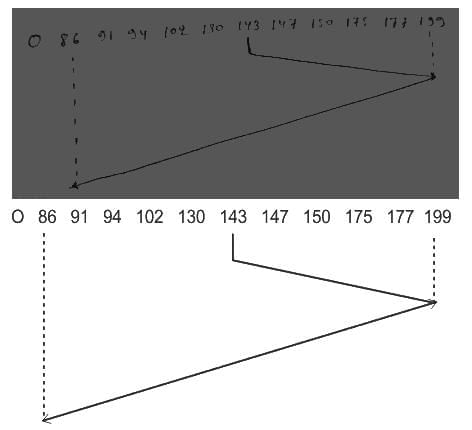
Total number of head movements = (199 -143) + (199 - 85)
Total number of head movements = 56 + 113 = 169
Q22: Given below are two statements:
Statement (I): If H is non empty finite subset of a group G and ab ∈ H ∀ a, b ∈ H, then H is also a group
Statement (II): There is no homomorphism exist from (Z, +) to (Q. +); where Z is set of integers and Q is set of rational number.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
Statement (I): If H is a non-empty finite subset of a group G and ab ∈ H ∀ a, b ∈ H, then H is also a group.
- This statement is correct under the condition that H also contains the identity element of G and that for each element in H, its inverse is also in H. These are key requirements to being a subgroup and therefore a group on its own.
Statement (II): There is no homomorphism exist from (Z, +) to (Q, +), where Z is the set of integers and Q is the set of rational numbers.
- This statement is false. A homomorphism does exist from (Z, +) to (Q, +). One such example could be the identity function f(x) = x where both addition operations remain preserved.
So, the answer would be Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
Q23: A multiplexes combines four 100 Kbps channels using a time slot of 2 bits. What is the bit rate ?
(a) 100 Kbps
(b) 200 Kbps
(c) 400 Kbps
(d) 1000 Kbps
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is 400 Kbps
A time division multiplexing system combines multiple channels by interleaving bits by time. The bit rate of the multiplexed channel is determined by the number of time slots and the bit rate of the individual channels.
To find the bit rate when multiplexing four 100 Kbps channels using a time slot of 2 bits, we can follow these steps:
1. Determine the total number of channels: There are 4 channels, each operating at 100 Kbps.
2. Calculate the total bit rate of the channels:
3. Consider the time slot size: The time slot of 2 bits means that each channel is transmitting 2 bits in each time slot. However, since we are combining the channels, the total bit rate does not change based on the size of the time slot for each channel.
Conclusion:
- The overall bit rate after multiplexing is: 3) 400 Kbps.
Q24: Arrange the following levels of interrupt protection within the Linux Kernel, in the order of increasing priority.
(A) user mode programs
(B) bottom half interrupt handlers
(C) kernel system service routines
(D) top half interrupt handlers
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B), (D), (C)
(b) (A), (C), (B), (D)
(c) (A), (C), (D), (B)
(d) (D), (A), (C), (B)
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (C), (B), (D)
The Linux Kernel handles different tasks at different priority levels to manage resources and functionality efficiently. Here is a short of each of these tasks in increasing levels of priority:
(A) User Mode Programs:
- These programs are applications that are running on your computer. They do not interact directly with the system hardware or with other programs and have the least system privilege level. They request system resources and services from the kernel.
(C) Kernel System Service Routines:
- These routines facilitate the user mode programs by providing system services. They operate at a higher privilege level than user programs since they interact directly with system structures and hardware, but they are not as prioritized as interrupt handlers.
(B) Bottom Half Interrupt Handlers:
- These handlers deal with the processing of interrupts, but not immediately. They handle the less critical part of the interrupt handling, often the work that can be deferred to a later point when the system is less busy.
(D) Top Half Interrupt Handlers:
- These handlers are responsible for dealing with interrupts immediately after they occur to ensure uninterrupted functioning of the system. Therefore, they have the highest priority. After attending to the immediate needs of an interrupt, they may schedule the rest of the work to the bottom half handlers.
So, the correct answer from the options you provided would be :(A), (C), (B), (D)
Q25: What is the output of the following program?
#include
int main()
{ int i=3;
while (i--)
{ int i=10;
i--;
printf("%d", i);
}
printf("%d", i);
}
(a) 990
(b) 9990
(c) 999 - 1
(d) 99 - 1
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is 999 - 1
The code you provided is a simple C program that contains two distinct integer variables both named "i". Although they share the same name, these variables are distinct as they exist in different scopes: one is within the main function and the other is inside the loop.
The initial 'i' variable is set to 3, and it decrements by 1 with each iteration of the while loop. Inside the loop, a new 'i' variable is declared and initialized to 10, and then immediately decremented to 9. This variable is only accessible within the loop and does not affect the outer 'i' variable.
The printf inside the loop will print the value of the local 'i' for each iteration, which will always be 9 as it gets reset to this value with each loop iteration. This will happen three times as the condition for the outer loop is i--, which will decrease i from 3 to 0.
After the loop concludes, the printf, outside the loop, will print the value of the 'i' variable which is in the scope of the main function.
So, the output of the program will be 999 - 1 (option 3)
Here's a step-by-step recap:
- Iteration 1: i (main variable)=3, i (local variable in loop)=9 -> print 9
- Iteration 2: i (main variable)=2, i (local variable in loop)=9 -> print 9
- Iteration 3: i (main variable)=1, i (local variable in loop)=9 -> print 9
- Main variable is now 0 after the final decrement
- Print main variable (i): -1
So, the output of the program should be "999 - 1". Note that there are no spaces or newlines printed between the values, and there's no newline printed at the end.
Q26: Let A= {a, b} and L = A*. Let x = {anbn, n > 0}. The languages L ∪ X and X are respectively :
(a) Not regular, Regular
(b) Regular, Regular
(c) Regular, Not regular
(d) Not Regular, Not Regular
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Regular, Not regular
1. 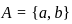
2. 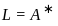 (the Kleene closure of A , which includes all possible strings over A , including the empty string)
(the Kleene closure of A , which includes all possible strings over A , including the empty string)
3. 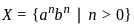 (the set of strings with equal numbers of 'a's and 'b's, with at least one 'a' and one 'b')
(the set of strings with equal numbers of 'a's and 'b's, with at least one 'a' and one 'b')
Now, let's consider 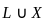 , the union of languages L and X :
, the union of languages L and X :
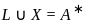
This language consists of strings with equal numbers of 'a's and 'b's, including the empty string. It is subset of A*. So, this language is regular, and its regular expression is 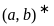
Now, let's consider X:
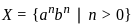
This language consists of strings with equal numbers of 'a's and 'b's, with at least one 'a' and one 'b'. This language is not regular, as it cannot be recognized by a regular grammar.
- L = A* is regular (all strings over {a, b}).
- X = {aⁿbⁿ, n > 0} is not regular (requires stack for equal counts).
- L ∪ X = A* (since A* includes all strings, including aⁿbⁿ), which is regular.
The answer (c) is correct.
So, the correct answer is: 3) Regular, Not regular
Q27: Which of the following are tautology?
(A) (P → (P ∧ Q)) → (P → Q)
(B) ((P → Q) → Q) → (P ∨ Q)
(C) ((P ∧ ¬ P) → Q) → ((P ∨ ¬ P) → R)
(D) (Q → (P ∧ ¬ P)) → (R → (P ∧ ¬ P))
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) Only
(b) (B) Only
(c) (A) and (B) Only
(d) (C) and (D) Only
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is (A) and (B) Only
(A) (P → (P ∧ Q)) → (P → Q)
= (¬ P v (P ∧ Q)) → (P → Q)
= (¬ P v P ∧ ¬ P v Q) → (P → Q)
= (¬ P v Q) → (P → Q)
= (¬ P v Q) → (¬ P v Q)
= ¬ (¬ P v Q) v (¬ P v Q)
= ¬ ¬ P ∧ ¬ Q v (¬ P v Q)
= P ∧ ¬ Q v (¬ P v Q)
= P v ¬ P ∧ ¬ Q v ¬ P v Q = 1
(B) ((P → Q) → Q) → (P ∨ Q)
= ((¬ P v Q) → Q) → (P ∨ Q)
= (¬ (¬ P v Q) v Q) → (P ∨ Q)
= (P ∧ ¬ Q) v Q) → (P ∨ Q)
= (P v Q ∧ ¬ Q v Q) → (P ∨ Q)
= (P v Q) → (P ∨ Q)
= ¬ (P v Q) v (P v Q)
= ¬ P ∧ ¬ Q v (P v Q)
= ¬ P v P ∧ ¬ Q v Q = 1
- C): ((P ∧ ¬P) → Q) → ((P ∨ ¬P) → R) = (true → Q) → (true → R) = Q → R (not a tautology).
- (D): (Q → (P ∧ ¬P)) → (R → (P ∧ ¬P)) = (Q → false) → (R → false) = ¬Q → ¬R = Q ∨ ¬R (not a tautology).
The answer (c) is correct.
So, above solution both A and B are tautology.
Q28: The average time required to search a storage location in memory and obtain its contents is called :
(a) Access time
(b) Latency time
(c) Response time
(d) Reading time
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Access time
Access time in computing refers to the time delay or latency between a request to an electronic system, and the access being completed or the requested information returned.
In the context of computer memory or storage, access time is the time interval between when a memory device receives a request to access a particular location and when the requested information begins to be output. The speed of this can vary depending on the type of memory/storage (e.g. RAM, hard disk drive, SSD).
Access time is composed of two main components:
- Seek Time: This is the time taken for the mechanical movements necessary to place the read/write head of a magnetic disk in position over the required track.
- Latency Time or Rotational Delay: This is the period waiting for the needed sector to rotate to a position under the drive head.
Usually, the term "access time" is associated with RAM, where it specifically refers to the time taken to locate and deliver the contents of a specific memory location.
Other options like 'Latency time', 'Response time', and 'Reading time' are parts of or relate to the overall access time. The correct option is "Access time".
Q29: A program that is used by other routines to accomplish a particular task, is called :
(a) Micro program
(b) Micro operation
(c) Routine
(d) Subroutine
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is Subroutine
Subroutine:
- A subroutine, also known as a function, method, procedure, or routine, is a set of instructions designed to perform a frequently used operation within a program. They can accept arguments, perform specific operations, and often return a result.
- When another routine or program needs to perform that operation, the subroutine can be called, or invoked. This aids code reusability, as the same subroutine can be used multiple times within a program or across different programs.
Other Related Points
Microprogram:
- This is a layer of hardware-level instructions or data structures involved in implementing higher-level machine code instructions in certain computers, especially those using CISC architecture. It may be regarded as a step-by-step process for the machine to follow, carrying out complex instructions as a sequence of simpler, micro-level operations.
Microoperation:
- Also known as a micro-action, this concept refers to the most basic tasks a computer's control unit can perform, such as fetching an instruction from memory or performing arithmetic operations. These are atomic, lower-level operations necessary to execute higher-level, more complex instructions.
Routine:
- This term typically refers to a sequence of programming instructions that perform a specific task, packaged as a unit—like a section of code. This piece of code can be written once and called by multiple main programs, thus promoting reusability and modularity. Often used in higher level programming languages. It's similar to a subroutine but often refers to larger operations.
Q30: In Linux, where is the user password stored ?
(a) /etc/password
(b) /root/password
(c) /etc/shadow
(d) /root/passwd
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is /etc/shadow
In Linux, user passwords are not actually stored in the /etc/passwd file. The /etc/passwd file contains basic information about user accounts, but not the actual passwords. Instead, the password information is typically stored in the /etc/shadow file.
The /etc/shadow file in Linux houses user passwords. When the field is unoccupied, it signifies that password authentication is not required for that user. For heightened security, it is imperative that each user on your system is assigned a password.
So, closest answer is /etc/passwd.
Q31: What is the output of the following program?
#include
# define SQR(x) (x*x)
int main()
{ int a, b = 3;
a=SQR(b+2);
printf("%d",a);
return 0;
}
(a) 25
(b) 11
(c) Garbage value
(d) 24
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 11
The code defines a macro SQR(x) that squares its argument. The macro is defined as (x*x). When SQR(b+2) is evaluated, it becomes (b+2*b+2), not (b+2)*(b+2), because of how the preprocessor substitutes macro definitions.
#include # define SQR(x) (x*x) int main() { int a, b = 3; a=SQR(b+2); printf("%d",a); return 0; }
So, given b=3, (b+2*b+2) will be equal to (3+2*3+2), which equals 11.
Hence, the answer is 2) 11.
Q32: The interface(s) that provide(s) I/O transfer of data directly to and from the memory unit peripheral is/are termed as:
(A) DMA (Direct Memory Access)
(B) IOP (Input-Output Processor)
(C) Serial Interface
(D) Parallel Interface
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) Only
(b) (B) Only
(c) (A) and (B) Only
(d) (C) and (D) Only
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is (A) and (B) Only
DMA (Direct Memory Access):
- DMA is a feature that allows peripherals to transfer data directly to and from the memory without the intervention of the CPU.
- Instead of the CPU being involved in each data transfer between peripherals (like storage devices, network interfaces, etc.) and memory, DMA enables the peripherals to communicate directly with the memory.
- This improves overall system efficiency by offloading data transfer tasks from the CPU.
IOP (Input-Output Processor):
- An IOP is a processor specifically designed to handle input and output operations. It serves as a dedicated unit for managing communication between peripherals and the rest of the system, including the memory.
- The IOP takes care of coordinating data transfers, handling interrupts, and managing other aspects of input and output. It helps to offload these tasks from the main CPU, allowing it to focus on more complex computations.
So, both DMA and IOP are interfaces or features that facilitate the direct transfer of data between peripherals and the memory unit without requiring constant involvement of the main CPU. They contribute to improving the efficiency and performance of the overall system by streamlining data transfer operations.
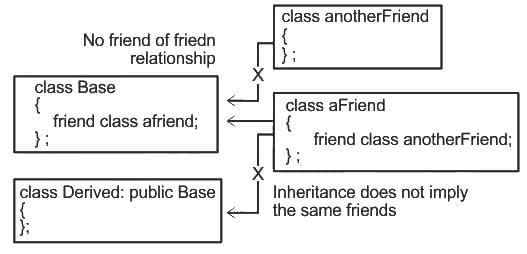
Q33: Given below are two statements:
Statement (I): The friend function and the member functions of a friend class directly access the private and protected data.
Statement (II): The friend function can access the private data through the member functions of the base class
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
Statement (I) The friend function and the member functions of a friend class directly access the private and protected data.is correct.
- In C++, friend function and friend classes have special privilege to access private and protected members of the class where they are declared as friends. They sort of break the encapsulation, which makes them highly privileged members.
Statement (I) The friend function can access the private data through the member functions of the base class is correct.
- A friend function is a non-class member function that is granted the rights to access private and protected elements of a class. Although it's not a part of the class, this external function holds special permission to interact with the restricted parts of the class.
Q34: In most general case, the computer needs to process each instruction with the following sequence of steps:
(A) Calculate the effective address
(B) Execute the instruction
(C) Fetch the instruction from memory
(D) Fetch the operand from memory
(E) Decode the instruction
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B), (C), (D), (E)
(b) (A), (B), (C), (E), (D)
(c) (C), (E), (A), (D), (B)
(d) (C), (E), (D), (A), (B)
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is (C), (E), (A), (D), (B)
Fetch instruction from memory (C):
- The first step in the execution cycle of an instruction is the instruction fetch, wherein the instruction is retrieved from memory. This is necessary because the Central Processing Unit (CPU) needs to know what operation to execute.
Decode the instruction (E):
- Once the instruction is fetched, it needs to be decoded or interpreted. During this step, the CPU's control unit identifies what operation is to be undertaken, based on the instruction's opcode.
Calculate the effective address (A):
- If the instruction has an operand, it's not usually the actual data but rather its address that is specified in the instruction. During this phase, the address for the operands is computed. The calculated effective address will be used to fetch the operand in the next step.
Fetch the operand from memory (D):
- Once the effective address has been calculated, the CPU can fetch the operand from memory. In other words, it retrieves the data that the operation will work on.
Execute the instruction (B):
- Finally, the action specified by the instruction is performed, typically a mathematical or logical operation on the fetched operand. The result of this operation may be stored back into memory, written to a register, or outputted depending on the specifics of the instruction.
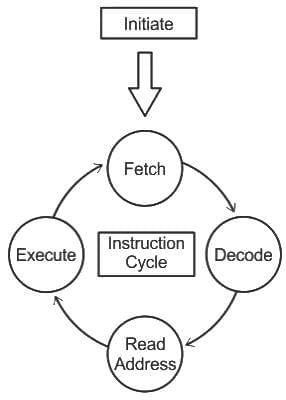
So, this explains why option 3) (C), (E), (A), (D), (B) is the correct sequence for these steps in the execution of an instruction.
Q35: Indexed/grouped allocation is useful as :
(A) It supports both sequential and direct access.
(B) Entire block is available for data.
(C) It does not require lots of space for keeping pointers.
(D) No external fragmentation.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) Only
(b) (B) and (C) Only
(c) (B) Only
(d) (A), (B) and (D) Only
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (B) and (D) Only
(A) It supports both sequential and direct access.
- Indexed/grouped allocation allows both sequential (one block after another) and direct (jumping straight to a desired block) access to data.
(B) Entire block is available for data.
- In indexed allocation, the entire block is indeed available for storing data. The index block, a separate entity, contains the pointers to the data blocks.
(D) No external fragmentation.
- Indexed allocation helps prevent external fragmentation as all files have their own index block that keeps track of the blocks associated with it.
However, option (C) is not correct because indexed allocation actually needs space to store pointers in the index block for each file, which can be considerably large for large files. Therefore, indexed allocation does require lots of space for keeping pointers.
Q36: In a genetic algorithm optimization problem the fitness function is defined as f(x) = x2 - 4x + 4. Given a population of four individuals with values of x: {1.5, 2.0, 3.0, 4.5}
What is the fitness value of the individual that will be selected as the parent for reproduction in one generation?
(a) 2.25
(b) 6.0
(c) 0.0
(d) 6.25
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is 6.25
In a genetic algorithm seeks to find the optimal solution to a problem, guided by the principle of survival of the fittest.
To find the fitness value of each individual in the population, we can use the given fitness function 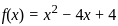 .
.
Let's calculate the fitness values for the individuals with the given values of x:
1. For x = 1.5: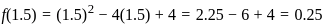
2. For x = 2.0: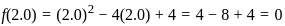
3. For x = 3.0: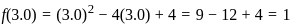
4. For x = 4.5: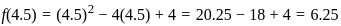
So, the fitness values for the individuals are: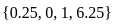
The individual with the highest fitness value is x = 4.5 with a fitness value of 6.25. Therefore, the correct answer is option 4) 6.25.
Q37: In “bit stuffing”, each frame begins and ends with a bit pattern in hexadecimal ?
(a) Ox8C
(b) Ox6F
(c) OxFF
(d) Ox7E
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is Ox7E
- Bit stuffing is a technique used in communications protocols to ensure that a special sequence of bits (the flag sequence) does not appear within the data portion of a frame. This is important to differentiate the start and end of the frame from its content. The flag sequence, often used to signify the start and end of a frame, must be unique, meaning that it shouldn't be mistaken for or mixed up with the payload data.
- In particular protocols such as High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC) and the related Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP) in byte-oriented mode, each frame starts and ends with a specific bit pattern, 0x7E in hexadecimal or 01111110 in binary. This specific sequence of bits is recognized by the receiving device as the start or end marker of a data frame.
- To avoid confusion between the special flag sequences and the data being transmitted, a process called bit stuffing or byte stuffing (based on whether the operation takes place on an individual bit or a whole byte of data) is used. If the sender recognizes that the same sequence of bits (the flag byte) is to be sent within the data, it inserts (stuffs) an extra bit (usually 0) into the data to differentiate the flag byte from the corresponding sequence in the content of the message.
- When the receiver identifies an extra 0 bit following five consecutive 1 bits within the data portion of the frame, it removes (de-stuffs) the 0 bit to retrieve the original data. However, if it spots the flag sequence (01111110), it interprets it as the start or end of a frame.
Therefore, bit stuffing is essential in differentiating between the data payload and the flag byte to ensure reliable communication.
Q38: Which of the following statements is/are NOT CORRECT about NUMA?
(A) LOAD and STORE instructions are used to access remote memory.
(B) There is a single address space visible to all CPU.
(C) Access to local memory is slower than access to remote memory.
(D) When the access time to remote memory is hidden, the system is called NC - NUMA.
(E) In CC-NUMA, Coherent caches are present.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) and (C) Only
(b) (B) and (D) Only
(c) (A) and (E) Only
(d) (C) and (D) Only
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is (C) and (D) Only
(A) LOAD and STORE instructions are used to access remote memory.
- This statement is CORRECT because in a NUMA system, a processor can access its own local memory faster than non-local memory (memory associated with a different processor), and the LOAD and STORE instructions are used for this memory access.
(B) There is a single address space visible to all CPU.
- This statement is CORRECT. All CPUs see a single shared address space which is broken into multiple nodes. Each node has local memory which it can access faster than memory in the other nodes.
(C) Access to local memory is slower than access to remote memory.
- This statement is INCORRECT. In a NUMA system, access to local memory is faster than access to remote memory (memory local to another processor or memory region).
(D) When the access time to remote memory is hidden, the system is called NC - NUMA.
- This statement is INCORRECT. When the high latency of remote memory access is hidden by caching or prefetching techniques, the system is called Cache-Only Memory Architecture (COMA), not NC-NUMA.
(E) In CC-NUMA, Coherent caches are present.
- This statement is CORRECT. CC-NUMA stands for Cache Coherent Non-Uniform Memory Access. In CC-NUMA, all nodes have a coherent view of the memory – meaning that a change of a value in one node's cache is effectively and timely propagated to the caches of the other nodes that have cached that value.
Q39: A system bus in which each data item is transferred during a time slice known in advance to both units source and destination is called:
(a) MIMD
(b) DMA
(c) asynchronous bus
(d) synchronous bus
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is synchronous bus
Synchronous Bus:
- This is a computer bus in which data is transferred on regular intervals that are set by a clock signal. Since the source and destination known about these intervals in advance, efficient data transmission can be achieved.
- This approach is used to maintain consistency and reliability of data transactions, although it does require close coordination between various system components.
Other Related Points
MIMD (Multiple Instruction, Multiple Data):
- In MIMD, multiple processors can execute different instructions on different data concurrently. It's a characteristic of a more advanced architecture for parallel computing or multiprocessing machines.
DMA (Direct Memory Access):
- This refers to a feature of computer systems that allows certain hardware subsystems to access main system memory independently of the central processing unit (CPU). It's used to speed up data transfer and improve system performance, as it allows devices to process data without the CPU, reducing its workload.
Asynchronous Bus:
- This refers to a bus in a computer system that operates at its own pace regardless of the main system clock. Data is transferred through poses, where each data piece waits for the previous piece to be fully transferred before it begins its transmission. This approach can lead to variations in transfer speed depending on a variety of factors, including system load.
Q40: Match List-I with List-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
(b) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
(c) A - IV, B - II, C - I, D - III
(d) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
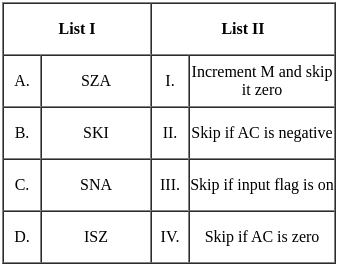
A. SZA:
- This is probably an instruction for "Skip if Zero Accumulator". In assembly language, the accumulator (AC) is a register where intermediate arithmetic and logic results are stored. If the AC is zero, this instruction would cause the program to skip the next instruction.
B. SKI:
- This could stand for "Skip if Input flag is on". In computer programming, a flag is a value that acts as a signal for a function or process. Therefore, this instruction would skip the next instruction if a specific input flag was raised or "on".
C. SNA:
- "Skip if Accumulator is Negative" seems an apt fit. Similar to SZA, this instruction would skip the next operation if the value in the accumulator is negative.
D. ISZ:
- This likely means "Increment and Skip if Zero". This means the designated memory location (M) would be incremented by one, and then if the result is zero, the next instruction would be skipped.
Thus, based on these s, the correct match is:
A. SZA - IV. Skip if AC is zero B. SKI - III. Skip if input flag is on C. SNA - II. Skip if AC is negative D. ISZ - I. Increment M and skip it zero
So, the correct choice is 4) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I.
Q41: In the context of Alpha Beta pruning in game trees which of the following statements are correct regarding cut off procedures ?
(A) Alpha Beta pruning can eliminate subtrees with certainly when the value of a node exceeds both the alpha and beta bounds.
(B) The primarily purpose of Alpha-Beta pruning is to save computation time by searching fewer nodes in the same tree.
(C) Alpha Beta pruning guarantees the optimal solution in all cases by exploring the entire game tree.
(D) Alpha and Beta bounds are initialized to negative and positive infinity respectively at the root note.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (C), (D) Only
(b) (B), (C), (D) Only
(c) (A), (B), (D) Only
(d) (C), (B) Only
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (B), (D) Only
- (A) Alpha Beta pruning can eliminate subtrees with certainty when the value of a node exceeds both the alpha and beta bounds. This is correct. If a node's value falls outside the range defined by alpha and beta, it can be pruned.
- (B) The primary purpose of Alpha-Beta pruning is to save computation time by searching fewer nodes in the same tree. This is correct. Alpha-Beta pruning reduces the number of nodes that need to be examined in the search tree, thereby speeding up the computation.
- (C) Alpha Beta pruning guarantees the optimal solution in all cases by exploring the entire game tree. This statement is incorrect. While alpha-beta pruning does find the optimal solution, it does not do so by exploring the whole tree. The whole point of alpha-beta pruning is to avoid having to explore the entire tree.
- (D) Alpha and Beta bounds are initialized to negative and positive infinity respectively at the root node. This one is correct. At the start of search, alpha (the value of the best option we have found so far for max) is initialized to negative infinity, and beta (the value of the best option we have found so far for min) is initialized to positive infinity.
So the correct answer is (A), (B), (D) Only.
Q42: Arrange the following in ascending order:
(A) Remainder of 4916 when divided by 17
(B) Remainder of 2446 when divided by 9
(C) Remainder of 15517 when divided by 17
(D) Last digits of the number 745
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B), (C), (D)
(b) (A), (B), (D), (C)
(c) (A), (C), (B), (D)
(d) (D), (C), (B), (A)
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (C), (B), (D)
(A) Remainder of 4916 when divided by 17.
- Recall that if we look at powers of 49 modulo 17, we find that they alternate between 32 (equivalent to 15 mod 17) and 1. That's because 49² = 2401, which is 17 * 141 + 1. Since 16 is even, 49^16 is equivalent to 1 mod 17. So the remainder is 1.
(B) Remainder of 2446 when divided by 9.
- The Remainder is 7.
(C) Remainder of 15517 when divided by 17.
- Since 155 is a multiple of 17, the remainder of 155n divided by 17 will always be 2, irrespective of the value of n. So the remainder is 2.
(D) Last digits of the number 745
- The cycle for the last digits of powers of 7 is 7, 9, 3, 1, repeating every 4th power. Therefore, the last digit of 745 (where 45 mod 4 = 1) will be 7.
So, the correct answer is option 3: (A), (C), (B), (D).
Q43: If the universe of discourse is set of integers, then which of the followings are TRUE?
(A) ∀n ∃m(n2 < m)
(B) ∃n ∀m(n < m2)
(C) ∃n ∀m(nm = m)
(D) ∃n ∃m(n2 + m2 = 6)
(E) ∃n ∃m(n + m = 4 ∧ n - m = 1)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B) and (C) Only
(b) (B) and (C) Only
(c) (C), (D) and (E) Only
(d) (C) and (E) Only
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is (B) and (C) Only
(B) ∃n ∀m(n < m2):
- This quantifier implies there is an integer n such that for all integers m, n is less than m^2. This is also true if we pick n to be one of the negative integers.
(C) ∃n ∀m(nm = m):
- This quantifier implies that there's an integer n for which nm equals m for every integer m. This is true if we consider n = 1 because 1 * m = m for all integer m.
(A) ∀n ∃m(n2 < m):
- This quantifier implies that for all integers n, there is an integer m that is greater than n2. it is false because square of any number is greater then not less then.
(D) ∃n ∃m(n2 + m2 = 6)
- There exist integers n and m such that n2 + m2 is equal to 6. This is not true because there are no integers n and m such that their squares add up to 6.
(E) ∃n ∃m(n + m = 4 ∧ n - m = 1)
- There exist integers n and m such that n + m is equal to 4 and n - m is equal to 1. This is false when n = 2 and m = 1.
Q44: Which of the following is/are NOT CORRECT statement?
(A) The first record in each block of the data file is known as actor record.
(B) Dense index has index entries for every search key value in the data file.
(C) Searching is harder in the B+ tree than B- tree as the all external nodes linked to each other.
(D) In extendible hashing the size of directory is just an array of 2d-1, where d is global depth.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B) and (C) Only
(b) (A), (C) and (D) Only
(c) (A), (B) and (D) Only
(d) (A), (B), (C) and (D) Only
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (C) and (D) Only
(A) The first record in each block of the data file is known as actor record.
- The first record in each block of the data file is not known as an actor record, this seems to be an incorrect usage of terminology in the context of databases.
(C) Searching is harder in the B+ tree than B- tree as the all external nodes linked to each other.
- This statement is incorrect. Searching in a B+ tree is not harder than in a B- tree. In fact, B+ trees are often preferred over B- trees for database indexing because they allow for efficient traversal through all keys (all keys are stored in the leaves in a sorted manner and leaves are linked for easy traversal).
(D) In extendible hashing the size of directory is just an array of 2d-1, where d is global depth.
- In extendible hashing, the size of the directory is not an array of 2d-1. It is actually an array of 2d, where 'd' stands for the global depth.
So, the correct answer from the options given is: 2) (A), (C) and (D) Only
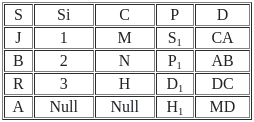
Q45: Consider the following relations X (S, Si, C) and Y (S, P, D).
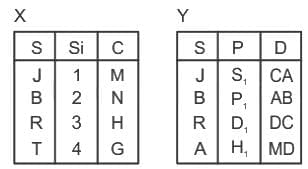 Result of X ⟖ x.s = y.sY is
Result of X ⟖ x.s = y.sY is
(a) 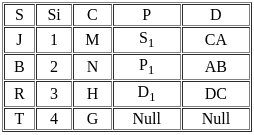
(b) 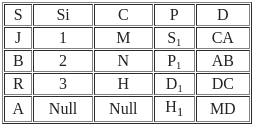
(c) 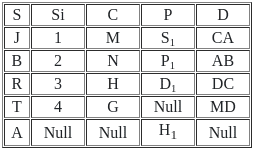
(d) None of these
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Option 2
A "Right Outer Join" is a concept from SQL (Structured Query Language), used in relational databases. It's a method of combining two tables based on a common column between them, showing all records from the 'right' table and matched records from the 'left' table.
The result of a right outer join contains all the records from the right table and any records in the left table that match the join condition. For the records in the right table that do not have a corresponding match in the left table, the result is NULL in the columns of the left table.
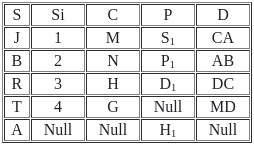
Q46: Consider the following relations X (S, Si, C) and Y (S, P, D).
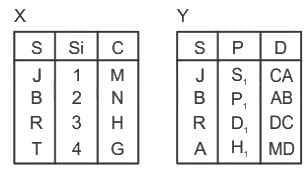 Number of tuples by applying right outer join on relation X and Y is/are :
Number of tuples by applying right outer join on relation X and Y is/are :
(a) 16
(b) 5
(c) 3
(d) 4
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is 4
A "Right Outer Join" is a concept from SQL (Structured Query Language), used in relational databases. It's a method of combining two tables based on a common column between them, showing all records from the 'right' table and matched records from the 'left' table.
The result of a right outer join contains all the records from the right table and any records in the left table that match the join condition. For the records in the right table that do not have a corresponding match in the left table, the result is NULL in the columns of the left table.
Here the above table is right outer join they have contain four row so correct answer is 4.
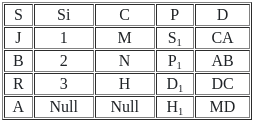
Q47: Consider the following relations X (S, Si, C) and Y (S, P, D).
 Find the number of tuples by applying the operation X⟕X.s = y.sY
Find the number of tuples by applying the operation X⟕X.s = y.sY
(a) 1
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 6
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 4
A "Left Outer Join" is another type of JOIN operation in SQL, which is used to combine rows from two or more tables based on a related column between them.
Unlike the Right Outer Join, the Left Outer Join returns all the records from the left table, and the matched records from the right table. If there is no match found in the right table, the result is NULL on the right-side part.
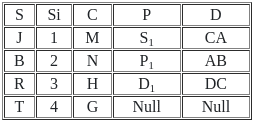
Here the above table is left outer join they have contain four row so correct answer is 4.
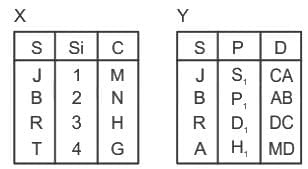
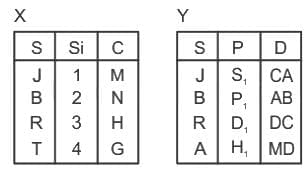
Q48: Consider the following relations X (S, Si, C) and Y (S, P, D).
 Number of tuples obtained by applying cartesian product over X and Y are :
Number of tuples obtained by applying cartesian product over X and Y are :
(a) 16
(b) 12
(c) 04
(d) 32
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is 16
In the context of relational databases and SQL, a Cartesian product (or CROSS JOIN) refers to a JOIN operation that returns the combination of every row of the first table with every row of the second table.
If table1 has n rows and table2 has m rows, the Cartesian product of these two tables will result in a table with n*m rows.
If table1 has 4 rows and table2 has 4 rows, the Cartesian product of these two tables will result in a table with 4*4 = 16 rows.
So the correct answer is 16
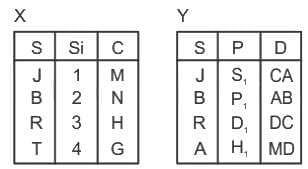
Q49: Consider the following relations X (S, Si, C) and Y (S, P, D).
 Which of the following join is used to get all the tuples of relation X and Y with Null values of corresponding missing values ?
Which of the following join is used to get all the tuples of relation X and Y with Null values of corresponding missing values ?
(a) Left outer join
(b) Right outer join
(c) Natural join
(d) Full outer join
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is Full outer join
A "Full Outer Join" (also known as Full Join) is used in SQL to combine rows from two or more tables based on a related column. The outcome of a Full Outer Join includes all the records from both the left and the right tables, and it matches rows from both tables where the join condition is met. If there isn't a match, the result is NULL on either the left or the right side (or both, in case of no common relation).
So the correct answer is Full outer join
Other Related Points
- A NATURAL JOIN is a type of join operation in SQL that is used to combine rows from two or more tables based on the columns they have in common. This can be particularly useful when you have two tables that contain related data, but do not have an explicitly defined foreign key relationship.
- Unlike other join types, NATURAL JOIN doesn't require a specific condition to match columns from one table with another, as it automatically matches columns with the same name in both tables. For example, if both tables have a column named 'customer_id', the NATURAL JOIN will use this column as the join condition.
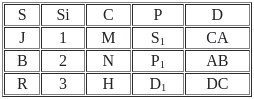
Q50: Match List-I with List-II
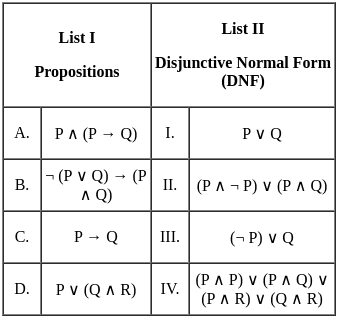
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(b) A - II, B - I, C - III, D - IV
(c) A - III, B - I, C - II, D - IV
(d) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is A - II, B - I, C - III, D - IV
Option A: P ∧ (P → Q)
- P ∨ ¬ P ∨ Q
- P ∧ ¬ P ∨ P ∨ Q
- This Propositions match from Disjunctive Normal Form list option II
Option B: ¬ (P ∨ Q) → (P ∧ Q)
- ¬ ¬ (P ∨ Q) v (P ∧ Q)
- (P ∨ Q) v (P ∧ Q)
- (P ∨ Q)
- This Propositions match from Disjunctive Normal Form list option I
Option C: P → Q
- P → Q
- ¬ P ∨ Q
- This Propositions match from Disjunctive Normal Form list option III
Option D: P ∨ (Q ∧ R)
- P ∨ (Q ∧ R)
- (P ∧ P) ∨ (P ∧ Q) ∨ (P ∧ R) ∨ (Q ∧ R)
- This Propositions match from Disjunctive Normal Form list option IV
Q51: Food X contains 6 units of Vitamin D per gram and 7 units of Vitamin E per gram and cost is Rs 12 per gram. Food Y contains 8 units of vitamin D per gram and 12 units of Vitamin E per gram and cost is Rs 20 per gram. The daily minimum requirements of vitamin D and E are 100 units and 120 units respectively.
Suppose x is quantity (in gram) of food X, y is quantity (in gram) of food Y. Answering the following question based on the above paragraph given.
The dual of the formulated LPP is :
(a) Max Z = 100u +120v
s.t
6u + 7v ≤ 12
8u + 12 v ≤ 20
u, v ≥ 0
(b) Max Z = 12u + 20u
s.t
6u + 7v ≤ 100
8u + 12 v ≤ 120
u, v ≥ 0
(c) Max Z = 100u +120v
s.t
6u + 7v ≤ 12
8u + 7 v ≤ 20
u, v are unrestricted
(d) Max Z = 100u + 120v
s.t
6u + 7v ≥ 12
8u + 12 v ≥ 20
u, v ≥ 0
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is Option 1
 The dual of a Linear Programming Problem (LPP) interchanges the role of the objective function coefficients and right-hand side constants from the primal problem. They also interchange the constraint coefficients matrix and relations.
The dual of a Linear Programming Problem (LPP) interchanges the role of the objective function coefficients and right-hand side constants from the primal problem. They also interchange the constraint coefficients matrix and relations.
In the primal problem, we're minimizing cost subject to constraints that ensure we have enough vitamins. In the dual, we'd be maximizing vitamin intake with cost constraints.
So, from the primal problem's constraints: 6x + 8y ≥ 100 (for Vitamin D) becomes 6u + 8v ≤ 12 (for the cost of Food X), and 7x + 12y ≥ 120 (for Vitamin E) becomes 7u + 12v ≤ 20 (for the cost of Food Y).
The objective changes as well, the minimization of cost becomes maximization of vitamins. So 'Min Z = 12x + 20y' changes to 'Max Z = 100u + 120v'.
So, the correct dual for the LP problem is:
Max Z = 100u + 120v
s.t 6u + 7v ≤ 12 8u + 12v ≤ 20 u, v ≥ 0
Q52: Food X contains 6 units of Vitamin D per gram and 7 units of Vitamin E per gram and cost is Rs 12 per gram. Food Y contains 8 units of vitamin D per gram and 12 units of Vitamin E per gram and cost is Rs 20 per gram. The daily minimum requirements of vitamin D and E are 100 units and 120 units respectively.
Suppose x is quantity (in gram) of food X, y is quantity (in gram) of food Y. Answering the following question based on the above paragraph given.
Which of the following are quantities (in grams) of food X and Y respectively when the cost of food is minimum :
(a) 0 and 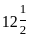
(b) 15 and 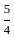
(c) 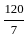 and 0
and 0
(d) 0 and 10
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is 15 and 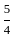
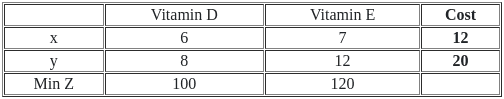
The cost function to minimize: Z = 12x + 20y
The nutrient requirements: 6x + 8y ≥ 100, 7x + 12y ≥ 120
The non-negativity constraints: x,y ≥ 0
We use trial and error method, we can substitute the given values for x and y from all four options into the constraint inequalities and validate which of those satisfy both constraints (6x + 8y ≥ 100 and 7x + 12y ≥ 120).
Option 1: 0 and 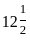
= 6x + 8y ≥ 100
= 6*0 + 8*12/2 ≥ 100
= 0 + 48 ≥ 100
= 48 ≥ 100 it is not greater then or equal to So it is not correct option.
Option 2: 15 and 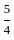
= 6x + 8y ≥ 100
= 6*15 + 8* 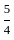 ≥ 100
≥ 100
= 90 + 20 ≥ 100
= 100 ≥ 100
= 7x + 12y ≥ 120
= 7*15 + 12* 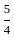 ≥ 120
≥ 120
= 105 + 15 ≥ 120
= 120 ≥ 120
Here both equation satisfy the condition so we not need to check other option.
So correct answer is Option 2: 15 and 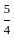
Q53: Food X contains 6 units of Vitamin D per gram and 7 units of Vitamin E per gram and cost is Rs 12 per gram. Food Y contains 8 units of vitamin D per gram and 12 units of Vitamin E per gram and cost is Rs 20 per gram. The daily minimum requirements of vitamin D and E are 100 units and 120 units respectively.
Suppose x is quantity (in gram) of food X, y is quantity (in gram) of food Y. Answering the following question based on the above paragraph given.
Which of the following constrains when formulating the LPP ?
(a) 6x + 7y ≤ 100, 8x + 12y ≤ 120, x, y ≥ 0
(b) 6x + 8y ≤ 100, 7x + 12y ≤ 120, x, y ≥ 0
(c) 6x + 7y ≥ 100, 8x + 12y ≥ 120, x, y ≥ 0
(d) 6x + 8y ≥ 100, 7x + 12y ≥ 120, x, y ≥ 0
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is 6x + 8y ≥ 100, 7x + 12y ≥ 120, x, y ≥ 0
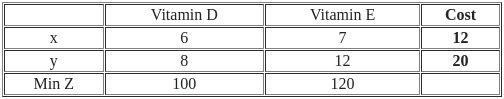
To formulate the constraints for the Linear Programming Problem (LPP), we need to consider the minimum daily requirements of vitamins D and E.
Since Food X contains 6 units of Vitamin D per gram and 7 units of Vitamin E per gram, and Food Y contains 8 units of Vitamin D per gram and 12 units of Vitamin E per gram, the constraints will be set up based on the minimum consumption to meet the daily vitamin requirements.
Given the minimum daily requirement of 100 units of Vitamin D and 120 units of Vitamin E, we need to make sure we are consuming at least this amount.
Therefore, the correct constraints for the problem are:
6x + 8y ≥ 100 (for Vitamin D requirement) and 7x + 12y ≥ 120 (for Vitamin E requirement).
Along with these, x, y ≥ 0 as the quantity of food cannot be negative.
So, the correct answer is: 6x + 8y ≥ 100, 7x + 12y ≥ 120, x, y ≥ 0
Q54: Food X contains 6 units of Vitamin D per gram and 7 units of Vitamin E per gram and cost is Rs 12 per gram. Food Y contains 8 units of vitamin D per gram and 12 units of Vitamin E per gram and cost is Rs 20 per gram. The daily minimum requirements of vitamin D and E are 100 units and 120 units respectively.
Suppose x is quantity (in gram) of food X, y is quantity (in gram) of food Y. Answering the following question based on the above paragraph given.
The minimum cost of food is:
(a) 205
(b) 250
(c) 330
(d) 200
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is 205
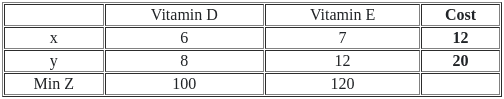
The cost function to minimize: Z = 12x + 20y
The nutrient requirements: 6x + 8y ≥ 100, 7x + 12y ≥ 120
The non-negativity constraints: x,y ≥ 0
We also find the previous question value of x and y so we put the value of x and y in the minimize function.
The cost function to minimize: Z = 12x + 20y
The cost function to minimize: Z = 12*15 +20*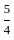
The cost function to minimize: Z = 180 + 25
The cost function to minimize: Z =205
So correct answer is 205
Q55: Food X contains 6 units of Vitamin D per gram and 7 units of Vitamin E per gram and cost is Rs 12 per gram. Food Y contains 8 units of vitamin D per gram and 12 units of Vitamin E per gram and cost is Rs 20 per gram. The daily minimum requirements of vitamin D and E are 100 units and 120 units respectively.
Suppose x is quantity (in gram) of food X, y is quantity (in gram) of food Y. Answering the following question based on the above paragraph given.
The cost funtion of total food is :
(a) Z = 6x + 7y
(b) Z = 8x + 12y
(c) Z = 12x + 20y
(d) Z = 20x + 12y
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Z = 12x + 20y
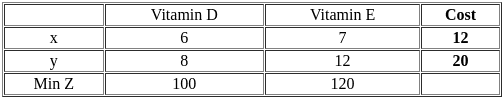
The cost function of total food based on the information provided would be the sum of the cost per gram of each type of food times the quantity of each.
For Food X it is Rs 12 per gram and for Food Y it is Rs 20 per gram.
If we denote the quantity of Food X as x and the quantity of Food Y as y, then the cost function is:
Z = 12x + 20y
So correct answer is Min Z = 12x + 20y
Q56: What is the probability that a positive integer selected at random from the set of positive integer not exceeding 100 is divisible by either 2 or 5 ?
(a) 10/5
(b) 3/5
(c) 2/5
(d) 1/5
Ans: B
Sol: Calculation
We need to find the probability that a positive integer, selected randomly from 1 to 100 is divisible by either 2 or 5.
First, find the total number of positive integers from 1 to 100, which is 100.
Divisible by 2:
Every second number is divisible by 2, so there are 100 / 2 = 50 such numbers.
Divisible by 5:
Every fifth number is divisible by 5, so there are 100 / 5 = 20 such numbers.
There is an intersection between these two sets of numbers, namely, those numbers which are divisible by both 2 and 5 (that is, numbers divisible by 10). To avoid counting these twice, we need to subtract these from the total.
Divisible by 10 (both 2 and 5):
Every tenth number is divisible by 10, so there are 100 / 10 = 10 such numbers.
So, numbers that are divisible by either 2 or 5 are 50 (divisible by 2) + 20 (divisible by 5) - 10 (divisible by both) = 60.
Now, the probability of a number randomly picked from 1 to 100 being divisible by either 2 or 5 is 60/100 = 3/5.
Hence, the correct answer is option 2) 3/5.
Q57: The sum of minimum and maximum number of final states for a Deterministic Finite Automata (DFA) having ‘P’ state is equal to :
(a) P
(b) P - 1
(c) P + 1
(d) P + 2
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is P + 1
Minimum Number of Final States (min):
- The minimum number of final states for a DFA can be 1.
- Therefore, we have min = 1.
Maximum Number of Final States (Max):
- The maximum number of final states for a DFA can be n.
- In this case, every state is a final state.
- Therefore, Max = P.
Sum of Minimum and Maximum Number of Final States:
- The sum of m and M is equal to 1 + n, which simplifies to n.
- Therefore, the answer is option C, n + 1.
Q58: Which of the following is not a palindromic subsequence of the string “ababcdabba” ?
(a) abcba
(b) abba
(c) abbbba
(d) adba
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is adba
A palindromic subsequence is one that remains the same when reversed. The given string is "ababcdabba".
From this string:
- "abcba" is a palindromic subsequence ('a', 'b', 'c', 'b', 'a').
- "abba" is a palindromic subsequence ('a', 'b', 'b', 'a').
- "abbbba" is not a palindromic subsequence. There are only two 'b's in the input string, and 'abbbba' would require at least four.
- "adba" is not a palindromic subsequence. There is no 'd' in the input string.
Therefore, the non-palindromic subsequences are 3) abbbba and 4) adba.
Q59: The selection of Spiral Model based on characteristics of requirements:
(A) Are requirements easily understandable and defined?
(B) Do we change requirements quite often?
(C) Can we define requirements early in the cycle?
(D) Requirements are indicating a complex to be built
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (C) Only
(b) (B) Only
(c) (B) and (D) Only
(d) (A) and (C) Only
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is (B) and (D) Only
The Spiral Model in software development is a risk-driven model which involves four phases: planning, risk analysis, engineering and evaluation. This model is ideal for large, complex and innovative projects where the requirements might not be clearly defined upfront or are highly likely to evolve during the course of the project.
Based on these characteristics, the right answer about the applicability of Spiral Model is:
- (B) Do we change requirements quite often? - This indeed aligns with the Spiral Model as changes can be introduced in the system in the subsequent phases, making it highly flexible.
- (D) Requirements are indicating a complex to be built - Spiral model is suitable for complex projects as the risk analysis phase allows for thorough identification and mitigation of any potential issues, especially important in a complex project.
Q60: Consider the following code segment:
int arr[ ] = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4};
int i=1, *ptr;
ptr=arr + 2;
arrange the following printf statements in the increasing order of their output.
(A) printf("%d", ptr[i]);
(B) printf ("%d", ptr[i+1]);
(C) printf ("%d", ptr[-i]);
(D) printf ("%d", ptr[-i+1]);
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) (C), (A), (B), (D)
(b) (C), (D), (A), (B)
(c) (D), (A), (B), (C)
(d) (A), (B), (D), (C)
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is (C), (D), (A), (B)
(A) printf("%d", ptr[i]);
- This will print the value of the 'i' index from the 'ptr', which is the array starting from the index '2'. So ptr[i] is equivalent to arr[2+i], which is arr[3] = 3.
(B) printf ("%d", ptr[i+1]);
- This will print the value of the 'i+1' index from the 'ptr'. ptr[i+1] is equivalent to arr[2+i+1], which is arr[4] = 4.
(C) printf ("%d", ptr[-i]);
- This accesses the element at the position '-i' from the starting point of 'ptr'. ptr[-i] is equivalent to arr[2-i] which is arr[1] = 1.
(D) printf ("%d", ptr[-i+1]);
- This accesses the element at the position '-i+1' from 'ptr'. ptr[-i+1] is equivalent to arr[2-i+1] which is arr[2] = 2.
So the increasing order of their output is (C) < (D) < (A) < (B).
This corresponds to choice 2) (C), (D), (A), (B).
Q61: Arrange the following steps in the correct order for a DHCP Client to renew its IP lease with a DHCP server:
(A) DHCP client sends a DHCPREQUEST message
(B) DHCP server acknowledges the renewal with a DHCPACK message
(C) DHCP client checks the local lease timer and initiates renewal
(D) DHCP server updates its lease database
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B), (C), (D)
(b) (C), (D), (B), (A)
(c) (C), (B), (A), (D)
(d) (C), (A), (B), (D)
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is (C), (A), (B), (D)
Steps in DHCP IP lease renewal:
(C) DHCP client checks the local lease timer and initiates renewal:
- A DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) client typically initiates a renewal process when 50% of its lease time has expired, though this can be configured differently. DHCP clients manage a lease timer which monitors the duration for which the allocated IP address is valid.
(A) DHCP client sends a DHCPREQUEST message:
- If the DHCP client determines that the lease is set to expire, it will request a lease renewal from the DHCP server. It does this by sending a DHCPREQUEST message to the server. This message contains the client's current IP address.
(B) DHCP server acknowledges the renewal with a DHCPACK message:
- The DHCP server receives the DHCPREQUEST message from the DHCP client. If the server determines that the request is valid and the IP address can be renewed, the server sends back a DHCPACK message to the client. This acknowledgement includes the renewed lease duration and any network configuration options that the server is set to distribute.
(D) DHCP server updates its lease database:
- Finally, after successfully renewing the client's lease, the DHCP server updates its own lease database to reflect this change. This is to keep track of all IP addresses it has leased out. It helps in future IP address allocation, ensuring that the DHCP server doesn't accidentally assign an already leased IP address to a different client.
Q62: Which of the following is TRUE ?
(a) The cost of searching an AVL tree is θ (log n) but that of binary search is 0(n)
(b) The cost of searching an AVL tree in θ (log n) but that of complete binary tree is θ (n log n)
(c) The cost of searching a binary tree is 0 (log n) but that of AVL tree is θ (n)
(d) The cost of searching an AVL tree is θ (n log n) but that of binary search tree is θ (n)
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is The cost of searching an AVL tree is θ (log n) but that of binary search is 0(n)
- AVL trees are a type of self-balancing binary search tree. The time complexity for search, insert, and delete operations in an AVL tree is O(log n), where "n" is number of nodes in the tree.
- This is because AVL trees ensure that the tree remains balanced, thus keeping the height at log n.
- On the other hand, a binary search tree (not necessarily balanced) could degenerate into something similar to a linked list in the worst-case scenario, leading to a time complexity of O(n) for aforementioned operations.
- The statement jumbles up terminologies a bit; binary search typically refers to an operation performed on sorted arrays rather than trees, and that indeed has a time complexity of O(log n). But if we understand that it's referring to a binary search tree, the statement is correct.
The other options incorrectly state the time complexities for AVL and binary trees.
Q63: Match List-I with List-II
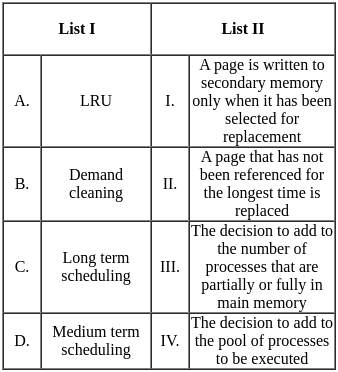
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - I, B - III, C - IV, D - II
(b) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
(c) A - III, B - II, C - I, D - IV
(d) A - IV, B - II, C - III, D - I
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
- A. LRU, which stands for Least Recently Used, is a page replacement algorithm. This policy replaces the page that has not been referenced for the longest time. So, LRU corresponds to II.
- B. Demand Cleaning refers to the policy where a page is written to secondary memory only when it has been selected for replacement. Hence, Demand cleaning corresponds to I.
- C. Long term scheduling is the decision to add to the pool of processes to be executed. So, Long term scheduling corresponds to IV.
- D. Medium term scheduling is the decision to add to the number of processes that are partially or fully in main memory. So, Medium term scheduling corresponds to III.
Q64: Which data structure is typically used to implement hash table ?
(a) Linked list
(b) Array
(c) Binary Tree
(d) Stack
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Array
Array:
- Arrays store a fixed-size sequential collection of elements of the same type.
- They are used for hash table implementations because you can directly access the data if the index is known, which aligns with the key-value nature of hash tables.
- The index becomes the hashed key, allowing for fast direct access.
Other Related Points
Linked List:
- A linked list is a linear data structure where each element is a separate object, called a 'node.' Each node contains a pointer to the next node along with the data. Linked lists are typically leveraged in stacks, queues, and even within hash tables to handle collisions (with separate chaining for instance), however, they are not usually used to implement the hash table itself.
Binary Tree:
- A binary tree is a tree data structure in which each node can have a maximum of two children, referred to as the left child and the right child. It's best suited for binary search tree or heap data structures, used for operations like sorting and searching, but it's not typically used for implementing hash tables.
Stack:
- A stack is a LIFO (Last In First Out) data structure. It allows operations at one end which is the top of the stack. It's used to reverse a data set, in function call implementations, and in algorithms like depth-first search. However, stacks are not typically used to implement hash tables, because they lack the direct access nature that hash tables offer.
Q65: Level - 0 DFD is also called as:
(a) Use case Diagram
(b) Sequence Diagram
(c) Context Diagram
(d) Prototype Diagram
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Context Diagram
Context Diagram:
- Also known as a Level 0 Data Flow Diagram (DFD), it provides a high-level view of an information system and does not go into details about processes.
- Context diagrams are typically included in a requirements document to show how the system interacts and will interface with other systems. In layman’s term, it can be termed as a bird’s eye view of the system environment.
Other Related Points
Use Case Diagram:
- This is a type of diagram from UML (Unified Modeling Language). It shows the relationships among actors and use cases within a system.
- A "use case" represents a distinct functionality of a system, a component, a package, or a class. "Actors" are people, or other systems, that interact with the system being represented.
Sequence Diagram:
- Also a type of diagram from UML, it represents the sequence of actions and interactions of different parts (or "actors") of a system over time.
- Each actor or component will have a "lifeline" and the interactions between them are represented by "arrows" indicating the flow or direction of interaction. It's particularly useful to represent the flow of logic within the system or process.
Prototype Diagram:
- This is not common terminology related to systems design or UML. However, "prototyping" is a common approach in system development, involving creation of an early, simplified model of a final system or product.
- This can be used to test concepts, designs, and interactions. This term might be referring to diagrams used during prototyping, but these can vary widely depending on the specifics of the project and the techniques used.
Q66: Which of the following statement are truth statements if universe of discourse is set of integers :
(A) ∀n(n2 ≥ 0)
(B) ∃n(n2 = 2)
(C) ∀n(n2 ≥ n)
(D) ∃n(n2 < 0)
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) and (B) Only
(b) (B) and (C) Only
(c) (C) and (D) Only
(d) (A) and (C) Only
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is (A) and (C) Only
(A) ∀n(n2 ≥ 0):
- This statement is true because the square of any integer is always greater than or equal to zero.
(B) ∃n(n2 = 2):
- This statement is false. No integer squared equals 2.
(C) ∀n(n2 ≥ n):
- This statement is true for all integers because the square of any integer is greater than or equal to the integer itself.
(D) ∃n(n2 < 0):
- This statement is false because the square of any integer cannot be less than zero.
So, the correct option is: (A) and (C) Only.
Q67: The prototyping model has the sequence:
(A) Customer Evaluation
(B) Quick design
(C) Requirements
(D) Implement
(E) Design
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (C) → (A) → (D) → (B) → (E)
(b) (B) → (C) → (A) → (D) → (E)
(c) (C) → (B) → (D) → (A) → (E)
(d) (E) → (B) → (C) → (D) → (A)
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer (C) → (B) → (D) → (A) → (E)
The prototyping model is a software development model where a prototype is built, tested, and then reworked as necessary until an acceptable prototype is achieved before the final solution is developed. It involves the following stages:
- Requirements: This is the initial step where the basic requirements of the software are collected from the client. These requirements are generally not very detailed at this stage, and are mainly focused on overall system functionality.
- Quick Design: In the prototyping model, an initial project design serves to outline the software requirement specifications. It includes all the essential specifications that the desired model should contain. This provides a basis to create a rough prototype.
- Implement: This is where the development of the prototype of the software takes place. Initial design is converted into a working model. This model doesn’t have to be perfect or fully functioned.
- Customer Evaluation: After the development of the initial prototype, it is sent to the customer for their evaluation. The customer tests the prototype, uses it, and identifies any modifications or enhancements they want to be included.
- Design: Based on the feedback given by the customer, necessary adjustments and improvements are made in the prototype, and the ‘Design’ phase is carried out. If the client isn’t satisfied, the cycle resumes—starting with revamping the quick design according to the refined intricacies given by the client.
Essentially, the Prototyping Model aims to reduce the inherent risks in offering a complex system, and allows for systems to be developed more accurately according to users' needs and wants.
Q68: Consider the three points P1(1, 2, 0), P2(3, 6, 20) and P3(2, 4, 6) and a view point C(0, 0, -10). Choose the correct options.
(A) P1 obscure P2, if viewed from C.
(B) P2 obscure P1, if viewed from C.
(C) P3 does not obscure P1, if viewed from C.
(D) P2 does not obscure P3, if viewed from C.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B) and (C) Only
(b) (A), (C) and (D) Only
(c) (B), (C) and (D) Only
(d) (A), (B) and (D) Only
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (C) and (D) Only
We can determine whether one point obscures another by examining the lines formed from the view point (C) to each point in question. Specifically, we need to find whether the given points (P1, P2, P3) are on the same line (i.e., they are collinear) formed with view point C. If the points are collinear, the point that is closer to the view point will obscure the farther one when seen from the view point.
The vector SOa formed by Segment OC, in this case, is directed from point O to point a in 3D space. If P1, P2, P3 and C are collinear, then vector CP1 = a1 * CP2, vector CP1 = a2 * CP3 and vector CP2 = a3 * CP3.
Let's calculate these vectors and check:
- Vector CP1: (1 - 0, 2 - 0, 0 - -10) = (1, 2, 10) Vector CP2: (3 - 0, 6 - 0, 20 - -10) = (3, 6, 30) Vector CP3: (2 - 0, 4 - 0, 6 - -10) = (2, 4, 16)
We can say that one vector is a scalar multiple of the another vector if all components are multiplied by the same scalar value. Therefore,
- CP2 = 3CP1 since (3, 6, 30) = 3(1, 2, 10)
- CP3 ≠ any multiple of CP1, or of CP2 as (2, 4, 16) ≠ any multiple of (1, 2, 10) or (3, 6, 30)
So, from point C,
- (A) P1 obscures P2, as P2 lies on the line segment from C to P1.
- (B) P2 does not obscure P1, as P1 is nearer to C on the same line segment.
- (C) P3 does not obscure P1, as they do not lie on the same line segment.
- (D) P2 does not obscure P3, as they do not lie on the same line segment.
So, the correct answer is: (A), (C) and (D) Only
Q69: Arrange the following encoding strategies used in Genetic Algorithms (GAS) in the correct sequence starting from the initial step and ending with the final representation of solutions:
(A) Binary Encoding
(B) Real valued Encoding
(C) Permutation Encoding
(D) Gray coding
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (D), (B), (A), (C)
(b) (B), (D), (A), (C)
(c) (C), (D), (A), (B)
(d) (B), (C), (A), (D)
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is (C), (D), (A), (B)
Permutation Encoding (C):
- In this encoding strategy, the representation of solutions is done by permuting the order of elements in the solution space. This is useful when the order or arrangement of elements matters.
Gray Coding (D):
- Gray coding is a binary numeral system where two successive values differ in only one bit. In the context of genetic algorithms, Gray coding is used to reduce the chance of introducing errors during the encoding and decoding processes.
Binary Encoding (A):
- Binary encoding is the most basic form of encoding where each parameter of a solution is represented as a string of binary digits (0s and 1s). It's a common and simple way to represent solutions in genetic algorithms.
Real-valued Encoding (B):
- Real-valued encoding is used when the parameters of the solution space are continuous. In this encoding, real numbers are used to represent the values of parameters. It allows for a more fine-grained representation of solutions in cases where the solution space is continuous.
So, the correct sequence is (C), (D), (A), (B), as given in option 3) (C), (D), (A), (B).
Q70: Match List-I with List-II
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - III, B - II, C - IV, D - I
(b) A - II, B - III, C - I, D - IV
(c) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
(d) A - II, B - IV, C - III, D - I
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
A. Bresenham algorithm -
- It's a line drawing algorithm that determines the points of an n-dimensional raster that should be selected in order to form a close approximation to a straight line between two points. It was developed to avoid floating point operations which were costly in machine cycles on the computers of the time.
B. Cohen-Sutherland algorithm
- It is a computer-graphics algorithm used for line clipping, that is, given a line in the plane specified by its endpoints and a rectangle (also specified by its endpoint), the algorithm efficiently finds the points where the line intersects the rectangle - that's why it's categorized under 'Line clipping algorithm'.
C. Sutherland-Hodgeman algorithm -
- This algorithm is used in computer graphics for clipping polygons. It works by extending each segment of the polygon to the edges of the clipping rectangle.
D. Z-Buffer algorithm -
- It's a depth sorting algorithm in 3D computer graphics, used for hidden surface removal. It basically works by testing pixel depth for each polygon. If a polygon's depth is greater (meaning it's behind others), it's not drawn.
Q71: Which of the following are commonly used parsing techniques in NLP (Natural Language Processing) for syntactic analysis.
(A) Top down parsing
(B) Bottom Up parsing
(C) Dependency parsing
(D) Statistical machine translation
(E) Earley parsing
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (C), (D), (E) Only
(b) (B), (C), (D), (E) Only
(c) (A), (B), (C), (E) Only
(d) (A) and (B) Only
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (B), (C), (E) Only
Top-down parsing, bottom-up parsing, dependency parsing, and Earley parsing are all techniques used for syntactic analysis in Natural Language Processing.
- (A) Top-down parsing starts from the top (or root node) and works down, trying to match the input sentence against the productions in the grammar.
- (B) Bottom-up parsing starts with the input and tries to reach the grammar's start symbol.
- (C) Dependency parsing focuses on the relationships between words in a sentence, taking into account their grammatical connections to each other
- rather than their position in the sentence.
- (E) Earley parsing is a type of chart parsing algorithm for parsing context-free languages that uses dynamic programming principles for efficiency.
- (D) Statistical Machine Translation is not a parsing technique but a type of language translation approach which uses statistical methods to draw from large amounts of text data to generate translations.
Q72: Match List-I with List-II
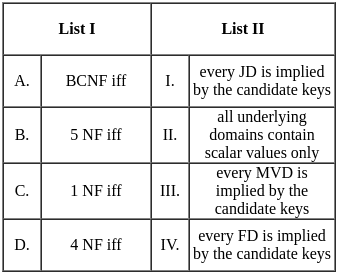
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - III, B - II, C - I, D - IV
(b) A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
(c) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
(d) A - IV, B - I, C - III, D - II
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
BCNF (Boyce-Codd Normal Form):
- BCNF is a higher version of 3NF (Third Normal Form) in relational database normalization.
- BCNF is a normalization form that is used when there are multiple candidate keys in a relation.
- The condition for a table to be in BCNF is that for each functional dependency (X -> Y), X should be a superkey.
- This "functional dependency is implied by the candidate keys" is exactly what is mentioned in option IV.
5NF (Project-Join Normal Form or Fifth Normal Form):
- This normal form is designed to reduce redundancy in relational databases recording multi-valued facts by isolating semantically related multiple relationships.
- A table is said to be in the Fifth Normal Form only if it is in 4NF and it cannot be decomposed into any number of smaller tables without loss of data.
- Here, "every JD (Join Dependency) is implied by the candidate keys" is the definition of 5NF which is option I.
1NF (First Normal Form):
- In this normal form, the data in the table is with no repeating groups i.e., there are no arrays or sets in any of its relations.
- Each attribute contains only atomic, or indivisible, values, hence the statement "all underlying domains contain scalar values only". So, option II is correct for 1NF.
4NF (Fourth Normal Form):
- A table is in the Fourth Normal Form when it is in the Boyce-Codd Normal Form and there are no multi-valued dependencies about a set of attributes in the table.
- In this normal form, we ensure that the semantic of storing grouped data is maintained by removing any dependencies of sets of values.
- This "every MVD (Multivalued Dependency) is implied by the candidate keys" is the definition of 4NF which is option III.
So, the correct arrangements are - A (BCNF) corresponds with IV, B (5NF) corresponds with I, C (1NF) corresponds with II, D (4NF) corresponds with III.
Q73: Match List-I with List-II
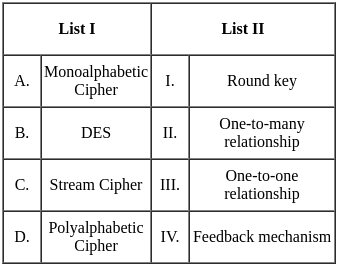
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
(b) A - III, B - IV, C - II, D - I
(c) A - I, B - III, C - IV, D - II
(d) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
A. Monoalphabetic Cipher - III. One-to-one relationship
- Monoalphabetic ciphers involve a one-to-one mapping of each plaintext letter to a corresponding ciphertext letter.
B. DES (Data Encryption Standard) - I. Round key
- DES uses round keys in its encryption and decryption process.
C. Stream Cipher - IV. Feedback mechanism
- Stream ciphers often use a feedback mechanism to generate a stream of key bits.
D. Polyalphabetic Cipher - II. One-to-many relationship
- Polyalphabetic ciphers involve a one-to-many relationship between plaintext and ciphertext, as each plaintext letter can be encrypted to multiple ciphertext letters depending on the key.
So, the correct match is:A - III, B - I, C - IV, D - II
Q74: Consider the following functions :
f(n) = 3n√n
g(n) = 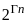
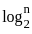
h(n) = n!
Which of the following is true ?
(a) h(n) is 0 (f(n))
(b) h(n) is 0 (g(n))
(c) g(n) is not 0 (f(n))
(d) f(n) is 0 (g(n))
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is f(n) is 0 (g(n))
The notation Ω(n) is the formal way to express the lower bound of an algorithm's running time. It measures the best case time complexity or the best amount of time an algorithm can possibly take to complete.
The notation O(n) is the formal way to express the upper bound of an algorithm's running time. It measures the worstcase time complexity of the algorithms.
Let's analyze the functions and their growth rates to determine which of the statements is true.
Given Functions:
1. f(n) = 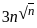
2. g(n) = 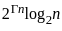
3. h(n) = n!
Analyzing the Growth Rates:
1. f(n) = 
This function grows very quickly due to the  term, which is larger than any polynomial but smaller than exponential functions like
term, which is larger than any polynomial but smaller than exponential functions like  .
.
2. g(n) = 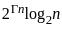
This function involves the Gamma function 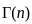 , which grows faster than factorial functions but depends on the context. Given that
, which grows faster than factorial functions but depends on the context. Given that 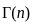 is closely related to (n 1)! , this function also grows extremely fast, much faster than polynomial functions.
is closely related to (n 1)! , this function also grows extremely fast, much faster than polynomial functions.
3. h(n) = n!
Factorial growth is very rapid and typically outpaces both polynomial and exponential functions for large n .
Comparing the Growth Rates:
h(n) compared to f(n) :
- h(n) = n! grows faster than f(n) =
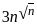 , so h(n) is not O(f(n)) . This eliminates Option 1.
, so h(n) is not O(f(n)) . This eliminates Option 1.
h(n) compared to g(n) :
- While h(n) = n! grows quickly, g(n) =
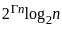 with
with 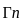 growing similarly to factorial but involving an extra exponential factor
growing similarly to factorial but involving an extra exponential factor 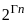 . This suggests that g(n) might grow faster, making h(n) not O(g(n)) . This eliminates Option 2.
. This suggests that g(n) might grow faster, making h(n) not O(g(n)) . This eliminates Option 2.
g(n) compared to f(n) :
- g(n) involves an exponential term
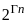 which grows much faster than
which grows much faster than 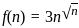 , implying that g(n) is not O(f(n)) . So, Option 3 is also incorrect.
, implying that g(n) is not O(f(n)) . So, Option 3 is also incorrect.
f(n) compared to g(n) :
- Since g(n) grows faster than f(n) , f(n) is O(g(n)) . This supports Option 4.
Conclusion:
The correct answer is:
3) g(n) is not O(f(n))
This indicates that g(n) grows faster than f(n) , meaning f(n) is not an upper bound on g(n) .
Here's a list of functions in asymptotic notation that we often encounter when analyzing algorithms, ordered by slowest to fastest growing:
Q75: 2-3-4 trees are B - trees of order 4. They are isometric of _____ trees.
(a) AVL
(b) AA
(c) 2 - 3
(d) Red-Black
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is Red-Black
- A 2-3-4 tree is a type of search tree data structure in computer science that is also known as a B-tree of order 4.
- In a 2-3-4 tree, each internal node can have 2, 3, or 4 child nodes, and the tree is balanced in such a way that all the leaves are at the same level.
- Red-Black trees are another type of binary search tree with additional properties that ensure balance.
- They are used to maintain a balanced search tree, which helps in ensuring efficient search, insertion, and deletion operations.
- The isometry between 2-3-4 trees and Red-Black trees means that there is a one-to-one correspondence between their structures.
- For every 2-3-4 tree, there exists a corresponding Red-Black tree, and vice versa, such that the operations on the trees are equivalent.
This isometric relationship makes it possible to convert between the two structures while preserving the order and balance properties. Therefore, the correct option is 4) Red-Black trees.
Q76: Which of the following statements are CORRECT?
(A) A process always check state of currently executing process to enter critical section.
(B) Spin locks uses busy waiting.
(C) Periodically testing a variable until some value appear is known as busy waiting.
(D) Critical region is a part of program, where shared memory is kept.
(E) Printer daemon, continuously checks to see if there are any file to be printed.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) and (B) Only
(b) (B) and (C) Only
(c) (B) and (D) Only
(d) (B) and (E) Only
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is (B) and (D) Only
(A) A process always check state of currently executing process to enter critical schema:
- This is not necessarily correct. A process does not always need to check the state of the currently executing process to enter the critical section. It just needs to ensure mutual exclusion i.e. if another process is executing in its critical section, then no other process can enter the critical section.
(B) Spin locks use busy waiting:
- This is correct. A spin lock is a type of lock where a thread repeatedly checks if the lock is free. If the lock is not free the thread continues to 'spin' in a loop (hence the name 'spin lock'), checking until the lock becomes free.
(D) Critical region is a part of program, where shared memory is kept:
- This is correct, a critical region or a critical section in a program is a place where shared resources, such as shared memory, are accessed. These critical sections need to be protected to prevent race conditions or data inconsistency when the resources are accessed by multiple threads or processes concurrently.
(E) Printer daemon, continuously checks to see if there are any file to be printed:
- This is partially correct. While a printer daemon can periodically check for new jobs, saying it "continuously checks" may not be fully representative of how it functions - it often responds to interrupts or other signals generated when a new print job arrives. This depends on the implementation of the software.
So the correct answer is 3) (B) and (D) Only.
Q77: Match List-I with List-II
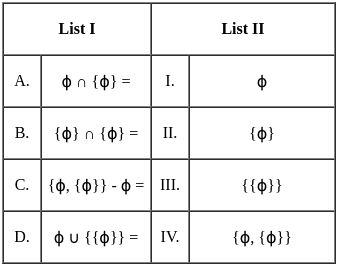
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - I, B - II, C - III, D - IV
(b) A - II, B - I, C - III, D - IV
(c) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
(d) A - I, B - II, C - IV, D - III
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is A - I, B - II, C - IV, D - III
In the context of Set Theory:
- ϕ denotes the empty set, also written as {}.
- ∩ denotes intersection, which means it gives the common elements in both sets.
- ∪ denotes union, which means it gives all unique elements from both sets.
- . denotes set difference, which means it gives elements of first set that are not in the second set.
Now, let's evaluate the set operations:
- A. ϕ ∩ {ϕ} = ϕ : Here the intersection of the empty set and a set consisting of the empty set is the empty set itself as there are no common elements. That means A should match with I.
- B. {ϕ} ∩ {ϕ} = {ϕ} : The intersection of a set consisting of the empty set and itself is the set with the empty set. That means B should match with II.
- C. {ϕ, {ϕ}} - ϕ = {ϕ, {ϕ}} : Here, the set difference give same set. So, C should match with IV.
- D. ϕ ∪ {{ϕ}} = {{ϕ}} : The union of the empty set and the set of the empty set is just the set containing the empty set. So, D should match with III.
Given these matching pairs, the correct answer from the given choices would be: A - I, B - II, C - IV, D - III
Q78: Which collision resolution technique involves maintaining a linked list of collided keys ?
(a) Linear probing
(b) Quadratic probing
(c) Chaining
(d) Double hashing
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Chaining
Chaining:
- Chaining is a technique where each cell in the hash table is treated as a separate linked list (or any dynamic data structure).
- When a collision occurs, the key-value pair is stored in the same slot, but as the next node in the linked list.
- This provides an intuitive and efficient way of handling collisions, and there is no need for an empty spot in the hash table to handle a collision.
- However, the disadvantage is potential inefficiency due to poor distribution of keys, which could result in a few chains growing very long while others are short or empty.
Other Related Points
Linear Probing:
- This is an open addressing technique where each cell of a hash table is treated as a slot that can store one key-value pair.
- When a collision occurs, the algorithm searches linearly in the table until it finds an empty slot.
- The drawback of linear probing is that it can lead to clustering, where a group of adjacent cells gets filled, increasing the average search time.
Quadratic Probing:
- Similar to linear probing, quadratic probing is also an open addressing method intended to deal with collisions.
- However, instead of searching linearly for an empty slot upon collision, quadratic probing searches the hash table for an empty slot by following a quadratic function (usually of the form i2, where i is the attempt number).
- This method reduces primary clustering, but a unique problem called secondary clustering can occur.
Double Hashing:
- Double hashing is a technique where two hash functions are used, one as a primary function and another as a secondary function.
- If a collision occurs with the first hash function, the second hash function is used to determine another location for the slot.
- This method is less susceptible to clustering than the linear and quadratic probing methods, but it requires more computational cost due to the use of two hash functions.
Q79: Match List-I with List-II according to input to the compiler phase that process it:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - IV, B - III, C - I, D - II
(b) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
(c) A - II, B - IV, C - I, D - III
(d) A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
List-I:
- A. Syntax tree: This is a tree representation of the syntactic structure of source code according to the formal grammar of the programming language.
- B. Intermediate representation: This is a less abstract computational syntax tree that is easier to compile into machine code.
- C. Token stream: This is the output from the lexical analyzer. It's a sequence of standardized symbols representing language components (operators, identifiers, keywords, etc).
- D. Character stream: This is the raw source code as input into the compiler.
List-II:
- I. Code generator: This phase of the compiler reads the intermediate representation and transforms it into target machine code.
- II. Semantic analyzer: The semantic analyzer uses the syntax tree to check the source code for semantic errors and gathers type information for the following code-generation phase.
- III. Lexical analyzer: This phase of the compiler reads raw source code (character stream) and transforms it into a series of tokens (token stream).
- IV. Syntax analyzer: Also known as a parser, this phase of the compiler reads the token stream from the lexical analyzer and groups the tokens into grammatically cohesive sections by constructing a syntax tree.
Process Flow:
- The raw source code (Character stream) is read by the Lexical analyzer that turns it into a series of Tokens (Token stream). This corresponds to D - III.
- The Syntax Analyzer or parser takes that Token stream and groups the tokens into hierarchically structured expressions to form a Syntax tree which follows the grammar rules of the language. This corresponds to C - IV.
- The Semantic Analyzer will then inspect the Syntax tree to check the source code for semantic consistency with the language definition. This corresponds to A - II.
- Finally, the Code generator takes the output from the Semantic Analyzer phase, usually an Intermediate representation, and transforms it into machine language instructions to get a final executable. This corresponds to B - I.
Hence, A-II, B-I, C-IV, and D-III is the correct relation.
Q80: The steps for analysis and design of object oriented system.
(A) Draw interaction diagrams
(B) Draw state chart and object diagram
(C) Draw use case and activity diagram
(D) Draw component and deployment diagram
(E) Draw class diagram
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (E) → (B) → (A) → (C) → (D)
(b) (B) → (A) → (E) → (D) → (C)
(c) (E) → (C) → (B) → (D) → (A)
(d) (C) → (A) → (E) → (B) → (D)
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is (C) → (A) → (E) → (B) → (D)
Object-oriented system design and analysis usually follows these steps:
- Define the system requirements through a use case diagram (C).
- Identify objects and their interactions through interaction (sequence or collaboration) diagrams (A).
- Shape the static structure of the system through a class diagram (E).
- Show different states an object goes through during its lifecycle using state chart diagrams and how objects are instantiated from classes using object diagrams (B).
- Finally, illustrate the physical aspect of the system using component and deployment diagrams (D).
Therefore, the correct option would be (C) → (A) → (E) → (B) → (D)
Q81: Given below are two statements:
Statement (I): A thread is a dispatchable unit of work that does not execute sequentially and is not interruptible
Statement (II): It is not possible to alter the behaviour of a thread by altering its context when thread is suspended
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
Statement (I): "A thread is a dispatchable unit of work that does not execute sequentially and is not interruptible."
- This statement is incorrect. A thread is a basic unit of execution within a process, and it does execute sequentially. Threads can be interrupted, and their execution can be preempted by the operating system scheduler, allowing other threads to run.
Statement (II): "It is not possible to alter the behavior of a thread by altering its context when the thread is suspended."
- This statement is also incorrect. The context of a thread includes its register values, program counter, and other execution-related information. When a thread is suspended, its context can be saved, modified, and then restored when the thread resumes execution. This allows for changes in the behavior of the thread.
Therefore, Statement I is incorrect, and Statement II is incorrect as well. The correct answer is option 2) "Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect.".
Q82: Test suite consists of :
(a) Set of defect cases
(b) Set of boundary cases
(c) Set of test cases
(d) Set of nested cases
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Set of test cases
Set of test cases:
- A test suite is a collection of test cases designed to assess the various functionalities and aspects of a software application. Each test case within the suite represents a specific scenario, condition, or interaction that needs to be tested. These scenarios can include normal operations, edge cases, and negative cases to ensure comprehensive coverage of the software.
- Test cases are written based on requirements and specifications, and they serve as a means to verify that the software behaves as expected. They cover different paths through the application to catch potential defects and ensure the overall quality of the software.
Other Related Points
- Set of defect cases: This typically refers to a collection of test cases designed to expose defects or bugs in the software. These tests are intended to verify that the system behaves correctly and to identify any issues that need to be addressed.
- Set of boundary cases: These are test cases that focus on the boundaries or limits of the input or system behavior. The goal is to ensure that the software handles values at the edges of acceptable ranges correctly. For example, if a system accepts input values between 1 and 10, boundary tests might include values like 1, 10, and values just beyond those limits.
Q83: Which of the statement is/are CORRECT?
(A) Moore and Mealy machines are finite state machines with output capabilities.
(B) Any given Moore machine has an equivalent Mealy machine.
(C) Any given Mealy machine has an equivalent Moore machine.
(D) Moore machine is not a finite state machine.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) and (B) Only
(b) (A), (B) and (C) Only
(c) (B) and (D) Only
(d) (A), (B) and (D) Only
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (B) and (C) Only
(A) Moore and Mealy machines are finite state machines with output capabilities.
- A finite state machine (FSM) is a mathematical model of computation that has a finite number of states and transitions between those states. FSMs are basic models used to design computer programs and digital electronic systems. Mealy and Moore machines are two types of FSMs.
- A Mealy machine is a type of FSM where the output values are determined by both its current state and the current inputs. This means that the output can change whenever there is a change to the input, even if the machine remains in the same state.
- A Moore machine, on the other hand, is a type of FSM where the outputs are determined only by the current state, and not the inputs. This means that the output only changes when the machine transitions to a different state.
(B) Any given Moore machine has an equivalent Mealy machine.
- This statement is true. For any given Moore machine, an equivalent Mealy machine can be constructed where the output associated with each transition in the Mealy machine is the output associated with the destination state in the Moore machine. The Mealy machine will necessarily have the same number of states as the Moore machine.
(C) Any given Mealy machine has an equivalent Moore machine.
- This statement is also true, but with a caveat. For any given Mealy machine, an equivalent Moore machine can indeed be constructed. However, the process for this is more complicated because the output of a Mealy machine can change based on the input and not just the state. As a result, the equivalent Moore machine might need more states than the original Mealy machine if two or more distinct outputs are produced in the same state depending upon the input.
(D) Moore machine is not a finite state machine.
- This statement is false. As stated above, a Moore machine is a type of finite state machine. Its distinguishing feature is that its output values are determined solely by its current state and not the inputs.
So, the correct choice from the options is: (A), (B) and (C) Only
Q84: Which of the following statement/s are CORRECT?
(A) NRZ is a bipolar scheme in which the positive voltage define bit is 0 (zero).
(B) NRZ-L and NRZ-I both have an average signal rate of N/2.
(C) The idea of RZ and NRZ-L are combined into Manchester scheme.
(D) NRZ-L and NRZ-I both have DC component problems.
(E) The minimum bandwidth of Manchester and differential Manchester is 3 times that of NRZ.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B) and (C) Only
(b) (A), (C), (D) and (E) Only
(c) (B), (C) and (D) Only
(d) (A), (B), (C) and (E) Only
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is (B), (C) and (D) Only.
(A) NRZ is a bipolar scheme in which the positive voltage defines bit is 0 (zero).
- This is incorrect. Non-return-to-zero (NRZ) is not a bipolar scheme. Also, in bipolar schemes, typically, the zero bit is represented by no voltage, not a positive one.
(B) NRZ-L and NRZ-I both have an average signal rate of N/2.
- This is correct. NRZ-level and NRZ-invert are binary coding schemes where the signal drops (but does not return to zero) in the middle of the bit period. The average signal rate in both cases is N/2.
(C) The idea of RZ and NRZ-L are combined into the Manchester scheme.
- This is correct. Manchester coding, used in data communication, combines elements of RZ (Return to Zero) and NRZ-L (Non-Return to Zero Level) to encode data.
(D) NRZ-L and NRZ-I both have DC component problems.
- This is correct. Both NRZ-L and NRZ-I maintain a constant voltage level for the entire bit period, which can create a direct current (DC) component when long sequences of identical bits are sent.
(E) The minimum bandwidth of Manchester and Differential Manchester is 3 times that of NRZ.
- This is incorrect. The minimum bandwidth for Manchester and Differential Manchester schemes is actually twice that of NRZ, not three times.
Hence, looking at every given statement, the correct ones are B, C and D.
Q85: Consider a Grammar E → E + n|E x n|n for a sentence n + n x n, the handles in the right-sentential form of the reduction are?
(a) n, E + n and E + n x n
(b) n, E + n and E + E x n
(c) n, n + n and n + n x n
(d) n, E + n and E x n
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is n, E + n and E x n
In the given grammar E → E + n | E x n | n, let's consider the sentence n + n x n.
The right-sentential form during the reduction process will be as follows:
- n + n x n (Start with the original sentence)
- E + n x n (Apply the reduction E → n)
- E x n (Apply the reduction E → E + n)
- E (Apply the reduction E → E x n)
Therefore, the correct option is: 4) n, E + n, and E x n
Q86: Which of the following graphs are trees ?
A. 
B. 
C. 
D. 
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) (A) and (B) Only
(b) (A), (B) and (D) Only
(c) (A) and (D) Only
(d) (A), (B), (C) and (D) Only
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is (A) and (B) Only
Tree:
- A tree is a type of graph that is acyclic, meaning there are no cycles or loops. It consists of nodes connected by edges in a hierarchical structure. Each node, except the root, has exactly one parent, forming a parent-child relationship.
- There are no loops or cycles in a tree structure.
- A tree is a connected graph, meaning there is a unique path between any pair of nodes.
- Each node in a tree (except the root) has exactly one parent.
- There is a unique topmost node called the root from which all other nodes are descendants.
- Trees are usually directed, meaning edges have a specific direction (from parent to child).
- Trees are commonly used for hierarchical data representation, such as file systems, organizational charts, and expression trees. Binary Search Trees (BSTs) are a specific type of tree used for efficient searching and sorting.
 Graph:
Graph:
- A graph is a more general structure that can be cyclic or acyclic. It consists of nodes (vertices) and edges connecting these nodes. There are no strict hierarchical relationships between nodes in a graph.
- A graph may or may not be connected. There can be isolated components within a graph.
- Nodes in a graph can have multiple incoming edges, meaning they can have multiple parents.
- There is no concept of a root node in a general graph.
- Graphs can be directed or undirected. In directed graphs, edges have a direction, while in undirected graphs, edges have no direction.
- Graphs are more general-purpose and can represent a wide range of relationships between entities. They are used in applications like social networks, road networks, dependency graphs, and more.
Option D is disconnected graph so it is not tree
Only option A and B are acyclic graph so correct answer is option 1.
Q87: Which of the following statement/s is/are NOT CORRECT?
(A) OSPF is based on distance-vector routing protocol.
(B) Both link-state and distance-vector routing are based on the least cost goal.
(C) BGP4 is based on the path-vector algorithm.
(D) The three-node instability can be avoided using split horizon combined with poison reverse.
(E) RIP is based on link state algorithm.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (D) and (E) Only
(b) (A) and (B) Only
(c) (B) and (C) Only
(d) (B), (C) and (E) Only
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (D) and (E) Only
(A) OSPF is based on distance-vector routing protocol. -
- This statement is NOT CORRECT. OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) is based on a link-state routing protocol, not a distance-vector protocol.
(B) Both link-state and distance-vector routing are based on the least cost goal. -
- This statement is CORRECT. Both of these protocols seek the path with the least overall "cost," where cost is a value that represents characteristics like bandwidth, delay, reliability, etc.
(C) BGP4 is based on the path-vector algorithm. -
- This statement is CORRECT. The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) version 4 is based on a path-vector algorithm rather than being purely distance-vector or link-state.
(D) The three-node instability can be avoided using split horizon combined with poison reverse. -
- This statement is NOT CORRECT. Both split horizon and poison reverse are methods to prevent routing loops in distance-vector protocols; however, they might not always be able to prevent "count-to-infinity" problems, including certain cases of three-node instability.
(E) RIP is based on link state algorithm. -
- This statement is NOT CORRECT. The Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is based on a distance-vector algorithm, not a link-state algorithm.
Q88: If N2 = N × N, N is set of natural numbers and R is relation on N2, s.t. RC N2 × N2 i.e. R ↔ xv = yu, then which of the following are TRUE?
(A) Reflexive
(B) Symmetric
(C) Transitive
(D) Assymmetric
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) and (B) Only
(b) (B) and (C) Only
(c) (A), (C) and (D) Only
(d) (A), (B) and (C) Only
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (B) and (C) Only
The properties of the relation R defined as R ↔ xv = yu.
(A) Reflexive:
- For a relation to be reflexive, (a, a) must be in the relation for every element a in the set.
- In this case, we have x = u and y = v. So, (u, u) and (v, v) must be in the relation.
- Since N is the set of natural numbers, for any natural number u or v, (u, u) and (v, v) are in the relation. Therefore, the relation is reflexive.
(B) Symmetric:
- For a relation to be symmetric, if (a, b) is in the relation, then (b, a) must also be in the relation for every pair (a, b). In this case, (x, y) is in the relation if and only if (y, x) is in the relation, as xv = yu implies yu = xv. Therefore, the relation is symmetric.
(C) Transitive:
- For a relation to be transitive, if (a, b) and (b, c) are in the relation, then (a, c) must also be in the relation for every triplet (a, b, c). In this case, if xv = yu and yw = zv, then multiplying these equations gives xw = zu, which implies (x, w) is in the relation. Therefore, the relation is transitive.
(D) Asymmetric:
- For a relation to be asymmetric, if (a, b) is in the relation, then (b, a) must not be in the relation for any pair (a, b). In this case, since (x, y) is in the relation if and only if (y, x) is also in the relation, the relation cannot be asymmetric.
Based on the analysis: The correct answer is: 4) (A), (B) and (C) Only
Q89: The work done by UDP is/are:
(A) Congestion control
(B) Flow control
(C) Retransmission
(D) Segments transmission
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) and (D) Only
(b) (C) Only
(c) (D) Only
(d) (B) and (C) Only
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is (D) Only
- UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is one of the core internet protocols. It belongs to the transport layer in the TCP/IP model, similar to TCP (Transmission Control Protocol).
- However, while UDP and TCP share the common goal of delivering data between devices, they are fundamentally different in their operation methods.
- UDP is a connectionless protocol. It does not establish a connection before sending data, thus there is no need for congestion control, flow control, or retransmission, which are all mechanisms aimed at ensuring reliable, ordered delivery of data.
- (A) Congestion control: A mechanism that prevents network congestion by controlling how much data can be sent at a time. TCP uses congestion control to prevent sending too much data at once, but UDP does not implement this.
- (B) Flow control: A method to control the rate at which data is transferred to make sure a fast sender cannot overwhelm a slow receiver. TCP includes flow control, but UDP does not.
- (C) Retransmission: A reliability mechanism in TCP where lost packets are detected and retransmitted. UDP does not have this mechanism — it sends packets without checking if they are received.
- (D) Segment transmission: This refers to the actual transfer of data. Both TCP and UDP perform this function. In UDP's case, it sends data in segments called datagrams. Each datagram is independent and does not require connection setup or teardown processes.
Therefore, out of the provided options, UDP performs only (D) Segment transmission. Hence the correct answer is 3) (D) Only.
Q90: Which of the statement are CORRECT?
(A) Constructors are invoked automatically when the objects are created.
(B) Constructors do not have return types, not even void and therefore they cannot return values.
(C) Constructors cannot be inherited though a derived class can call the base class constructors.
(D) Constructors can be declared as virtual.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A), (B) and (D) Only
(b) (A), (B) and (C) Only
(c) (B), (C) and (D) Only
(d) (A), (C) and (D) Only
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (B) and (C) Only
(A) Constructors are invoked automatically when the objects are created - Correct.
- In object-oriented programming, a constructor is a special method that is automatically called when an object is created. Its purpose is to initialize the new object's attributes.
(B) Constructors do not have return types, not even void and therefore they cannot return values - Correct.
- Constructors are primarily used to initialize object attributes. They do not return values, and specifying a return type for them can lead to compiler errors.
(C) Constructors cannot be inherited though a derived class can call the base class constructors - Correct.
An object of a subclass type will automatically call its superclass's constructor as part of its creation process, but the constructor itself isn't an inheritable part of the superclass.
(D) Constructors can be declared as virtual - Incorrect.
- Virtuality applies to functions that you want to be executed polymorphically, where the specific implementation depends on the actual run-time type of the object.
- Constructors don't work this way: when you create an object of a derived class, it's the derived constructor that you want to run.
- The base class constructor is called automatically already, before the derived class constructor, so there is no need for virtuality.
Q91: Which of the following is not a field in TCP header ?
(a) Sequence Number
(b) Checksum
(c) Fregmentation offset
(d) Window size
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Fragmentation offset
Fragmentation Offset:
- This is not a field in the TCP header; rather, it is a field in the IP header. The IP protocol allows large packets to be fragmented into smaller fragments for transmission over networks with smaller Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) sizes.
- The fragmentation offset field in the IP header indicates the position of a fragment in the original, unfragmented packet.
Other Related Points
Sequence Number:
- This field in the TCP header is used to identify the order of the bytes sent in a TCP connection. It is crucial for ensuring that the data is received in the correct order and for handling retransmissions.
Checksum:
- The checksum field in the TCP header is used for error-checking purposes. It helps verify the integrity of the TCP header and data. The sender calculates the checksum based on the contents of the TCP header and data, and the receiver verifies it to detect any transmission errors.
Window Size:
- The window size field in the TCP header is used to manage flow control in a TCP connection. It indicates the amount of data, in bytes, that can be sent by the sender before an acknowledgment is required from the receiver. Adjusting the window size allows for efficient data transfer and congestion control.
Q92: Which of the following statements is TRUE ?
(a) Virtual functions do not implement polymorphism
(b) Virtual functions do not permit calling of derived class functions using a base class pointer
(c) We can never build an object from a class containing a pure virtual function
(d) Pure virtual functions can never have a body
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is We can never build an object from a class containing a pure virtual function.
- A pure virtual function is a function that is declared in a base class but does not have an implementation in that base class. Instead, it must be implemented in any non-abstract derived class.
- The syntax for a pure virtual function usually looks something like this: virtual void MyPureVirtualFunction() = 0; The "= 0" is what makes the function "pure."
- Abstract classes are classes that have at least one pure virtual function. The purpose of an abstract class is to provide an appropriate base class from which other classes can inherit. Abstract classes cannot be used to instantiate objects and serves only as an interface. Attempting to instantiate an object of an abstract class causes a compilation error.
- Thus, an abstract class is basically a blueprint for other classes. It's not for creating objects directly, but for setting up a common standard for derived classes.
So, "We can never build an object from a class containing a pure virtual function." Because a class with a pure virtual function is an abstract class, and you can't directly instantiate an abstract class. You can only use them as base classes in inheritance structures.
Q93: In a feed forward neural network with the following specifications:
Input layer has 4 neurons, hidden layer has 3 neurons and output layer has 2 neurons using the sigmoid activation function for given input values [0.5, 0.8, 0.2, 0.6] as well as the initial weights for the connections.
W1: [0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.2]
W2: [0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.2] Input layer to hidden layer weights
W3: [0.3, 0.5, 0.7, 0.2]
W4: [0.4, 0.1, 0.3]
W5: [0.5, 0.2, 0.4] Hidden layer to output layer weights
What is the output of the output layer when the given input values are passed through neural network? Round the answer to two decimal places :
(a) [0.62, 0.68]
(b) [0.72, 0.78]
(c) [0.82, 0.88]
(d) [0.92, 0.98]
Ans: A
Sol: The correct answer is [0.62, 0.68]
To compute the output of the neural network, we need to follow these steps:
- Compute the input to the hidden layer by taking the dot product of the input values and the weights (adding a bias term, which is 1, for each neuron in the hidden layer).
- Apply the sigmoid activation function to each element of the hidden layer.
- Compute the input to the output layer by taking the dot product of the hidden layer outputs and the weights (adding a bias term, which is 1, for each neuron in the output layer).
- Apply the sigmoid activation function to each element of the output layer.
Calculations:
1. Compute the input to the hidden layer:
2. W2:
3. W3:
4. W4:
5. W5:
Rounding to two decimal places, the correct output of the output layer is approximately  .
.
Q94: A ______ point of fuzzy set A is a point x ∈ X at which μA(x) = 0.5
(a) Core
(b) Support
(c) Crossover
(d) α - cut
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is Crossover
- In fuzzy set theory, the term "crossover point" is used to refer to a point in the set where the membership function μA(x) equals to 0.5.
- The membership function of a fuzzy set is a generalization of the indicator function in classical sets.
- In a crisp set, the indicator function only gives values 0 (non-membership) or 1 (full membership).
- However, in a fuzzy set, the membership function gives a degree of membership within the interval [0,1] and is allowed to take any value in this range.
- A crossover point in the fuzzy set is essentially the point where degree of membership to the set is exactly 0.5, meaning that it's precisely in the middle ground between being fully in and fully out of the set.
- The concept of the crossover point is part of why fuzzy logic is well-suited to handling uncertainty or ambiguity, since it allows for this sort of partial membership.
Q95: “CREATE TABLE T” in SQL is an example of :
(a) Normalization
(b) DML
(c) DDL
(d) Primary key
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is DDL
DDL (Data Definition Language):
- Data Definition Language includes SQL commands such as CREATE, ALTER, DROP, and TRUNCATE which are used to define or change the structure of the database objects.
- The "CREATE TABLE T" command is indeed a DDL command as it's used to create a new table structure within the database.
Other Related Points
- Normalization: Normalization in databases is a process to minimize redundancy and dependency by organizing fields and table of a database. It typically involves dividing large tables into smaller ones and defining relationships between them to increase the clarity, efficiency, and integrity of the data.
- DML (Data Manipulation Language): Data Manipulation Language commands are used to manage and manipulate data in an existing database structure. Key DML commands include SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE.
- Primary key: A primary key is a column (or set of columns) in a table whose values uniquely identify every row in that table. The primary key plays a critical role in relational databases by providing a way of distinguishing each record in a table from every other record.
Q96: Three address codes can be represented in special structures known as:
(A) Quadruples
(B) Triples
(C) Patterns
(D) Indirect Triples
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) and (B) Only
(b) (A), (B) and (D) Only
(c) (B) and (C) Only
(d) (B), (C) and (D) Only
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (B) and (D) Only
Three-address code (TAC) is an intermediary form of source code that sits between high-level code and assembly/low-level code, often used in a compiler's intermediate representation of the source code. In TAC, all operations take at most two operands, and an assignment is performed as well. Therefore, up to three addresses (or items) are referenced in each line of code: two for the operands and one for the resulting value's assignment.
This code can be represented in special structures, including:
- Triples: In triples, the operation is defined in one row by three fields: op (the operation), arg1 and arg2 (the arguments), and result (the place to store the resulting operation). Each row, or instruction, is implicitly defined by its position in the table. So, if there is an instruction like 'sub a, b', it means 'subtract b from a'.
- Quadruples: The quadruples structure is similar to the triples structure, but it includes an additional field for the result so that each operation does not depend on its physical position in the sequence. This makes it easier to carry out transformations on the code sequence, as this additional field for the result gives more flexibility, particularly in the process of optimization.
- Indirect Triples: Indirect triples use the concept of triples but give the advantage of quadruples. It decouples the usage of an expression from its physical location in the sequence. It consists of a position-independent data structure like quadruples, which can effectively alter the sequence of expressions without modifying the triples.
The option (C) Patterns is not a known structure for representing three address codes. Therefore, the correct answer is (A), (B) and (D), or Option 2.
Q97: Given as 4 GB (= 4.3 × 109 bytes) of virtual space and typical page size of 4 KB and each page table entry is 5 bytes. How many virtual pages would this imply ? What is the size of whole page table ?
(a) 107500 and 20480 bytes
(b) 215000 and 40960 bytes
(c) 10750 and 10240 bytes
(d) None of the above
Ans: D
Sol: The correct answer is None of the above
The number of virtual pages represented by this space can be calculated by dividing total virtual space by the size of an individual page:
4.3 * 109 bytes (total virtual space) / 4 * 103 bytes (size of individual page) = 1.075 * 106 pages
So given that we're dealing with close enough to 1,075,000 pages and each table entry is 5 bytes, the total size of the whole page table would be:
1.075 * 106 entries * 5 bytes/entry = 5.375 * 106 bytes = 5375 KB or around 5.375 MB.
Points Given question was some mistake so UGC dropped the question.
Q98: Hash functions are used to produce the message digests which are then encrypted with a private key to get:
(a) Public key
(b) Digital signature
(c) Cipher text
(d) Data Encryption Standard
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is Digital signature
Digital Signature:
- A digital signature is a cryptographic technique used to ensure the authenticity and integrity of a message or document.
- It involves taking a hash (message digest) of the content and encrypting it with the sender's private key.
- The recipient can use the sender's public key to decrypt the signature and verify that the message hasn't been tampered with and was indeed signed by the sender.
Other Related Points
- Public Key: In public-key cryptography, there are two keys: a public key and a private key. The public key is used for encryption and is shared with others, while the private key is kept secret and used for decryption. Messages encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted by the corresponding private key. However, the process you described doesn't directly involve producing public keys from message digests.
- Cipher Text: Cipher text is the output of the encryption process. When you encrypt a message, it turns into cipher text, which is the unreadable form of the original message. This process typically involves using a symmetric or asymmetric key algorithm to transform the message into a secure, coded format.
- Data Encryption Standard (DES): DES is a symmetric-key algorithm for data encryption. It uses a single key for both encryption and decryption. The process involves multiple rounds of permutation and substitution. While DES is a classic encryption algorithm, it's considered outdated and has been largely replaced by more secure algorithms like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard).
Q99: Which one of the following statements are CORRECT?
(A) Granularity is the size of data item in a database.
(B) Two operations in a schedule are said to be conflict if they belong to same transaction.
(C) Two schedulers are said to be conflict equivalent if the order of any two conflicting operations is the same in both schedules.
(D) Write operations which are performed without performing the write operation are known as Blind Writes.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (A) and (B) Only
(b) (A), (B) and (C) Only
(c) (A), (B) and (D) Only
(d) (B) and (C) Only
Ans: B
Sol: The correct answer is (A), (B) and (C) Only
(A) Granularity is the size of a data item in a database.
- Granularity refers to the level of detail or size of the data that is stored in a database. It can vary from fine granularity (smaller, more detailed data items) to coarse granularity (larger, less detailed data items). The statement is correct.
(B) Two operations in a schedule are said to be conflict if they belong to the same transaction.
- In the context of database transactions, operations are considered conflicting if they involve the same data item and at least one of them is a write operation. The statement is correct.
(C) Two schedulers are said to be conflict equivalent if the order of any two conflicting operations is the same in both schedules.
- Conflict equivalence in schedulers means that if two schedules result in the same final state, they are conflict equivalent if the order of conflicting operations (operations that access the same data item and at least one is a write operation) is the same in both schedules. The statement is correct.
(D) Write operations which are performed without performing the read operation are known as Blind Writes.
- This statement is incorrect. Blind Writes typically refer to write operations performed without checking or reading the existing content. If a write operation is performed without a prior read, it doesn't necessarily make it a Blind Write.
Therefore, the correct statements are (A), (B), and (C).
Q100: Arrange the following phases of a compiler as per their order of execution (start to end)
(A) Target code generation
(B) Syntax Analysis
(C) Code optimization
(D) Semantic Analysis
(E) Lexical Analysis
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (B), (E), (D), (A), (C)
(b) (E), (D), (B), (A), (C)
(c) (E), (B), (D), (C), (A)
(d) (B), (D), (E), (A), (C)
Ans: C
Sol: The correct answer is (E), (B), (D), (C), (A)
Lexical Analysis (E):
- This is the first phase where the source code is analyzed to recognize and tokenize the basic elements, such as keywords, identifiers, literals, and operators.
Syntax Analysis (B):
- In this phase, the compiler checks whether the tokens generated by the lexical analysis form a valid syntactic structure according to the grammar of the programming language. It builds a parse tree or syntax tree to represent the structure.
Semantic Analysis (D):
- This phase ensures that the program makes sense semantically. It checks for things like variable declarations, type compatibility, and other semantic rules. The goal is to ensure that the program has a meaningful interpretation.
Code Optimization (C):
- This phase is not always mandatory, but it involves enhancing the intermediate code to make it more efficient. Various techniques are applied to optimize the code, such as loop unrolling, constant folding, and dead code elimination.
Target Code Generation (A):
- Once the syntax and semantics are verified, the compiler generates an intermediate code or target code. This code is usually in a form that is easier to optimize and convert into machine code.
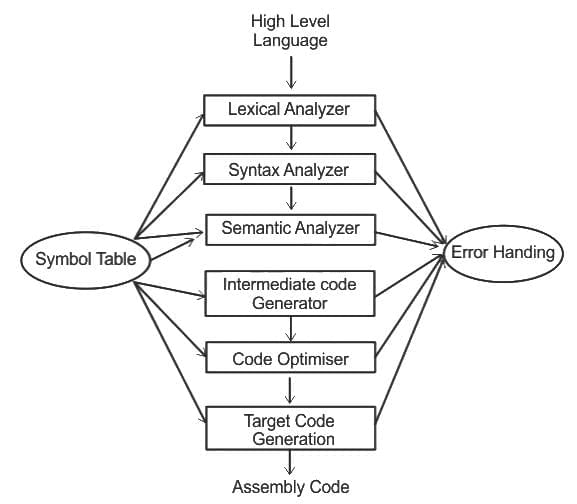
So, the correct order is (E), (B), (D), (C), (A).
FAQs on UGC NET Past Year Question Paper II: Computer Science (7 Dec 2023 Shift I) - UGC NET Past Year Papers
| 1. What is the UGC NET exam and what purpose does it serve? |  |
| 2. What subjects are covered in Paper 2 of the UGC NET exam for Computer Science? |  |
| 3. How is the UGC NET exam structured in terms of marking and duration? |  |
| 4. What are the eligibility criteria for appearing in the UGC NET exam for Computer Science? |  |
| 5. How can candidates prepare effectively for the UGC NET Computer Science exam? |  |