Class 7 Social Science Chapter 4 Question Answers - New Beginnings: Cities and States
Short Answer Questions
Q1: How did the Second Urbanisation differ from the rural life after the Harappan period?
Ans: After the Harappan cities declined, people lived in small villages for about 1000 years. The Second Urbanisation brought the growth of new cities, trade, and political systems in the Ganga plains and beyond.
Q2: What do archaeological excavations tell us about janapadas and mahajanapadas?
Ans: Excavations reveal city layouts, fortifications, coins, and tools that help us understand life in these ancient settlements. These findings match details from ancient texts.
 Ruins of complex at Kaushambhi
Ruins of complex at Kaushambhi
Q3: Why were cities like Rajagriha and Kauśhāmbī fortified?
Ans: These capitals were fortified with moats and narrow gateways to protect against attacks. Fortification showed the need for safety in growing urban centers.
Q4: How did trade routes contribute to the rise of cities during this time?
Ans: Trade routes connected regions, allowing the movement of goods, people, and ideas. This helped cities grow into major centers of commerce and culture.
Q5: Describe the role of the council in early janapadas.
Ans: The sabhā or samiti advised the raja and helped make decisions. In some cases, they even had the power to replace an unfit ruler.
Q6: What were the key duties of a raja in a monarchy?
Ans: A raja collected taxes, built forts, kept an army, and maintained law and order. His position was usually passed down to his son.
Q7: How were ganas or sanghas different from monarchies?
Ans: In ganas or sanghas, decisions were made by discussion or voting, not by one ruler. This was an early form of collective leadership.
Q8: How did iron tools improve farming?
Ans: Iron tools were sharper and stronger than earlier tools, allowing farmers to clear more land. This made large-scale farming easier and more productive.
Q9: How did early coins help in trade?
Ans: Punch-marked coins made of silver helped standardize trade. They made buying and selling easier across different regions.
Q10: How was the varna system organized in Vedic society?
Ans: The varna system divided people into four groups based on their roles: priests, warriors, traders, and workers. These roles were passed down in families.
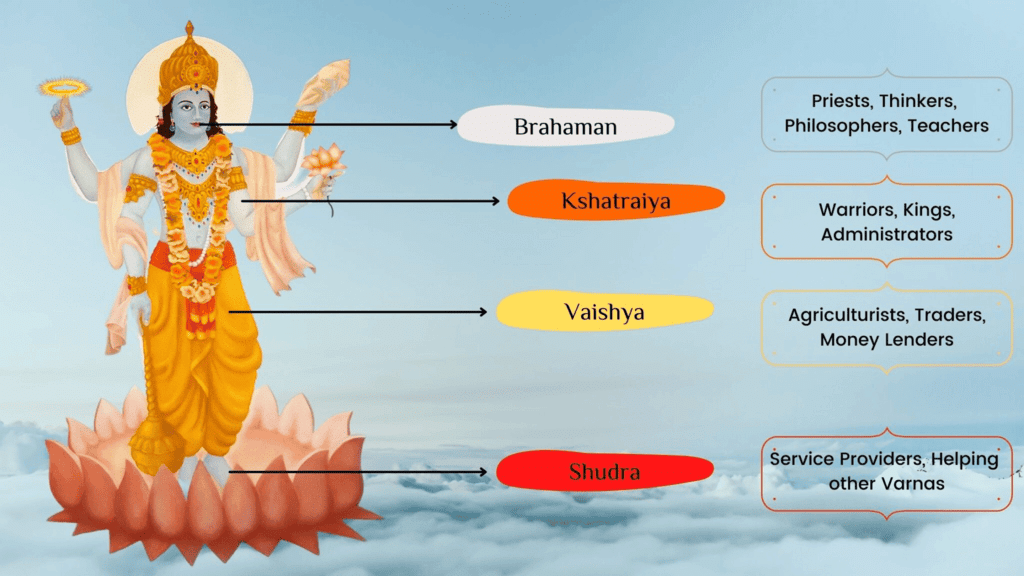 Varna System
Varna System
Q11: What kind of work did people in different jātis do?
Ans: Each jāti had a traditional occupation, such as farming, pottery, or metalwork. These jobs were passed down and shaped their social identity.
Q12: How did southern kingdoms like the Cholas, Cheras, and Pandyas develop?
Ans: These kingdoms grew in south India through trade and agriculture. Ancient Tamil literature records their rulers and rich culture.
Long Answer Questions
Q1: What factors led to the growth of mahajanapadas in the Ganga plains?
Ans:
- The Ganga plains had fertile soil, which supported farming and fed large populations.
- Nearby mountains provided iron ore to make tools and weapons.
- Trade networks developed along rivers and roads, connecting different regions.
- These factors supported stronger economies and armies.
- As a result, many janapadas merged into powerful mahajanapadas.
- The plains became a center of India’s Second Urbanisation.
Q2: How did the gana-sangha system show early democratic traditions in India?
Ans:
- In the gana-sangha system, decisions were made by a council rather than a single ruler.
- Members discussed matters and voted, sometimes even choosing or removing their raja.
- This system encouraged shared leadership and public participation.
- It was used in places like Vajji and Malla.
- These early republics were among the world’s first democratic systems.
- Though not perfect, they showed early democratic values.
Q3: Explain the impact of Buddhism and Jainism during this period.
Ans:
- Buddhist and Jain teachings spread across India through monks, nuns, and pilgrims.
- They taught values like non-violence, truth, and simple living.
- These religions attracted people from different jātis and offered alternatives to the strict varna system.
- They supported education and art, influencing Indian culture deeply.
- Their messages were spread through both oral traditions and written texts.
- This helped unite diverse regions under shared ideas.
 Buddhism and Jainism
Buddhism and Jainism
Q4: What were the cultural contributions of this period in art and learning?
Ans:
- This period saw growth in sculpture, architecture, and painting influenced by religious and social ideas.
- Scholars and teachers spread knowledge through new schools of thought.
- Artistic styles developed in cities, temples, and monasteries.
- This laid the foundation for the great art of later empires.
- Cultural exchange through trade routes enriched these contributions.
- Cities became centers of both learning and creativity.
Q5: Describe the features and significance of punch-marked coins.
Ans:
- Punch-marked coins were India’s first coins, made of silver and stamped with symbols.
- They helped make trade easier and more organized.
- Each mahajanapada issued its own coins, but they were used widely across regions.
- These coins were not only used locally but also traded with other countries.
- Their use shows the rise of market-based economies.
- They marked a shift from barter to monetary systems.
 Punch Marked Coins
Punch Marked Coins
Q6: How did the varna-jāti system evolve, and what were its effects?
Ans:
- The varna-jāti system began as a flexible way to organize work and society.
- Early on, people could change occupations based on need.
- Over time, roles became hereditary and rigid, limiting social mobility.
- This led to inequality and unfair treatment of lower jātis.
- British rule later made the system even more fixed and discriminatory.
- Despite its flaws, the system shaped Indian society for centuries.
Q7: What was the role of trade routes like Uttarapatha and Dakshinapatha in this period?
Ans:
- The Uttarapatha connected northwest India to the Ganga plains and eastern cities.
- The Dakshinapatha linked central India to the south.
- These trade routes helped goods, people, and ideas move across regions.
- They connected inland cities to coastal ports involved in foreign trade.
- As a result, economic and cultural exchange increased across the subcontinent.
- Roads also supported military and religious journeys.
- These routes helped unify India during this time.
Q8: How did cities like Śhiśhupalgarh reflect urban planning and trade in ancient India?
Ans:
- Śhiśhupalgarh in Odisha had a square layout with wide roads and strong fortifications.
- It served as the capital of Kalinga and shows advanced planning for safety and trade.
- Artifacts found here suggest active local and foreign trade.
- The city had public spaces, planned streets, and gateways for movement.
- It reflects how cities became centers of power and culture.
- Urban design supported both economic growth and security.
|
23 videos|274 docs|12 tests
|
















