Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Question Answers - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Q1. How will you find out the direction of the magnetic field produced by current-carrying conductor?
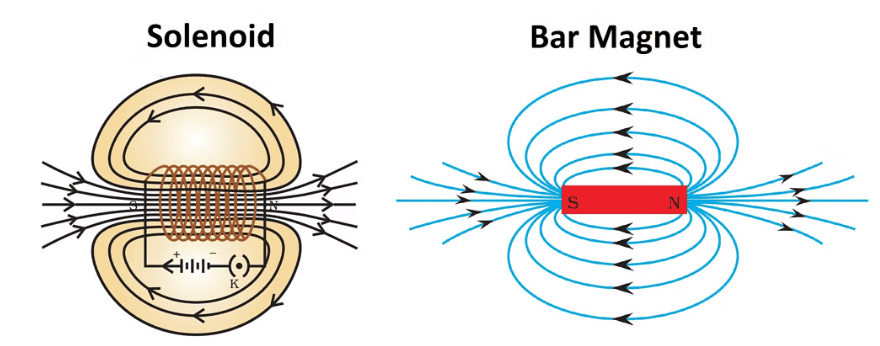
Ans: The direction of the magnetic field created by a straight wire carrying current can be found using the right-hand thumb rule. Here’s how it works:
- Hold the wire with your right hand.
- Point your thumb in the direction of the current.
- Your fingers will curl around the wire, indicating the direction of the magnetic field lines.
- Hold the wire so your thumb points up towards A.
- Your fingers will curl in an anti-clockwise direction.
- This shows that the magnetic field lines also move anti-clockwise around the wire.
Q2. What type of core should be put inside a current-carrying solenoid to make an electromagnet?
Ans: A soft iron core is placed inside a solenoid to create an electromagnet. This arrangement significantly enhances the strength of the magnetic field due to the following reasons:
- The soft iron core becomes magnetised through induction.
- This process increases the overall magnetic field strength produced by the solenoid.
Q3. Explain what is short-circuiting and overloading in an electric supply.
Ans: Short-circuiting: This happens when the insulation on the live and neutral wires is damaged, causing them to touch. The result is a circuit that allows a very large current to flow, which generates significant heat. This excessive heat can create a fire hazard. Overloading: In domestic wiring, the current depends on the power ratings of the appliances in use. If several high-power appliances are switched on at the same time, they draw a large current from the circuit. This situation is known as overloading. The increased current can heat the copper wires to dangerous temperatures, also posing a fire risk.
Q4. Give two reasons why different electrical appliances in a domestic circuit are connected in parallel.
Ans: Two reasons why different electrical appliances in a domestic circuit are connected in parallel:
- If one appliance is switched off or fails, others continue to operate without interruption.
- All appliances receive the same voltage from the main supply, ensuring consistent performance.
Q5. Why is a fuse wire made of a tin-lead alloy and not copper?
Ans: A fuse wire is made of a tin-lead alloy for several reasons:
- Low melting point: This allows the fuse to melt quickly during a fault.
- High melting point of copper: Copper would not melt fast enough in a short circuit.
- Using a tin-lead alloy ensures the fuse operates effectively, protecting the circuit.
Q6. What is a fuse wire? What is the advantage and disadvantage of using a thick fuse wire?
Ans: A fuse is an essential device that protects electrical circuits. It consists of a wire made from a metal, such as tin or a tin alloy, which has a low melting point. When a high current flows through the circuit, the fuse wire heats up and melts due to short-circuiting or overloading. This action breaks the circuit and stops the current, preventing damage to connected appliances.
- Advantage: A thick fuse wire can carry a higher current without melting, offering better protection for circuits with high current demands.
- Disadvantage: It may not melt quickly enough during a fault condition, potentially leading to damage in the circuit or appliances.
Q7. What are magnetic field lines? How is the direction of a magnetic field at a point determined? Mention two important properties of the magnetic field lines.
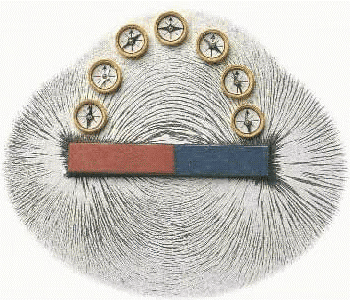
Ans: The space around a magnet where magnetic force acts is called a magnetic field. Magnetic field lines are visual tools that show the direction a north pole would move if placed at any point in the field. To find the direction of the magnetic field at a specific point:
- Imagine a hypothetical north pole at that point.
- Observe the direction in which this north pole would move due to the magnetic field.
- The tangent at any point on a field line indicates the direction a north pole would move if placed there.
- The density of the lines shows the strength of the magnetic field: closer lines mean a stronger field.
Q8. State the rule to determine the direction of a (i) magnetic field produced around a straight conductor-carrying current, (ii) force experienced by a current-carrying straight conductor placed in a magnetic field which is perpendicular to it, and (iii) current induced in a coil due to its rotation in a magnetic field. (iv) Current induced in a circuit by the changing magnetic flux due to the motion of a magnet.
Ans: (i) The direction of the magnetic field around a current-carrying conductor can be determined using Maxwell's right-hand thumb rule:
- Hold the wire in your right hand.
- Point your thumb in the direction of the current.
- Your fingers will curl around the conductor, showing the direction of the magnetic field lines.
- Extend your thumb, forefinger, and middle finger of your left hand at right angles.
- The forefinger points in the direction of the magnetic field.
- The middle finger points in the direction of the current.
- The thumb indicates the direction of the force acting on the conductor.
- Hold your right hand with the thumb, forefinger, and middle finger at right angles.
- The forefinger shows the direction of the changing magnetic field.
- The thumb indicates the motion of the conductor.
- The middle finger gives the direction of the induced current.
Q9. What is the function of an earth wire? Why is it necessary to earth the metallic appliances?
Ans: The earth wire is crucial for safety in electrical devices. It connects the metal body of an appliance to the ground, significantly reducing the risk of electric shocks. Here's how it works:
- In a typical household circuit, there are three wires:
- Live wire
- Neutral wire
- Earth wire
- The earth wire is connected to the device at one end and to the ground at the other.
- This connection is referred to as the device being earthed or grounded.
- Any excess current flows safely to the ground.
- It helps prevent electric shocks to users.
|
80 videos|661 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Question Answers - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
| 1. What are the magnetic effects of electric current? |  |
| 2. How can we demonstrate the magnetic effect of electric current in a simple experiment? |  |
| 3. What is the right-hand rule in the context of magnetic fields? |  |
| 4. What are some applications of the magnetic effects of electric current? |  |
| 5. What is an electromagnet and how does it work? |  |
















