Short Answer Questions: Nature of Matter: Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Ques 1. Suggest separation technique(s) one would need to employ to separate the mixture: Common salt, water and sand
Ans: Sedimentation, decantation, filtration and evaporation
Sedimentation is the process where solid particles settle at the bottom of a liquid. This is followed by decantation, which involves carefully pouring off the liquid, leaving the solid behind. Next, filtration is used to separate solids from liquids using a filter paper. Finally, evaporation removes the liquid, leaving behind any dissolved solids.
- Sedimentation: Particles settle at the bottom.
- Decantation: Pouring off the liquid.
- Filtration: Using filter paper to separate solids.
- Evaporation: Removing liquid to leave solids.
Ques 2. The 'sea-water' can be classified as a homogeneous as well as a heterogeneous mixture. Comment.
Ans: Sea-water can be classified as both a homogeneous and a heterogeneous mixture due to the following reasons:
- It is considered homogeneous because it contains dissolved salts, creating a uniform solution.
- It is also seen as heterogeneous because it includes various insoluble components, such as sand, microbes, and shells.
Ques 3. What would you observe when
(a) an aqueous sugar solution is heated to dryness.
Ans: When an aqueous solution of sugar is heated to dryness:
- The water evaporates, leaving sugar behind in the container.
- If heated further, the sugar may become charred.
(b) a mixture of iron filings and sulphur powder is heated strongly.
Ans: When a mixture of iron filings and sulphur powder is heated strongly, a chemical reaction occurs, resulting in the formation of ferrous sulphide.
Ques 4. Classify the following as physical or chemical properties
(c) Metallic sodium is soft enough to be cut with a knife.
Ans: Metallic sodium is soft enough to be cut with a knife. This characteristic demonstrates the softness of sodium, which is a physical property.
Ques 5. Name the process associated with the following
(e) Settling of sand when a mixture of sand and water is left undisturbed for some time.
Ans: When mixture of sand and water is left undisturbed, the sand settle at the bottom of water, thus this is the process of sedimentation.
Ques 6. An element is sonorous and highly ductile. Under which category would you classify this element? What other characteristics do you expect the element to possess?
Ans: Since the element is sonorous and ductile, it can be classified as a metal. Other expected characteristics of metals include:
- Good conductivity of heat and electricity
- Lustrous appearance
- Malleability (can be shaped into thin sheets)
Ques 7. Fill in the blanks: Ice, water and water vapour look different and display different _________ properties but they are ___________ the same.
Ans: Physical, chemically
Ques 8. Sucrose (sugar) crystals obtained from sugarcane and beetroot are mixed together. Will it be a pure substance or a mixture? Give reasons for the same.
Ans: Pure substance, since it contains a single component, i.e. sucrose.
Ques 9. Non metals are usually poor conductors of heat and electricity. They are non-lustrous, non-sonorous, non-malleable and are coloured.
(a) Name a non-metal which exists as a liquid at room temperature.
Ans: Bromine
(b) Name a non-metal which is required for combustion.
Ans: Oxygen
Ques 10. Classify the substances given in Figure into elements and compounds
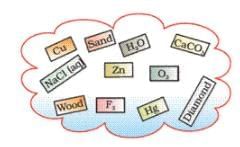
Ans: Elements: Cu, Zn, O2, F2, Hg, Diamond
Compound: CaCO3, NaCl(aq), H2O,
Ques 11. Which of the following are not compounds?
(a) Chlorine gas
(b) Potassium chloride
(c) Iron
(d) Iron sulphide
(e) Aluminium
(f) Iodine
(g) Carbon
(h) Carbon monoxide
(i) Sulphur powder
Ans: Chlorine gas, iron, aluminium, iodine, carbon, and sulphur powder are not compounds.
- Chlorine gas is a diatomic molecule, consisting of two chlorine atoms.
- Iron and aluminium are both elements, not chemically combined with others.
- Iodine is also an elemental substance.
- Carbon can exist as a pure element, such as in graphite or diamond.
- Sulphur powder is a form of elemental sulphur.
|
54 videos|262 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on Short Answer Questions: Nature of Matter: Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What is the difference between an element, a compound, and a mixture? |  |
| 2. Can you provide examples of elements, compounds, and mixtures? |  |
| 3. How can you separate the components of a mixture? |  |
| 4. What are some properties that distinguish compounds from mixtures? |  |
| 5. Why is understanding the nature of matter important in science? |  |
















