Class 8 Science - Question Answers Microorganisms Friend or Foe- 1
Ques 21: Neha went to a party and she ate a variety of foodstuff there, on reaching home she started vomiting and had stomach ache. What do you think why it is so?
Ans: It is because of food poisoning. Food poisoning could be due to the consumption of food spoilt by some microorganisms.
Ques 22: How do we preserve cooked food at home?
Ans: We preserve cooked food at home by using preservatives like salt, sugar and edible oil. Common salt has been used to preserve meat and fish. It is also used to preserve amla, raw mangoes, tamarind, etc. Jams, jellies, and squashes are preserved using sugar. Vegetables, fruits, and pickles are often preserved by oil and vinegar.

Ques 23: Why a mango gets spoilt and rotten after few days but a mango pickle does not spoil for a long period of time?
Ans: A mango spoilt and rotten after a few days, but a mango pickle does not spoil for a long period of time because mango pickles contain salt, which acts as a preservative and prevents the growth of microorganisms in it.
Ques 24: What are preservatives and their importance?
Ans: Preservatives are substances that help prevent the growth of microorganisms in food. They can be natural or synthetic. Here are some key points about preservatives:
- Common Examples: Salt and sugar are natural preservatives used in pickles to inhibit microbial growth.
- Synthetic Preservatives: Sodium benzoate and sodium metabisulphite are widely used in products like jams and squashes.
- Importance: Preservatives are crucial for extending the shelf life of food and preventing spoilage.
Ques 25: Why is milk boiled before storage or consumption?
Ans: Boiling milk is essential for safety and preservation. Here are the key reasons:
- Boiling kills many microorganisms that can cause illness.
- Milk should be heated to about 70°C for 15 to 30 seconds.
- After boiling, the milk is quickly chilled to prevent the growth of any remaining microbes.
- This process helps ensure that the milk remains safe for storage and consumption.
Ques 26. What are viruses? Name some common diseases in humans caused by viruses.
Ans. Viruses are microscopic organisms. They, however, reproduce only inside the cells of the host organism, which may be a bacterium, plant or animal. Some diseases like cold, influenza (flu), polio and chicken pox are caused by viruses.
Ques 27. How do microorganisms survive under adverse conditions?
Ans. Under unfavourable conditions of temperature and water, they generally form a hard and tough covering called a cyst. This protects them. When favourable conditions come, they emerge from their shell, multiply and go through their life cycles.
Ques 28. How do microorganisms act as a cleaning agent of nature?
Ans. Microorganisms play a vital role in cleaning the environment by:
- Breaking down organic waste such as vegetable peels and animal remains into harmless substances.
- Decomposing dead plants and animals, which helps recycle nutrients back into the soil.
- Enhancing soil fertility by fixing nitrogen, which is essential for plant growth.
These processes contribute to a cleaner and healthier ecosystem.
Ques 29. Explain the commercial use of microorganisms.
Ans. Microorganisms are used for large-scale production of alcohol, wine and acetic acid (vinegar). Yeast is used for commercial production of alcohol and wine. For this purpose, yeast is grown on natural sugar present in grains. Yeast converts the sugar into alcohol. This process is called fermentation. Microorganisms are also used to prepare medicines like antibiotics.
Ques 30. Mention some beneficial effects of bacteria.
Ans. Beneficial effects of bacteria:
(i) They help fix nitrogen to increase soil fertility.
(ii) They are used to make vinegar, curd etc.
(iii) They help clean the environment by decomposing organic wastes.
(iv) They are also used to make medicines like antibiotics.
Ques 31. Explain the various types of bacteria.
Ans. The bacteria are classified into three types on the basis of their shape:
(i) Rod shaped (Bacillus): These are long and rod-shaped bacteria like Lactobacillus.
(ii) Round shaped (Coccus): They are round shaped like Streptococcus.
(iii) Spiral: These are comma-shaped bacteria like Triponema.
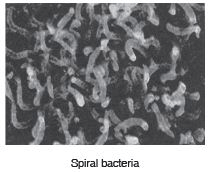
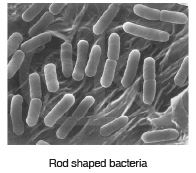
Ques 32. What are antibiotics? Explain with the help of examples.
Ans. The medicines which are used to kill or stop the growth of the disease-causing microorganisms are called antibiotics. The first antibiotic is Penicillin. It was discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1929. These days, a large number of antibiotics are produced by bacteria and fungi. For example: Streptomycin, Tetracycline and Erythromycin.
Ques 33. Explain the discovery of Penicillin.
Ans. In 1929, Alexander Fleming was studying disease-causing bacteria when he discovered something unexpected. He noticed spores of a small green mould on one of his culture plates. This mould prevented the growth of bacteria and even killed many of them. From this observation, the mould, known as penicillin, was developed into a significant antibiotic. This marked a major breakthrough in medicine, leading to the treatment of various bacterial infections.
Ques 34. Explain how a vaccine works.
Ans. A vaccine works by training the immune system to recognise and combat disease-causing microbes. Here’s how it functions:
- When a microbe enters the body, the immune system produces antibodies to fight it.
- The body remembers how to produce these antibodies for future encounters.
- If a vaccine containing dead or weakened microbes is introduced, the body responds by creating the necessary antibodies.
- These antibodies remain in the body, providing long-term protection against the disease.
This process helps prevent various diseases, including cholera, tuberculosis, and polio.
Ques 35. Describe the role of blue-green algae and bacteria in the fertility of soil.
Ans. Some bacteria and blue-green algae are able to fix nitrogen from the atmosphere to enrich the soil with nitrogen and increase its fertility. These microbes are commonly called biological nitrogen fixers. In this way, bacteria and blue-green algae increase the soil fertility.
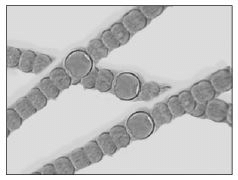

Ques 36. Explain the cleaning action of microorganisms.
Ans. The microorganisms are called the cleaning agents of nature. Collect wastes from plants, vegetables, and fruits in your nearby surroundings. Put them in a pit meant for waste disposal. After some time, it decomposed and was converted to manure by the action of microorganisms. In this way, the waste products are converted into useful manure by the action of microbes. This is the way by which microorganisms act as cleaning agents of nature.
Ques 37. How do microorganisms spoil food?
Ans. Microorganisms grow on the food materials and multiply rapidly. They release toxins in the food and make them unfit to consume. They break down food molecules into amines and change the taste, texture, and appearance of food.
Ques 38. What do you mean by food poisoning?
Ans. Some microorganisms settle on food. They release toxic substances into the foodstuff. This makes the food contaminated and unfit for use. This is called food poisoning. If anyone consumes this food, it can produce fatal results. Serious illness is caused, and the patient gets frequent vomiting and loose motion. This physical condition can even lead to death. So it is very important that we preserve food to prevent it from being spoilt.
Ques 39. What is pasteurisation of milk?
Ans. Pasteurised milk can be consumed without boiling as it is free from harmful microbes. The milk is heated to about 70ºC for 15 to 30 seconds and then suddenly chilled and stored. By doing so, the growth of microbes prevents the milk from growing. This process was discovered by Louis Pasteur, and it is called pasteurisation.
|
90 videos|415 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Science - Question Answers Microorganisms Friend or Foe- 1
| 1. What are microorganisms? |  |
| 2. How are microorganisms helpful to humans? |  |
| 3. Can microorganisms be harmful to humans? |  |
| 4. How can we prevent the spread of harmful microorganisms? |  |
| 5. Are all microorganisms visible to the naked eye? |  |






















