Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Economics for GCSE/IGCSE > Scarcity
Scarcity | Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Finite Resources & Unlimited Wants
- The fundamental economic issue is the scarcity of resources. In economics, these resources are referred to as factors of production.
- Resources are limited compared to the boundless wants and needs of individuals. Essential needs such as shelter, food, and clothing fall under needs, while non-essential desires like improved housing or luxury items like yachts are categorized as wants.
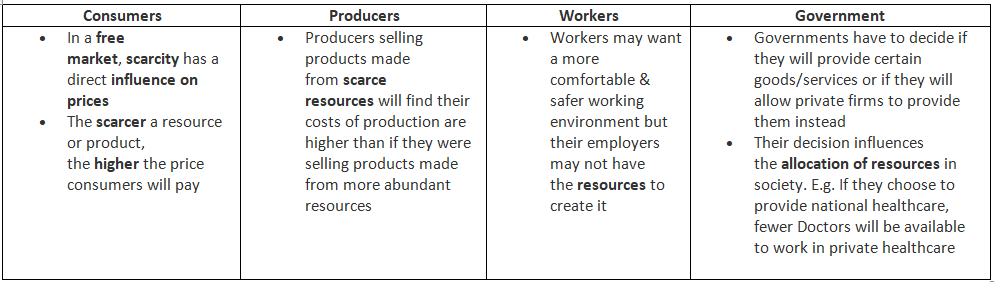
- Given this scarcity, choices must be made by producers, consumers, workers, and governments regarding the most efficient allocation of these resources.
- Economics examines scarcity and its effects on resource distribution within society.
All Stakeholders in an Economy Face The Basic Economic Problem
Economic & Free Goods
Economic Goods
- Economic goods are valuable because they are scarce relative to demand.
- Producers seek to supply economic goods to earn profits.
- Any item that carries a price tag is classified as an economic good.
Free Goods
- Free goods are characterized by their abundance in the supply chain.
- Due to their abundance, selling free goods does not result in profits.
- For example, drinking water historically was a free good, but with population growth and pollution, it has transitioned into an economic good.
Question for ScarcityTry yourself: What are economic goods?View Solution
The document Scarcity | Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Economics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
71 videos|104 docs|48 tests
|
FAQs on Scarcity - Economics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is the concept of finite resources and unlimited wants in economics? |  |
Ans. Finite resources refer to the limited availability of natural and human resources that are used to produce goods and services, while unlimited wants refer to the never-ending desire of individuals for goods and services that exceed the available resources.
| 2. How does scarcity play a role in the concept of finite resources and unlimited wants? |  |
Ans. Scarcity is the fundamental economic problem that arises due to limited resources and unlimited wants. It forces individuals, businesses, and governments to make choices on how to allocate scarce resources efficiently to satisfy unlimited wants.
| 3. What are economic goods and free goods in relation to finite resources and unlimited wants? |  |
Ans. Economic goods are goods and services that are scarce and have a cost associated with them, requiring individuals to make trade-offs in their consumption. Free goods, on the other hand, are abundant and do not have a cost attached to them.
| 4. How do finite resources and unlimited wants impact the pricing of goods and services in the market? |  |
Ans. The imbalance between finite resources and unlimited wants leads to competition for scarce resources, which influences the pricing of goods and services in the market. Higher demand for limited resources can drive up prices, while abundant resources may lead to lower prices.
| 5. How can individuals and businesses effectively manage finite resources and unlimited wants to achieve economic sustainability? |  |
Ans. Individuals and businesses can practice sustainable consumption and production methods, prioritize needs over wants, and make informed choices to optimize resource allocation and minimize wastage in order to achieve economic sustainability in the long run.
Related Searches




















