Passive Voice | Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension (VARC) - CAT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Structure of Active and Passive Voice |

|
| Important Rules for Active and Passive Voice |

|
| Rules for Converting Active to Passive Voice |

|
Introduction
Voice in grammar refers to how the action of a verb is expressed in a sentence, indicating whether the subject is performing the action (active voice) or receiving it (passive voice).

For instance,
In the active voice sentence, "He loves me,"
- "he" is the subject,
- "loves" is the verb, and
- "me" is the object.
In its passive counterpart, "I am loved by him."
- The subject is "I,"
- The verb is "am loved," and
- The object is "him."
The transformation from active to passive voice involves changing the verb form, with the addition of auxiliary verbs like "be," "do," or "have" to convey tense or mood. Despite differences in structure, the meaning of the sentence remains unchanged. Essentially, active sentences focus on the one acting, while passive sentences highlight the recipient of the action.
The change in voice does not alter the core meaning of the sentence
Structure of Active and Passive Voice
Active voice describes a sentence where the subject is the doer of an action. Its structure is as follows-
Subject + Verb + Object
Passive voice expresses action that is carried out on the subject of the sentence. Its structure is-
Object + Verb + Subject
Important Rules for Active and Passive Voice
- In passive voice sentences, the subject of the active voice (e.g., "they") becomes the object.
- Passive voice typically employs the third form of the verb, also known as the past participle (e.g., eat, ate, eaten).
- The auxiliary verb "be" (am, is, are, was, were) is added before the past participle based on the verb's tense.
- Generally, the preposition "by" is used before the object in passive voice sentences.
- In cases where the intended meaning is clear, the subject in passive voice sentences can sometimes be omitted.
- The decision to omit the subject depends on judgment and context.
Active and Passive Voice Rules Chart
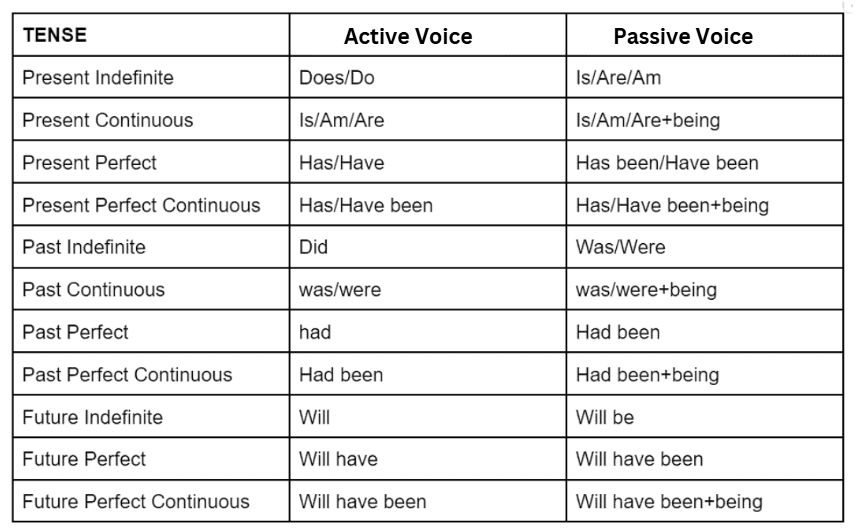
Rules for Converting Active to Passive Voice
- The object of the active verb becomes the subject of the passive voice.
- The active sentence’s subject becomes the object of the passive sentence (or is dropped). The finite form of the verb is changed to past participle or V3 form.
- The preposition “by” is used before the passive object.
Active and Passive Voice Rules For All Tenses
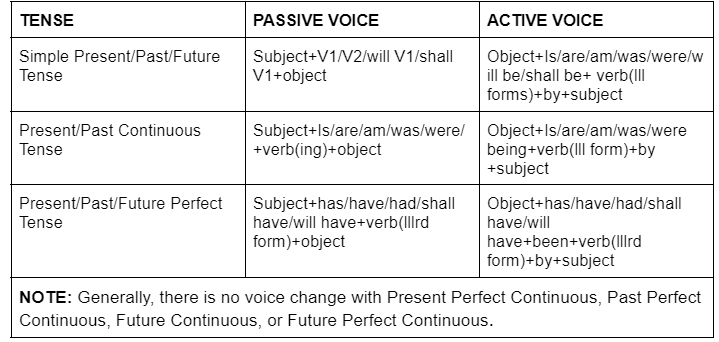
Active and Passive Voice Rules in Imperative Sentences
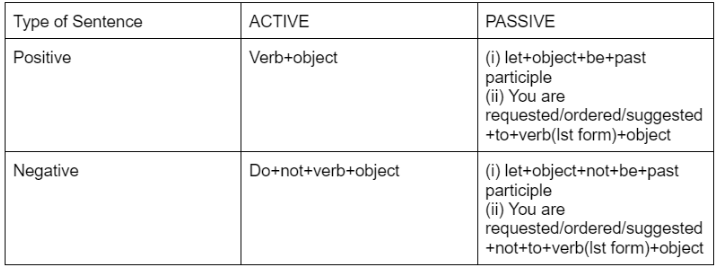
Active and Passive Voice Rules for “To Be” Sentences

Active and Passive Voice Rules for Modal Verbs
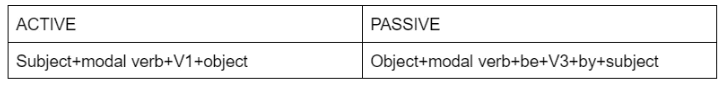
Active and Passive Rules for Di-Transitive Verbs
Some verbs take two objects, for example:
Active: Samdish gave the beggar an old t-shirt.
Passive: (i) An old t-shirt was given to the beggar by Samdish.
(ii) The beggar was given an old t-shirt by Samdish.
Active and Passive Rules for Sentences with the Intransitive Verb
Such sentences are known as Mid-voice or Quasi-Passive voice. They seem to be in active voice, but their meaning is in the passive voice, and they have intransitive verbs, like without a direct object.
Active: Honey tastes sweet.
Passive: Honey is sweet when it is tasted.
|
163 videos|581 docs|126 tests
|
FAQs on Passive Voice - Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension (VARC) - CAT
| 1. What is the passive voice in English grammar? |  |
| 2. How do I form a passive voice sentence? |  |
| 3. When should I use passive voice instead of active voice? |  |
| 4. Can all sentences be converted to passive voice? |  |
| 5. What are some common mistakes to avoid when using passive voice? |  |
















