Oxidation & Reduction | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Introduction
Oxidation occurs in a chemical reaction when there is a loss of electrons and a gain of Oxygen. On the other hand, reduction happens in a reaction when there is a gain of electrons and a loss of Oxygen. In simple words, Oxidation is the addition of Oxygen, whereas reduction is the loss of Oxygen in a reaction.
Oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously in a chemical reaction. One element loses the electron while the other gains it. Such reactions are called oxidation-reduction reactions or Redox reactions.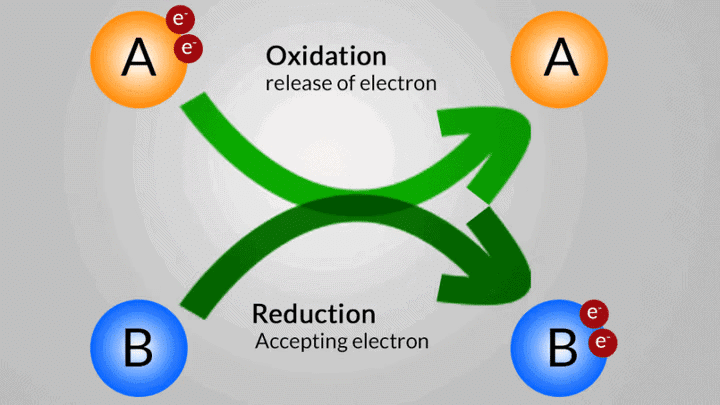
Oxidation
Oxidation can be defined as a loss of electrons or hydrogen and gain of Oxygen. Oxidation reaction happens when an atom or compound loses one or more than one electron.
Some elements like sodium, magnesium and iron lose electrons more quickly than others. They are called easily oxidised compounds.
In the case of oxidation following happens:
- Addition of Oxygen or electronegative element
- Loss of hydrogen or electropositive element
- Increase in positive charge
- Decrease in negative charge
Examples of oxidation reactions
2 MgO + O2 → 2 MgO (addition of oxygen)
H2S + Cl2 → HCl + S (removal of hydrogen)
Reduction
If a substance loses oxygen during a reaction, it is said to be reduced. Reduction reactions happen when a compound gains one or more electrons or loses oxygen..
In the reduction reaction following happens:
- Addition of hydrogen
- Loss of Oxygen
Examples of the reduction reaction
NH3 + HCl → NH4Cl (addition of hydrogen)
2 KClO3 → 2 KCl + 3 Cl2 (removal of oxygen)
Oxidation and Reduction in terms of Oxygen transfer
- In early chemistry, oxidation and reduction were terms associated with oxygen.
- Oxidation meant gaining oxygen and Reduction meant losing oxygen.
- The term ‘reduction’ comes from Latin and means ‘-to lead back’.
- Therefore, anything that leads back to the free metal state is referred to as a reduction reaction.
Magnesium undergoes both oxidation and reduction in reactions with different reactants.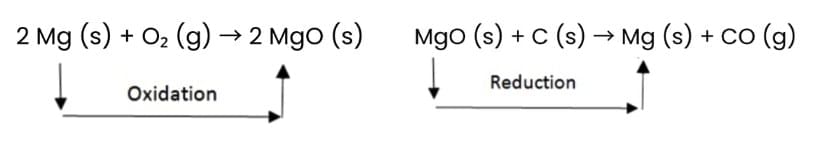
Understanding Redox Reaction
Oxidation and reduction reactions most of the time co-exists in a reaction. Together it is called oxidation-reduction reaction or Redox reaction.
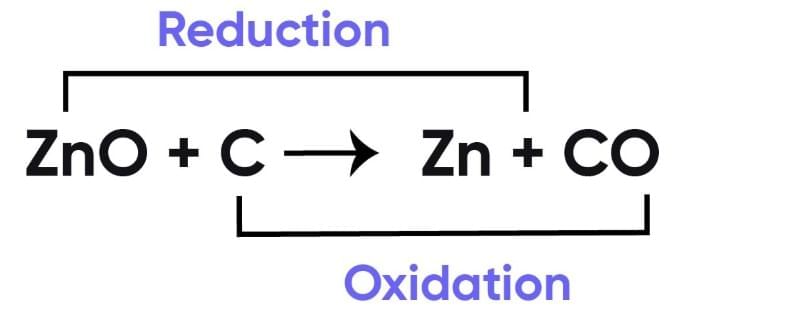
What are Reducing and Oxidizing Agents?
Oxidising agent
- Substance which gets reduced is called Oxidizing Agent.
- In other words, a substance that oxidizes another substance is called an Oxidizing agent.
- An oxidising agent is also known as an oxidant.
Reducing agent
- Substance which gets oxidised is called Reducing Agent.
- In other words, a substance that reduces another substance is called a Reducing agent.
- It is also referred to as a reductant.
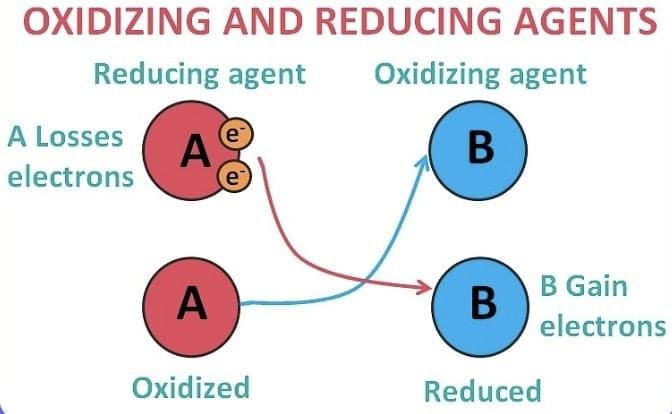
Understanding Redox reaction with an example
Rusting is a classic example of a redox reaction. Oxygen steals electrons from iron when it rusts. While Oxygen is reduced, iron is oxidised. The result is iron oxide, also known as rust. The unoxidised or pure form of iron is distinct from the oxidised form found in rust.
In a simple redox process, the following equation illustrates an evident example of oxygen transfer:
CuO + Mg → Cu + MgO
Ionic compounds include copper(II) oxide and magnesium oxide. If you write the above as an ionic equation, you’ll notice that the oxide ions are spectator ions.
Magnesium decreases the copper(II) ion in the preceding reaction by transferring electrons and neutralising its charge. As a result, magnesium acts as a reducing agent. Another way to phrase it is that the copper(II) ion removes electrons from the magnesium ion, resulting in the formation of a magnesium ion. The copper(II) ion functions as an oxidizer.
Common Redox Reactions
The three common redox reactions are discussed below:
1. Combustion reaction – It is a type of redox reaction which occurs between molecular oxygen and compound to form oxygen-containing products.
2C8H18+25O2 → 16CO2(g)+18H2O
2. Disproportionation reaction – It is a type of redox reaction where a single reactant is reduced and oxidized. It is also known as an auto-oxidation reaction.
3ClO−(aq) → ClO3−(aq)+2Cl−(aq)
3. Single replacement reaction – It is a type of redox reaction that involves two elements switching places within a compound. It is also known as a single displacement reaction.
Zn(s)+2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq)+H2(g)
How to Balance Redox Reaction?
- Assign the elements with oxidation numbers.
- Write half-reactions for reduction and oxidation.
- Multiplication of half-reaction number to equalize.
- A chemical reaction in which one of the reactants is decreased and the other is oxidized is a reduction / oxidation (redox) reaction.
- Reduction and oxidation apply to the transition between elements or compounds of electrons which is characterized by the state of oxidation.
- As their amount of oxidation increases, an atom is oxidized and reduced when the amount of oxidations reduces. The essential functions of life, such as photosynthesis and breathing, include redox reactions.
- There are a few more steps involved in balancing a redox reaction than balancing a normal chemical equation. The most critical step is to determine if there is still a redox reaction.
Redox Reaction and Oxidation Number
In the oxidation process, there is an increase in the oxidation number. While in reduction, there is a decrease in the oxidation number.
- An increase in oxidation number means loss of electrons
- Decrease in oxidation number means a gain of electrons
Consider the reaction that follows.
CO2(g) + H2(g) = CO(g) + H2O(g)
In this reaction, the total number of electrons in each atom’s valence shell remains constant.
The oxidation status of these atoms changes during this process. Carbon’s oxidation state grows from +2 to +4, while hydrogen’s oxidation state declines from +1 to 0.
Therefore when an atom’s oxidation number increases, it is oxidised. When an atom’s oxidation number decreases, it is reduced.
Conclusion
Oxidation and reduction reaction when taken place simultaneously , is also known as Redox reaction. It can be confusing how Oxidation and reduction takes place and who loses or gains electrons. Our comprehensive guide will help you clear the concept of oxidation and reduction.
|
80 videos|653 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Oxidation & Reduction - Science Class 10
| 1. What is the difference between oxidation and reduction? |  |
| 2. How can oxidation and reduction be understood in terms of electron transfer? |  |
| 3. What is an oxidizing agent and how does it work? |  |
| 4. How do you balance a redox reaction? |  |
| 5. Can you provide a simple example of a redox reaction? |  |






















