Origin of Life | Biology Class 12 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Understanding Evolution and the History of Life |

|
| Origin of Life |

|
| Theories on the Origin of Life |

|
| Evolution of Life Forms: A New Perspective |

|
Understanding Evolution and the History of Life
Evolutionary Biology examines how life on Earth has changed over vast periods. To understand this, we must first grasp what evolution truly means. Evolution refers to the changes that occur in plants and animals over millions of years. Before exploring this in detail, it is important to consider the big picture: the evolution of Earth, the stars, and even the universe.
The Beginning of Life
We will explore the story of how life began and developed on our planet, set against the Earth's evolution and the unfolding of the universe. This story involves enormous time spans and complex processes, forming the foundation for understanding the vast diversity of life observed today.
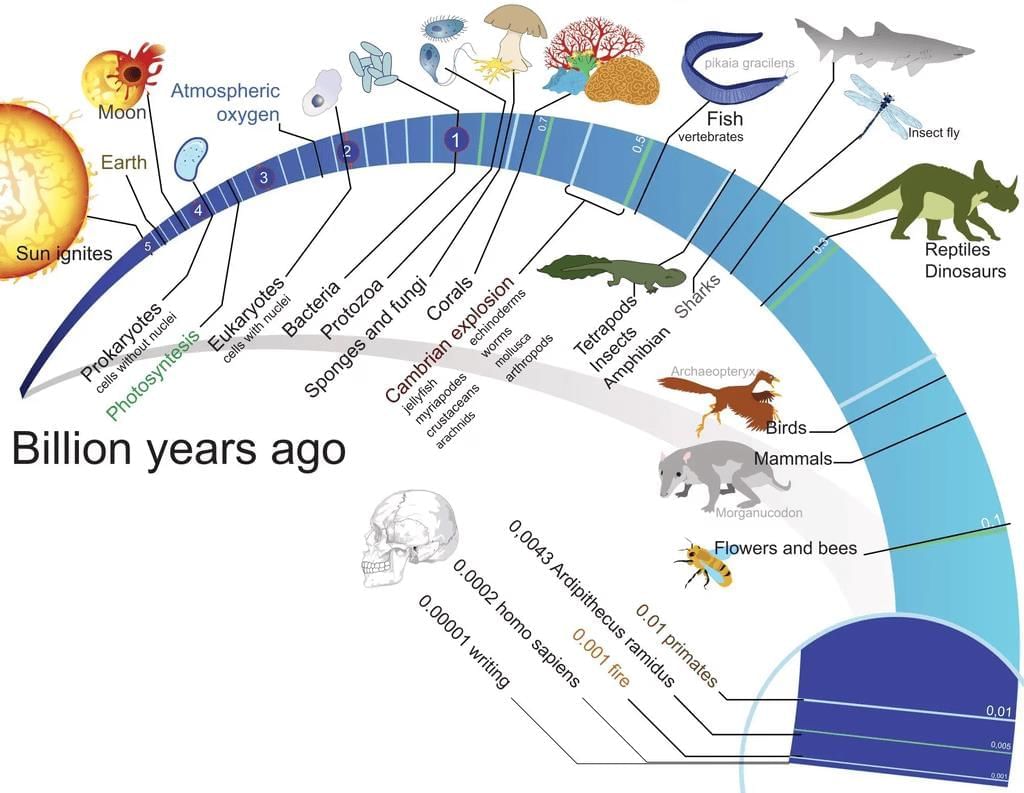
Origin of Life
Life on Earth and the Universe
- When we observe stars in the night sky, we are essentially looking back in time. Because stars are extremely distant, their light takes millions of years to reach us. Thus, the starlight we see began its journey millions of years ago from trillions of kilometres away. In contrast, objects around us are seen in real time. Hence, observing stars is akin to peering into the past.
- The origin of life is considered a special and unique event in the universe’s history. The universe is immense and about 13.8 billion years old, consisting of vast clusters of galaxies, with each galaxy containing stars, gas, and dust. Earth represents only a tiny speck within this enormous cosmos.
The Big Bang theory explains the universe's beginning as a massive explosion. Following this event, the universe expanded and cooled, initially forming only hydrogen and helium. These gases later condensed under gravity to form galaxies, including the Milky Way, which contains our solar system.
- Formation of Earth: Earth formed about 4.5 billion years ago within the Milky Way galaxy. Initially, Earth lacked an atmosphere. As it cooled, gases such as water vapour, methane, carbon dioxide, and ammonia were released from its molten interior, enveloping the surface.
- Role of UV Rays: Ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun were vital in breaking down water vapour into hydrogen and oxygen. The lighter hydrogen escaped into space, while oxygen combined with ammonia and methane to produce water, carbon dioxide, and other gases. This process also contributed to the formation of the ozone layer.
- Formation of Oceans: Continued cooling caused water vapour to condense and precipitate as rain, filling surface depressions and forming the oceans. Life is believed to have emerged approximately four billion years ago, about 500 million years after Earth’s formation.
Theories on the Origin of Life
1. Life from Outer Space (Panspermia Theory)
- Suggests that life may have come to Earth from outer space.
- Ancient Greek philosophers believed tiny life units called spores travelled between planets.
- These spores might have landed on Earth, giving rise to life.
- The theory remains of interest to some modern astronomers.
2. Spontaneous Generation Theory
- Earlier belief that life could arise on its own from decaying matter like mud or straw.
- Disproved by Louis Pasteur through controlled experiments.
- Pasteur showed that sterilised (boiled) solutions remained lifeless unless exposed to air.
- Concluded that life comes only from pre-existing life.
3. Chemical Evolution Theory (Oparin–Haldane Hypothesis)
- Proposed by A. I. Oparin (Russia) and J. B. S. Haldane (England).
- Suggested that the first life originated from non-living organic molecules.
- Early Earth had a reducing atmosphere (no oxygen, rich in methane and ammonia).
- Conditions such as high temperature and volcanic activity favoured formation of complex molecules like RNA and proteins.
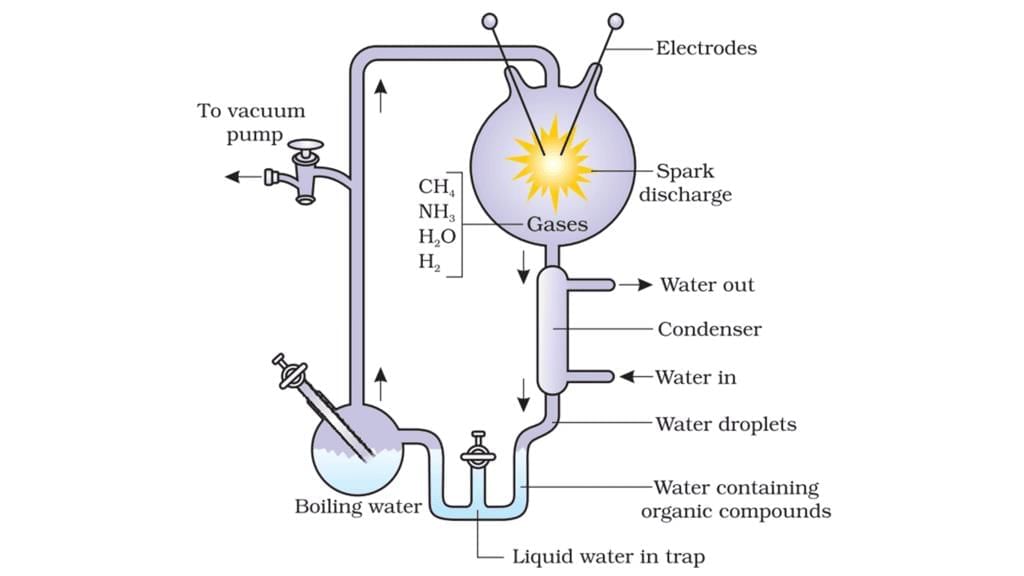
4. Miller’s Experiment (1953)
- Conducted by Stanley L. Miller to test Oparin–Haldane’s idea.
- Simulated early Earth’s atmosphere with gases: methane, hydrogen, ammonia, and water vapour.
- Passed electric sparks (lightning simulation) at about 800°C.
- Produced amino acids, the building blocks of proteins.
- Later experiments formed sugars, nitrogen bases, pigments, and fats.
- Similar organic compounds have been found in meteorites, supporting chemical evolution.
- However, the exact process by which the first self-replicating life form appeared is still unknown.
5. Early Life Forms:
- The earliest non-cellular life forms appeared about 3 billion years ago.
- These were likely large molecules such as RNA, proteins, or polysaccharides.
- These molecules had the ability to replicate themselves.
- The first true cellular organisms emerged around 2 billion years ago.
- These earliest cellular life forms were unicellular (single-celled).
- All early life existed in aquatic environments (water-based).
- The most accepted view is that life gradually arose through evolutionary processes from non-living molecules.
- However, the exact process by which these primitive cells evolved into the vast diversity of life seen today remains uncertain and under research.
Evolution of Life Forms: A New Perspective
Theory of Special Creation
- The traditional religious view held that all living organisms were created exactly as they exist today, without any change over time.
- This theory also posited that Earth is only about 4,000 years old.
Charles Darwin's Observations
- During his voyage on the H.M.S. Beagle, Darwin observed that living organisms share similarities with both each other and extinct ancient species.
- He noted that many life forms had become extinct, while new species had appeared, indicating a gradual process of biological change—evolution.

Natural Selection
- Darwin proposed that individuals within a population show variations in traits. Those with characteristics better suited to their environment—such as climate, food availability, and physical conditions—are more likely to survive and reproduce.
- This process, called natural selection, results in the fittest individuals producing more offspring, passing on their advantageous traits to future generations.
Alfred Wallace's Contribution
- Around the same time as Darwin, Alfred Wallace, a naturalist in the Malay Archipelago, reached similar conclusions about evolution and natural selection.
Common Ancestors and Geological History
- Over time, new species have appeared, but all living organisms share common ancestors from different geological periods.
- Earth’s geological history spans billions of years, closely aligning with biological evolution, which supports the view that Earth is much older than the few thousand years proposed by earlier beliefs.
|
59 videos|290 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on Origin of Life - Biology Class 12 - NEET
| 1. What is the Panspermia hypothesis regarding the origin of life? |  |
| 2. How do scientists study the origins of life on Earth? |  |
| 3. What evidence supports the idea that life could exist elsewhere in the universe? |  |
| 4. What role did RNA play in the early evolution of life? |  |
| 5. How does evolution explain the diversity of life on Earth? |  |





















