Wren and Martin Summary: Nouns | Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension (VARC) - CAT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is a Noun? |

|
| Types of Nouns |

|
| Gender in Nouns |

|
| Number in Nouns |

|
| Cases in Nouns |

|
| Rules of Nouns |

|
| Conclusion |

|
What is a Noun?
A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea. It is one of the most important parts of speech, as it helps identify and describe the world around us.
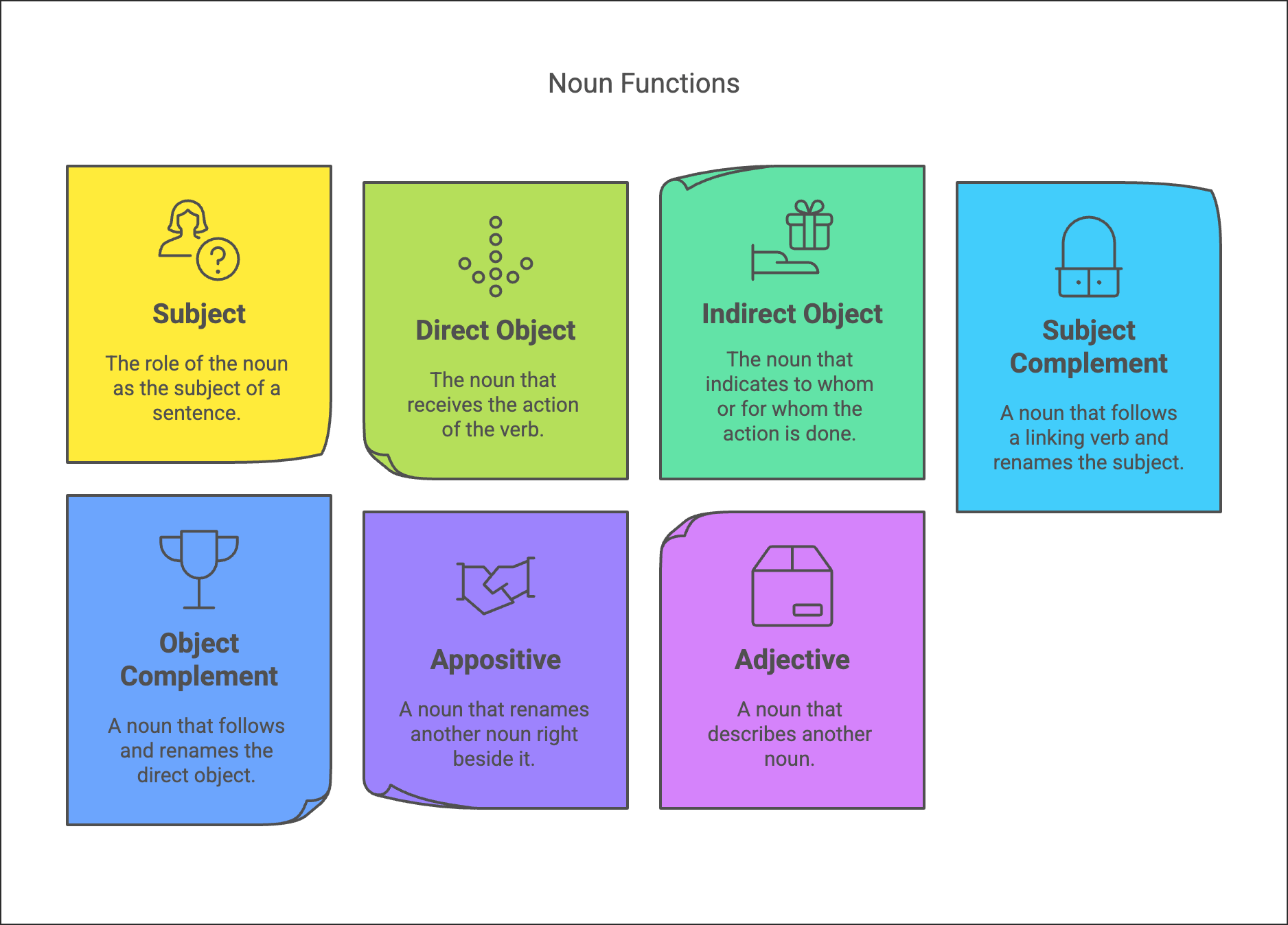
In a sentence, nouns can serve various roles, including:
- Subject: The noun performing the action (e.g., "The dog barks.").
- Direct Object: The noun receiving the action directly (e.g., "She bought a book.").
- Indirect Object: The noun receiving the action indirectly (e.g., "He gave Lisa a gift.").
- Subject Complement: The noun that renames or describes the subject (e.g., "She is a teacher.").
- Object Complement: The noun that renames or describes the object (e.g., "They named the baby Emma.").
- Appositive: The noun that adds information about another noun (e.g., "My friend, Alex, is visiting.").
- Adjective (Noun as Modifier): The noun used to modify another noun (e.g., "History book," "gold ring").
Nouns form the foundation of language, making them essential for communication and sentence structure.
Examples of Nouns
- Name of a Person: Zuker, Max, Xavier, Joseph, etc
- Name of an Animal: Kangaroo, Dolphin, Jackal, etc.
- Name of a Place: Boston, Australia, India, etc.
- Name of a Thing: Table, Computer, Chair, etc.
- Name of an Idea: Happiness, Superstitions, Excitement, etc.
Types of Nouns
- Proper Nouns: These name specific, unique people, places, or things, like "Asoka," "Sita," "Kolkata," or "India." They always start with a capital letter to show they’re special. For example, "India" is a proper noun because it’s one specific country, not just any country.
- Common Nouns: These are general names for a group of similar things, like "king," "girl," "city," or "country." They don’t get capital letters unless they start a sentence. For example, "girl" could mean any girl, not one specific person.
Special Notes:
Sometimes proper nouns can act like common nouns. In "Kalidas is the Shakespeare of India," "Shakespeare" isn’t just a person’s name—it’s used to mean "a great dramatist." This shows how proper nouns can take on a general meaning.
Common Nouns have two special types:
- Collective Nouns: These name a group of people or things treated as one unit. Examples are "crowd" (lots of people together), "team" (players working as one), or "fleet" (a group of ships). For instance, "a herd of cows" means all the cows as a single group.
- Abstract Nouns: These name things we can’t see, hear, or touch—like qualities ("kindness," "courage"), actions ("running," "laughter"), or states ("peace," "childhood"). For example, "happiness" is abstract because it’s a feeling, not a physical object.
Countable and Uncountable Nouns
- Countable Nouns: These name things we can count one by one, like "book," "apple," or "dog." You can say "two books" or "an apple" because they’re separate items. They also have plural forms, like "books" or "dogs."
- Uncountable Nouns: These name things we can’t count individually, like "milk," "sand," or "happiness." You can’t say "two milks" or "a sand"—they’re seen as one big mass or idea with no clear boundaries. They don’t have plural forms.
Countable nouns are like individual pieces you can number, while uncountable nouns are like stuff that doesn’t split into separate parts easily. For example, "chairs" (countable) vs. "furniture" (uncountable)—you can count chairs, but not furniture as a whole.
Gender in Nouns
Nouns can show gender based on what they name:
- Masculine Gender: Names males, like "man," "bull," or "king." These are for male people or animals.
- Feminine Gender: Names females, like "woman," "cow," or "queen." These are for female people or animals.
- Common Gender: Can be male or female, like "teacher," "child," or "cat." You don’t know the gender until more info is given.
- Neuter Gender: Names things with no gender, like "chair," "river," or "book." These are lifeless objects.
Extra Points:
- In English, gender matches the real-life sex of the person or animal—not like in some languages where words have gender for no clear reason (e.g., in Spanish, "mesa" (table) is feminine). English keeps it simple and logical.
- We can also use personification, which is when we give human traits to non-human things, like saying "The sun smiles" (masculine) or "The moon is beautiful" (feminine). This is mostly in stories or poems for effect.
How to Make Feminine Nouns:
- Use a totally different word: "brother" becomes "sister."
- Add a suffix like "-ess": "prince" becomes "princess."
- Change a word around it: "landlord" becomes "landlady."
Number in Nouns
Nouns can be singular (just one) or plural (more than one). Here’s how we change them:
How to Form Plurals:
- Add "-s" to most nouns: "cat" becomes "cats."
- Add "-es" if the noun ends in "-s," "-sh," "-ch," "-x," or "-o": "bus" becomes "buses," "potato" becomes "potatoes."
- If it ends in "-y" after a consonant, change "-y" to "-i" and add "-es": "city" becomes "cities" (but "day" becomes "days" because "y" follows a vowel).
- Some nouns are irregular and change completely: "man" becomes "men," "child" becomes "children."
- A few add "-en": "ox" becomes "oxen."
- Some don’t change at all: "sheep" stays "sheep," whether one or many.
Special Cases:
- Some nouns are always plural: "scissors" or "pants"—you can’t say "one scissor."
- Some look plural but act singular: "news" (e.g., "The news is bad") or "physics."
- Collective nouns like "cattle" or "people" are singular in form but often mean many: "The cattle are grazing."
- In compound nouns (two words together), make the main word plural: "brothers-in-law," not "brother-in-laws."
- Words from other languages might keep their own rules: "datum" (Latin) becomes "data," "cactus" becomes "cacti."
- A few nouns have two plurals with different meanings: "brothers" (family) vs. "brethren" (group members).
English has lots of plural rules because it mixes words from many languages. Most are simple, but irregular ones (like "mice" from "mouse") don’t follow patterns—you have to learn them.
Cases in Nouns
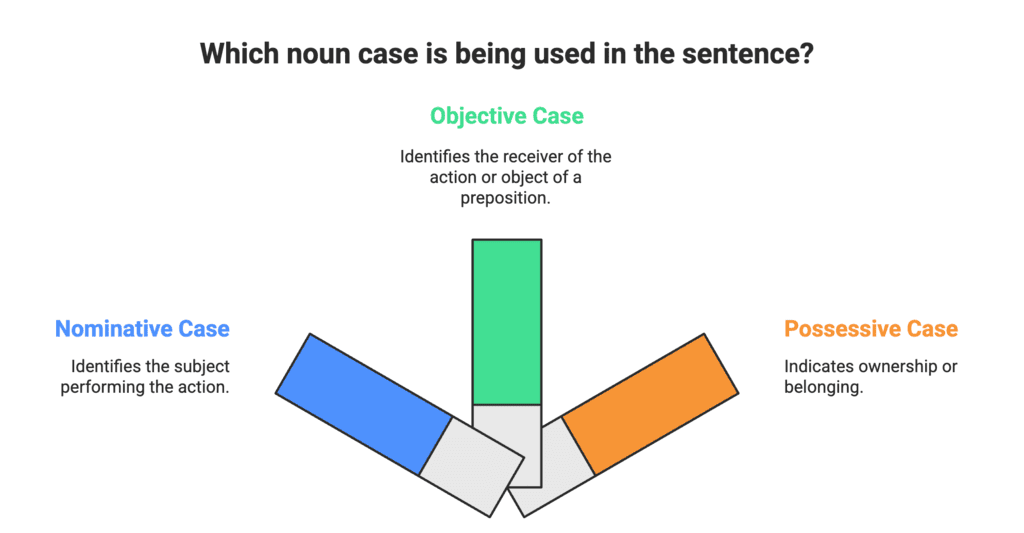
Cases tell us what a noun is doing—acting, receiving, or owning. Nouns change "case" depending on their job in a sentence:
- Nominative Case (Subjective Case): The doer of the action, like "Ravi" in "Ravi kicked the ball." Ask "Who kicked?"—it’s Ravi, so he’s nominative.
- Objective Case (Accusative Case): The receiver of the action, like "ball" in "Ravi kicked the ball," or after prepositions, like "table" in "on the table." Ask "Kicked what?"—it’s the ball.
- Possessive Case (Genitive Case): Shows who owns something, like "Ravi’s" in "Ravi’s ball." Ask "Whose ball?"—it’s Ravi’s.
Forming the Possessive Case:
- Add "'s" to singular nouns: "dog’s bone" (one dog).
- Add just "’" to plurals ending in "-s": "dogs’ bones" (many dogs).
- Add "'s" to plurals not ending in "-s": "children’s toys."
Uses of the Possessive Case:
- Mostly for people or animals: "the cat’s tail."
- Sometimes for time or space: "a week’s vacation," "a mile’s distance."
- Also in personification: "the storm’s fury."
Nouns in Apposition:
- When one noun explains another, like "Sita, my sister," both are in the same case. Here, "Sita" and "my sister" are nominative because they’re the subject.
Rules of Nouns
Let us look at some of the most important rules of ‘Nouns’. These rules will allow you to use nouns with confidence and accuracy. Usually, in any exam related to grammar, questions revolve around only these rules.Rule 1: Singular Nouns Used as Plural
Some nouns are singular in meaning but are used as plural and take plural verbs.
Examples:
The cattle are grazing in the field.
People are indifferent to strangers in big cities.
Rule 2: Always Plural Nouns
Some nouns are always used in the plural form and take plural verbs.
Examples:
I cannot find my trousers; where are they?
She ordered a pair of spectacles; they are classy.
Rule 3: Always Singular Nouns
Some nouns always take singular verbs.
Examples:
Mathematics is my favourite subject.
The news of his success is true.
Rule 4: Numerals with Nouns
When a specific numeral precedes nouns indicating measure, number, money, length, or weight, the nouns that follow remain in their singular form.
For instance:
She bought two dozen eggs. (Not "dozens")
Rule 5: Collective Nouns in Singular & Plural Forms
Collective nouns can be used in both singular and plural forms, depending on the context.
- For example, "the government" refers to a singular collective body, while "the jury" can be seen as a singular group with potentially differing opinions.
- "The government is a key institution." Here, "government" is used as a singular collective noun.
- "The jury was split in its views." In this case, "jury" is also used as a singular collective noun, despite the individual members having different opinions.
Rule 6: Nouns with Different Singular and Plural Meanings
Some nouns have different meanings in singular and plural forms.
Examples:
Good means virtue, while goods mean property.
Iron is a metal, while irons refer to chains.
Rule 7: Material Nouns Do Not Take Articles
Material nouns generally do not take 'a' or 'an'.
Incorrect: My mother likes a gold and not a silver.
Correct: My mother likes gold and not silver.
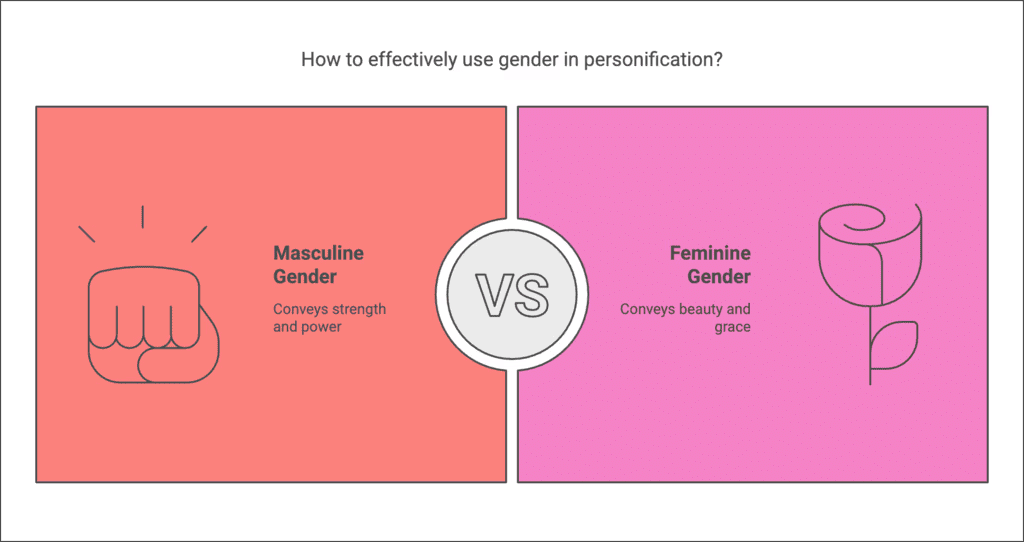
Rule 8: Personification of Neuter Gender Nouns
Masculine gender is used for strength and power, while feminine is used for beauty and grace.
Examples:
The Sun was shining with all his might.
It is our duty to protect Mother Earth.
Rule 9: Titles and Artistic Works Are Singular
The names of books, artworks, and television shows are considered singular in grammar, even if they may sound plural.
Examples:
- The Palace of Illusions is a wonderful book.
- Game of Thrones is my favourite series.
Rule 10: Gender Usage in Small Creatures and Collectives
(a) For small creatures or young children, neuter gender is used.
Examples:
The baby wants food, or it will cry.
The butterfly moved its wings.
(b) Collective nouns take neuter gender, even for living beings.
Examples:
The team gave its best performance.
The army is at its best.
Conclusion
- It is crucial for effective and precise communication to have a firm grasp of the various types and rules governing nouns.
- Familiarity with the usage of singular and plural forms, collective nouns, and the distinction between countable and uncountable nouns significantly enhances both writing and speaking abilities.
- With consistent practice, you will become proficient in applying these grammatical rules.
- This proficiency will contribute to your grammatical accuracy and overall improvement in language skills.
|
184 videos|572 docs|126 tests
|
FAQs on Wren and Martin Summary: Nouns - Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension (VARC) - CAT
| 1. What is a noun? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of nouns? |  |
| 3. How can you identify a noun in a sentence? |  |
| 4. Can a noun be used as a subject and an object in the same sentence? |  |
| 5. Are there any exceptions or irregularities in noun formation? |  |
















