NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 - Polynomials (Exercise 2.1)
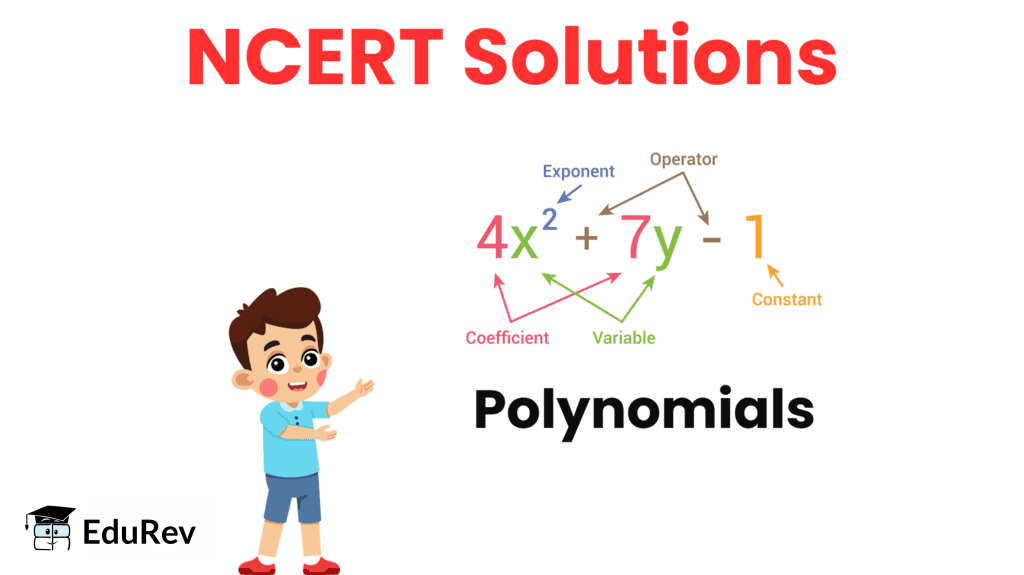
Q1. Which of the following expressions are polynomials in one variable and which are not? State reasons for your answer.
(i) 4x2 – 3x + 7
Ans: A polynomial in one variable refers to an expression where the exponent of the variable is a whole number.
In this polynomial, only one variable is involved which is ‘x’ and the exponents of the variable are all whole numbers.
Therefore, the given expression is a polynomial in one variable ‘x’.
(ii) y2 + √2
Ans: In this polynomial, only one variable is involved which is ‘y’ and the exponent of the variable is a whole number. Therefore, the given expression is a polynomial in one variable ‘y’.
(iii) 3√t + t√2
Ans: In this expression, it is given that the exponent of variable ‘t’ in term ‘3√t ’ is 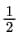 . This exponent is not a whole number. Therefore, the given algebraic expression is not a polynomial in one variable.
. This exponent is not a whole number. Therefore, the given algebraic expression is not a polynomial in one variable.
(iv) y + 2/y
Ans: We can rewrite this expression as: y + 2y−1.
In this expression, it is given that the exponent of the variable y in term ‘2y−1’ is − 1. This exponent is not a whole number. Therefore, the given algebraic expression is not a polynomial in one variable.
(v) x10 + y3 + t50
Ans: In this polynomial, there are 3 variables involved which are ‘x, y, t’.
Therefore, the given algebraic expression is not a polynomial in one variable.
Q2. Write the coefficients of x2 in each of the following:
(i) 2 + x2 + x
Ans: The expression 2 + x2+x can be written as 2 + (1)x2 + x
We know that, coefficient is the number which multiplies the variable.
Here, the number that multiplies the variable x2 is 1
The coefficient of x2 in 2 + x2 + x is 1.
(ii) 2 – x2 + x3
Ans: The expression 2 – x2 + x3 can be written as 2 + (–1)x2 + x3
We know that, coefficient is the number (along with its sign, i.e., – or +) which multiplies the variable.
Here, the number that multiplies the variable x2 is -1 the coefficients of x2 in 2 – x2 + x3 is -1.
(iii) (π/2)x2 + x
Ans: The expression (π/2)x2 + x can be written as (π/2)x2 + x
We know that, coefficient is the number (along with its sign, i.e., – or +) which multiplies the variable.
Here, the number that multiplies the variable x2 is π/2.
the coefficients of x2 in (π/2)x2 +x is π/2.
(iv)√2x - 1
Ans: The expression √2x - 1 can be written as 0x2+√2x-1 [Since 0x2 is 0]
We know that, coefficient is the number (along with its sign, i.e., – or +) which multiplies the variable.
Here, the number that multiplies the variable x2 is 0, the coefficients of x2 in √2x - 1 is 0.
Q3. Give one example each of a binomial of degree 35, and of a monomial of degree 100.
Ans: The degree of a polynomial is the highest power of the variable in the polynomial. It represents the highest exponent of the variable within the algebraic expression.
Therefore,
- Binomial of degree 35: A polynomial having two terms and the highest degree 35 is called a binomial of degree 35
Example: 3x35+5 - Monomial of degree 100: A polynomial having one term and the highest degree 100 is called a monomial of degree 100
Example: 4x100
Q4. Write the degree of each of the following polynomials:
(i) 5x3 + 4x2 + 7x
Ans: The highest power of the variable in a polynomial is the degree of the polynomial.
Here, 5x3 + 4x2 + 7x = 5x3 + 4x2 + 7x1
The powers of the variable x are: 3, 2, 1
The degree of 5x3 + 4x2 + 7x is 3 as 3 is the highest power of 'x' in the expression.
(ii) 4 – y2
Ans: The highest power of the variable in a polynomial is the degree of the polynomial.
Here, in 4–y2,
The power of the variable y is 2
The degree of 4 – y2 is 2 as 2 is the highest power of 'y' in the expression.
(iii) 5t – √7
Ans: The highest power of the variable in a polynomial is the degree of the polynomial.
Here, in 5t–√7,
The power of the variable t is 1.
The degree of 5t–√7 is 1 as 1 is the highest power of 't' in the expression.
(iv) 3
Ans: The highest power of the variable in a polynomial is the degree of the polynomial.
Here, 3 = 3 × x0
The power of the variable here is: 0
The degree of 3 is 0.
Q5. Classify the following as linear, quadratic and cubic polynomials:
Ans: We know that,
Linear polynomial: A polynomial of degree one is called a linear polynomial.
Quadratic polynomial: A polynomial of degree two is called a quadratic polynomial.
Cubic polynomial: A polynomial of degree three is called a cubic polynomial.
(i) x2 + x
Ans: The highest power of x2 + x is 2
The degree is 2
Hence, x2 + x is a quadratic polynomial
(ii) x – x3
Ans: The highest power of x–x3 is 3
The degree is 3
Hence, x–x3 is a cubic polynomial
(iii) y + y2 + 4
Ans: The highest power of y+y2+4 is 2
The degree is 2
Hence, y+y2+4 is a quadratic polynomial
(iv) 1 + x
Ans: The highest power of 1 + x is 1
The degree is 1
Hence, 1 + x is a linear polynomial.
(v) 3t
Ans: The highest power of 3t is 1
The degree is 1
Hence, 3t is a linear polynomial.
(vi) r2
Ans: The highest power of r2 is 2
The degree is 2
Hence, r2 is a quadratic polynomial.
(vii) 7x3
Ans: The highest power of 7x3 is 3
The degree is 3
Hence, 7x3 is a cubic polynomial.
|
40 videos|560 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 2 - Polynomials (Exercise 2.1)
| 1. What are polynomials? |  |
| 2. What is the degree of a polynomial? |  |
| 3. What is the remainder theorem of polynomials? |  |
| 4. How do we find the roots of a polynomial equation? |  |
| 5. What is the factor theorem of polynomials? |  |

















