NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 - Control and Coordination
Page No. 105
Q1: What is the difference between a reflex action and walking?
Ans:
- Reflex action is the involuntary action that occurs in response to stimuli.
- They occur without the involvement of conscious areas of the brain.
- All the reflex actions are unconscious.
- Reflex action occurs brain and spinal cord of the central nervous systems.
- This kind of response occurs within a fraction of a second.
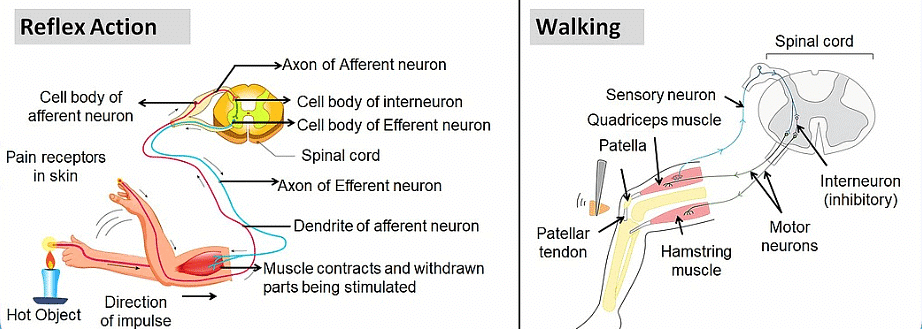
- On the other hand, voluntary actions are those which occur under the control of the cerebellum of the brain.
- Walking is learnt as we grow. Walking is controlled by the brain. This kind of response takes a longer time.
Q2: What happens at the synapse between two neurons?
Ans: The small empty space between two nerve cells is called a synapse. At a synapse, a chemical substance is produced at the end of an axon of one nerve cell that reaches the other nerve cell through the dendrite. Thus, information is transmitted from one nerve cell to another nerve cell by a synapse.
 DendriteQ3: Which part of the brain maintains the posture and equilibrium of the body?
DendriteQ3: Which part of the brain maintains the posture and equilibrium of the body?
Ans: Cerebellum, a part of the hindbrain is responsible for maintaining posture and equilibrium of the body.
Q4: How do we detect the smell of an agarbatti (incense stick)?
Ans: The thinking part of our brain is the forebrain. It has separate areas that are specialized for hearing, smelling, sight, taste, touch, etc. The fore-brain also has regions that collect information or impulses from various receptors.
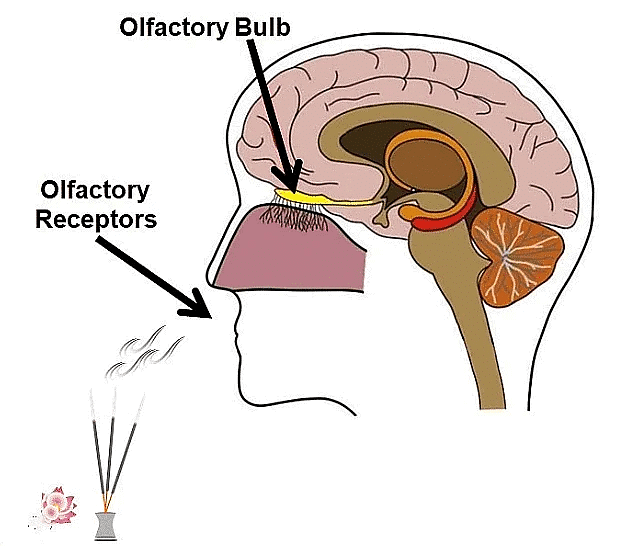 When the smell of an incense stick reaches us, our forebrain detects it. Then, the forebrain interprets it by putting it together with the information received from other receptors and also with the information already stored in the brain.
When the smell of an incense stick reaches us, our forebrain detects it. Then, the forebrain interprets it by putting it together with the information received from other receptors and also with the information already stored in the brain.
Q5: What is the role of the brain in reflex action?
Ans: Reflex actions are sudden responses, which do not involve any thinking.
- For example, when we touch a hot object, we withdraw our hand immediately without thinking as thinking may take time which would be enough to get us burnt.
- The sensory nerves that detect heat are connected to the nerves that move the muscles of the hand.
- Such a connection of detecting the signal from the nerves (input) and responding to it quickly (output) is called a reflex arc.
- The reflex arcs (connections present between the input and output nerves) meet in a bundle in the spinal cord.
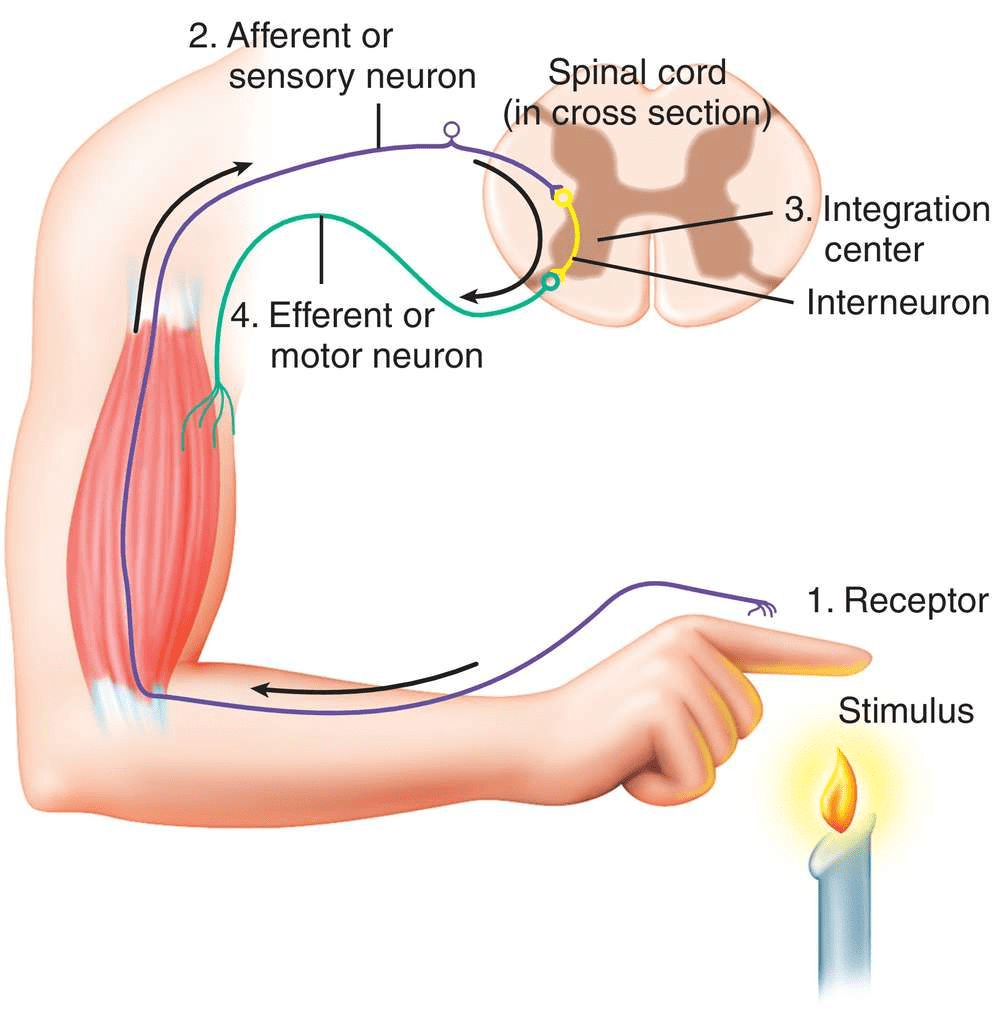 Reflex arcs are formed in the spinal cord and the information (input) reaches the brain. The brain is only aware of the signal and the response that has taken place. However, the brain has no role to play in the creation of the response.
Reflex arcs are formed in the spinal cord and the information (input) reaches the brain. The brain is only aware of the signal and the response that has taken place. However, the brain has no role to play in the creation of the response.
Page No. 108
Q1: What are plant hormones?
Ans: Plant hormones are the fluid that are secreted within the plant also known as phytohormones. Plant hormones regulate the growth and development of the plant.
Examples of plant hormones include:
- Auxin - promotes cell elongation and growth.
- Gibberellins - stimulate stem growth.
- Cytokinins - encourage cell division.
Q2: How is the movement of leaves of the sensitive plant different from the movement of a shoot towards light?
Ans: 
Q3: Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes growth.
Ans: Auxin is an example of a growth-promoting plant hormone. Auxins are responsible for cell elongation in the shoot and accelerates growth.
Q4: How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support?
Ans: When the tip of a tendril touches a support, then the auxins present in its tip move to that side of tip which is away from the support. Auxins promote growth. So, due to more auxins in it, the side of tendril away from the support grows faster (and becomes longer) than the side which is in contact with the support and makes the tendril twirl (or bend) around the support.
Q5: Design an experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism.
Ans: To demonstrate hydrotropism in plants.
Procedure:
- Plant a seedling in a vessel containing soil.
- Adjacent to the seedling, put a porous pot containing water.
- Leave this setup for a few days.
Observation:
On examining the roots, it is observed that the roots bend towards the source of water and do not grow straight.
Result:
It confirms that the plant shows hydrotropism as the roots bend towards the porous pot of water. As hydrotropism is a plant growth response in which the direction of growth is determined by a stimulus of a gradient in water concentration.
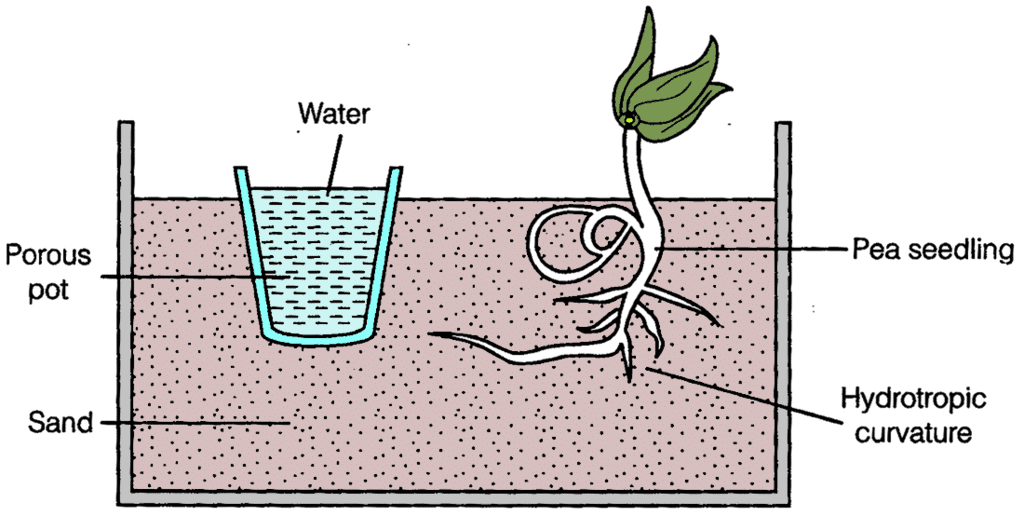 Experiment of Hydrotropism
Experiment of Hydrotropism
Page No. 111
Q1: How does chemical coordination take place in animals?
Ans: Chemical coordination in animals occurs through hormones. A hormone is a chemical messenger that regulates the physiological processes in living organisms.
- It is secreted by glands.
- The regulation of physiological processes and control and coordination by hormones comes under the endocrine system.
- The nervous system along with the endocrine system in our body controls and coordinates the physiological processes.
Q2: Why is the use of iodized salt advisable?
Ans: It is advised to use iodised salt because thyroid gland needs iodine to produce thyroxin hormone. Thyroxin hormone controls all the metabolic activities of our body like metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and protein etc. Due to the deficiency of thyroxin a disease called goitre is caused.
Q3: How does our body respond when adrenaline is secreted into the blood?
Ans: The heartbeat increases when adrenaline is secreted into the blood so that more oxygen is supplied to our muscles. The blood supply to the digestive system and skin decreases because the small arteries around the muscles of these organs contract. This turns the direction of blood towards our skeletal muscles. The breathing rate also increases due to the contractions of the diaphragm and rib muscles. All these responses enable us to face the situations of fear and anger.
Q4: Why are some patients with diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin?
Ans: Diabetes is caused due to less or no secretion of the hormone insulin by the pancreas. In such a person, blood sugar level is high. Insulin converts extra sugar present in the blood into glycogen. Thus, patients suffering from diabetes are given insulin injections on to control their blood sugar levels.
Page No. 112
Exercises
Q1. Which of the following is a plant hormone?
(a) Insulin
(b) Thyroxin
(c) Oestrogen
(d) Cytokinin
Ans: (d) Cytokinin
Cytokinin is a plant hormone whereas Insulin, Thyroxin and, Oestrogen are the hormones produced by animals.
Q2. The gap between two neurons is called a
(a) dendrite.
(b) synapse.
(c) axon.
(d) impulse.
Ans: (b) Synapse
The gap between two neurons is called a synapse. At the synapse, chemicals are released that help transmit signals to the next neuron.
Q3. The brain is responsible for
(a) thinking.
(b) regulating the heartbeat.
(c) balancing the body.
(d) all of the above.
Ans: (d) all of the above
The brain is responsible for thinking, regulating the heartbeat and balancing the body.
Q4. What is the function of receptors in our body? Think of situations where receptors do not work properly. What problems are likely to arise?
Ans: Receptors are sensory structures (organs/tissues or cells) present all over the body. The receptors are either grouped in the case of the eye or ear or scattered in the case of the skin.
Functions of receptors:
- They sense external stimuli such as heat or pain.
- They also trigger an impulse in the sensory neuron which sends a message to the spinal cord.
When the receptors are damaged, the external stimuli transferring signals to the brain are not felt. For example, in the case of damaged receptors, if we accidentally touch any hot object, then our hands might get burnt as damaged receptors cannot perceive the external stimuli of heat and pain.
Q5. Draw the structure of a neuron and explain its function.
Ans:
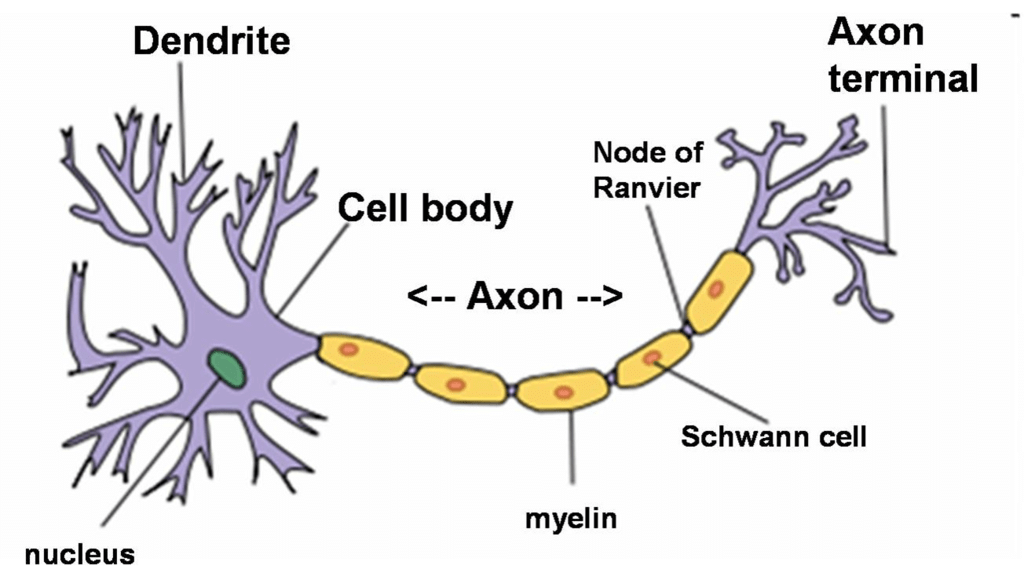 Structure of Neuron
Structure of Neuron
Functions of the three parts of a neuron:
- Axon: It conducts messages away from the cell body.
- Dendrite: It receives information from the axon of another cell and conducts the messages towards the cell body.
- Cell body: It contains a nucleus, mitochondria, and other organelles. It is mainly concerned with maintenance and growth.
Q6. How does phototropism occur in plants?
Ans: The movement in any part of a plant due to light is called phototropism. The shoot of plant shows positive phototropism and roots show negative phototropism.
Phototropism in plants occurs due to the hormone auxin. When light falls on one side of a plant, the secretion of auxin hormone is more in the part away from the light. Hence, auxin causes growth in length of the cells in shady part. So, the plant appears to bend towards light.
Q7. Which signals will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury?
Ans:
(i) All the involuntary actions will get disturbed.
(ii) Reflex actions will be disturbed because reflexes are located in the spinal cord. Therefore, the quick responses required to safe guard the body will not take place.
Q8. How does chemical coordination occur in plants?
Ans: Chemical coordination in plants takes place with the help of plant hormones. In most of the regions where division takes place (meristematic regions) stimulus cells secrete chemical compounds (hormones). These substances identify the information by stimulating the other nearby cells and communicating the information.
Q9. What is the need for a system of control and coordination in an organism?
Ans: An organism needs control and coordination system for the following functions :
(i) To save the body of the organisms from the harmful changes in the environment.
(ii) To control the speed of voluntary and involuntary actions.
(iii) To have the capability to think and learn for responding to any stimuli.
Q10. How are involuntary actions and reflex actions different from each other?
Ans: 
Q11. Compare and contrast nervous and hormonal mechanisms for control and coordination in animals.
Ans:

Q12. What is the difference between the manner in which movement takes place in a sensitive plant and the movement in our legs?
Ans:

|
80 videos|653 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 - Control and Coordination
| 1. What is the role of hormones in control and coordination in animals? |  |
| 2. How do plants respond to stimuli? |  |
| 3. What are the differences between the nervous system and the endocrine system in terms of control and coordination? |  |
| 4. What are reflex actions, and how do they relate to control and coordination? |  |
| 5. Why is homeostasis important in the context of control and coordination? |  |

















