NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Chapter 3 Climates of India
The Big Questions (Page 45)
Q1: What makes India’s climate so diverse?Ans:
- India's varied geography—mountains, deserts, plateaus, and coasts—creates different climates.
- Latitude (distance from the Equator) and altitude (height above sea level) affect temperature and rainfall.
- Places near the sea have mild weather, while inland areas have extreme temperatures.
- Winds and topography (land shape) also influence rainfall and temperature.
 Climate of India
Climate of India
Q2: What are the monsoons? How are they formed?
Ans:
- Monsoons are seasonal winds that bring heavy rainfall, important for farming in India.
- In summer, warm land pulls in moist air from the ocean, causing rainfall (Southwest Monsoon).
- In winter, cool land pushes dry winds to the sea, causing dry weather (Northeast Monsoon).
- Monsoons form due to differences in temperature and pressure between land and sea.
Q3: What is the effect of climate on economy, culture, and society?
Ans:
- Good or bad monsoon affects farming, food supply, and prices in markets.
- Many festivals and traditions are linked to seasons and harvests, like Baisakhi and Onam.
- People wear different clothes, grow different crops, and build homes based on the climate.
- Industries also need stable climate and water supply to work properly.
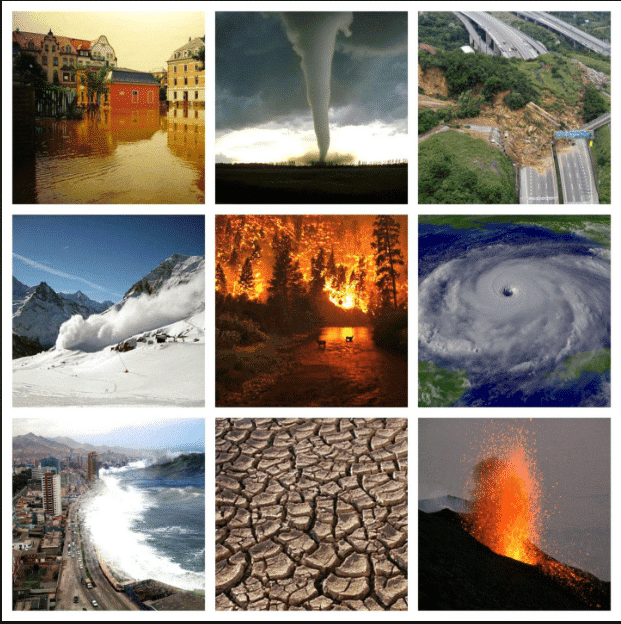 Natural Disasters
Natural Disasters
Q4: How can understanding the climate help us to prepare for natural disasters?
Ans:
- Knowing the climate helps predict disasters like cyclones, floods, and droughts.
- Weather departments (like IMD) give warnings in advance to protect people and property.
- Government teams (like NDRF) can plan rescue efforts and move people to safety.
- This helps reduce loss of life, damage to homes, and harm to crops or animals.
Q5: What is climate change? What are its consequences?
Ans:
- Climate change means long-term changes in weather patterns caused by human actions.
- Burning fossil fuels and cutting trees release greenhouse gases, which trap heat and cause global warming.
- Effects include extreme weather, shorter winters, crop failure, and harm to small industries.
- Solutions include using renewable energy, planting trees, and reducing pollution.
Back Questions (65 & 66)
Q1: Match the climatic factors with their effects: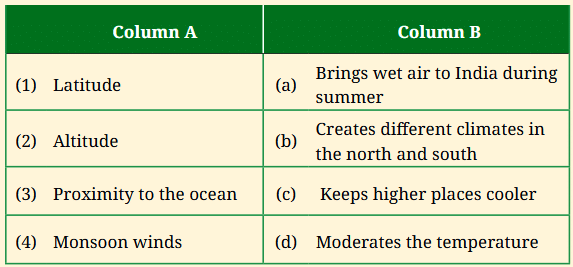
Ans: 
1. Latitude (b) Creates different climates in the north and south: Latitude determines how much sunlight an area receives. Areas near the Equator are warmer, while those further north or south are cooler, like South India being warmer than North India.
2. Altitude (c) Keeps higher places cooler: At higher altitudes, the air is thinner and cooler. Hill stations like Shimla and Darjeeling are cooler than the plains due to their high altitude.
3. Proximity to the ocean (d) Moderates the temperature: Coastal areas are less affected by extreme temperatures because the sea keeps the temperature more even, making places like Mumbai cooler in summer and warmer in winter compared to inland cities like Nagpur.
4. Monsoon winds (a) Brings wet air to India during summer: The monsoon winds carry moist air from the ocean, bringing heavy rainfall to India during the summer months, which is essential for agriculture, especially in regions like Kerala and Maharashtra.
Q2: Answer the following questions:
a) What is the difference between weather and climate?
Ans:
Weather refers to the atmospheric conditions at a specific time and place. It changes frequently and can be sunny, rainy, windy, or cloudy.
Climate, on the other hand, is the long-term pattern of weather in a particular region over many years, usually decades. It includes the average weather conditions and seasonal changes in temperature, precipitation, and other atmospheric elements.
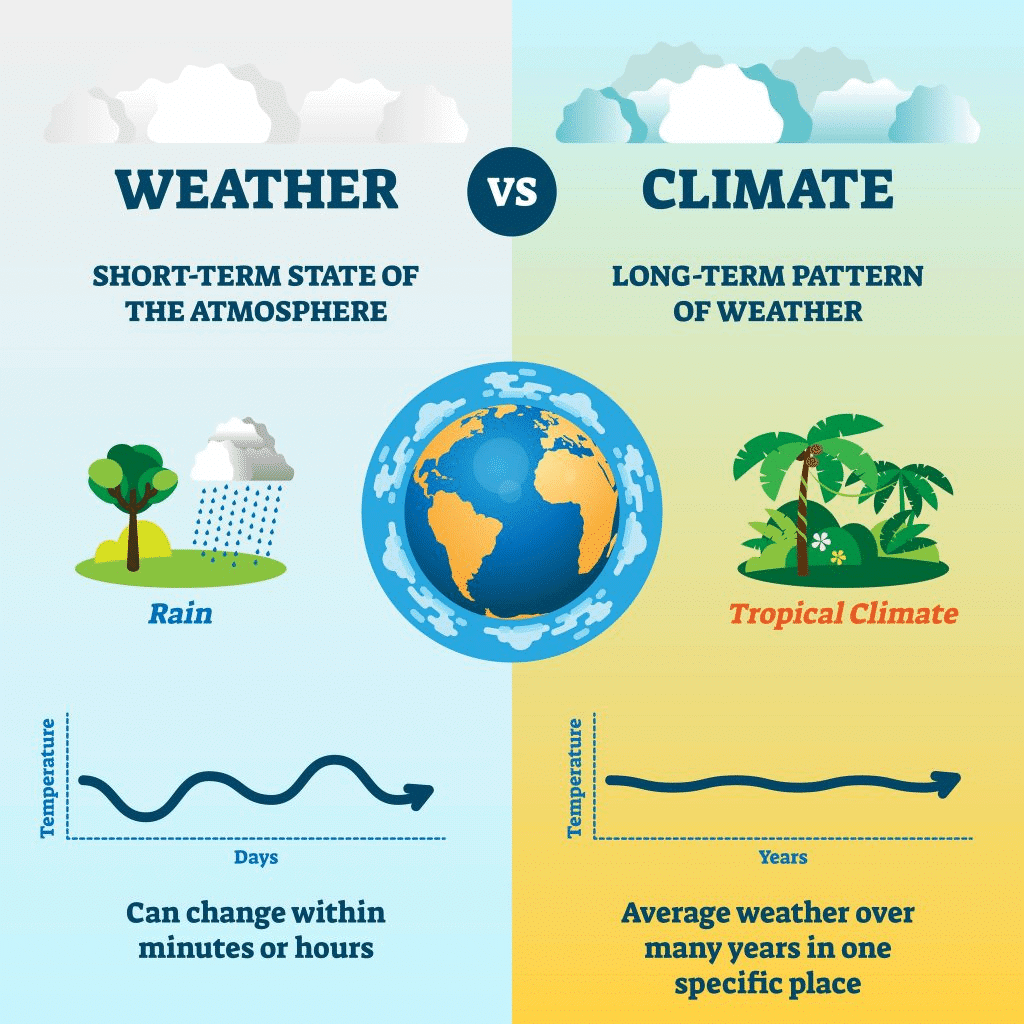 Difference between Weather and Climate
Difference between Weather and Climate
b) Why do places near the ocean have milder temperatures than places far away from it?
Ans: Places near the ocean have milder temperatures because the sea has a moderating effect on the climate. Water heats up and cools down more slowly than land. This means that coastal areas experience cooler summers and warmer winters compared to inland areas. For example, Mumbai, being near the sea, has cooler summers than Nagpur, which is further inland.
c) What role do monsoon winds play in affecting India’s climate?
Ans: Monsoon winds bring heavy rainfall to India during the monsoon season (from June to September). These winds blow from the southwest towards the land, carrying moisture from the Indian Ocean. As the moisture-laden winds rise over the Western Ghats, they cool and condense to form rain. This rainfall is vital for agriculture, especially for crops like rice, and plays a major role in the climate of India.
d) Why is Chennai warm or hot throughout the year, while Leh is cold?
Ans:
- Chennai is located near the coast and experiences a tropical climate. The sea moderates its temperature, keeping it hot and humid throughout the year.
- Leh, on the other hand, is located in the Himalayas at a high altitude. This causes it to have an alpine climate, where the temperature is much cooler, even during the summer, and cold in winter.
Q3: Look at a map of India given at the end of this book. Identify the climate for these cities—Leh, Chennai, Delhi, Panaji, and Jaipur.

Q4: Draw the monsoon cycle in summers and winters on a map of India.
Ans:
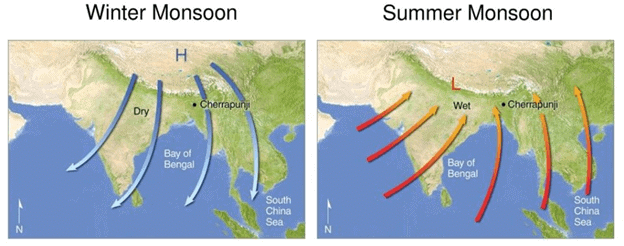
- Summer Monsoon (June to September): Winds blow from the southwest (from the Indian Ocean) bringing moisture and rain to India. The rains start in the southern tip and move northward, covering the entire subcontinent by mid-July.
- Winter Monsoon (October to February): Winds reverse and blow from land to the sea, bringing dry weather and cool temperatures. These winds bring some moisture to parts of East and South India.
Q5: Make a colourful poster showing festivals in India linked to farming and weather (e.g., Baisakhi, Onam).
Ans: Instructions for students:
Create a poster with images or drawings of festivals such as:
- Baisakhi (celebrating the harvest of wheat in Punjab),
- Onam (celebrating the rice harvest in Kerala),
- Pongal (harvest festival in Tamil Nadu).
Include images of farmers, crops, and celebrations such as dances and traditional food associated with these festivals.
Here is the sample Poster:  Seasons influencing festivals
Seasons influencing festivals
Q6: Imagine you are a farmer in India. Write a short diary entry about how you would prepare for the rainy season.
Ans: Diary Entry: “Today, I am preparing for the rainy season. I’ve cleaned my fields and checked the irrigation system to ensure it works well when the rains start. I’ve also arranged my seeds and tools in good condition. The monsoon rains are important for my crops, especially for rice. I will plant the seeds as soon as the rains arrive. I hope the rains come on time so my crops can grow well and I can have a good harvest.”
Q7: Identify a natural disaster (e.g., cyclone, flood, landslide, or forest fire) and write a short essay that includes the causes and impacts. Suggest actions that individuals, communities, and the government can take to reduce the impact.
Ans: Essay on Cyclones:
Causes:Cyclones are formed when low-pressure systems develop over warm ocean waters. The warm air rises and draws in more air, which picks up moisture. When the system strengthens, it can lead to high winds, heavy rain, and the formation of a cyclone.
Impacts:
- Loss of life and property.
- Destruction of crops and farmlands.
- Damage to infrastructure, such as roads and buildings.
- Soil erosion and destruction of natural habitats.
Actions to Reduce the Impact:
- Individuals: Stay informed about weather warnings, have an emergency kit ready, and evacuate if necessary.
- Communities: Build better, stronger houses that can withstand cyclonic winds and set up evacuation plans.
- Government: Improve early warning systems, build disaster-resilient infrastructure, and train disaster response teams. Conduct regular drills for preparedness.
|
23 videos|272 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Chapter 3 Climates of India
| 1. What are the major seasons in India according to the climate classification? |  |
| 2. How do the geographical features of India influence its climate? |  |
| 3. What is the role of the monsoon in India's climate? |  |
| 4. How does climate vary in different regions of India? |  |
| 5. What are the effects of climate change on India's weather patterns? |  |

















