NCERT Solution (Part - 1) - Bills of Exchange | Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
Quick Recap
A Bill of Exchange and Promissory Note both are legal instruments which facilitate the credit sale of goods by assuring the seller that the amount will be recovered after a certain period. Both of these legal instruments under the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881. There are 3 parties to a bill of exchange: Drawer, Drawee, Payee.
Let’s look at the NCERT solutions for Bills of Exchange.
Page Number: 332
Short answers:
Q1: Name any two types of commonly used negotiable instruments.
Answer: The two types of commonly used negotiable instruments are:
1. Cheques
2. Bills of exchange
Q2: Write two points of distinction between bills of exchange and promissory note.
Answer: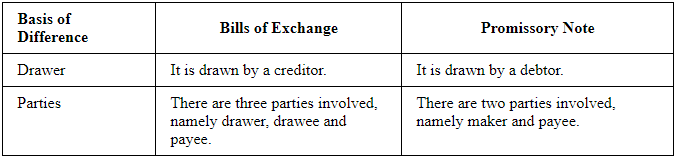
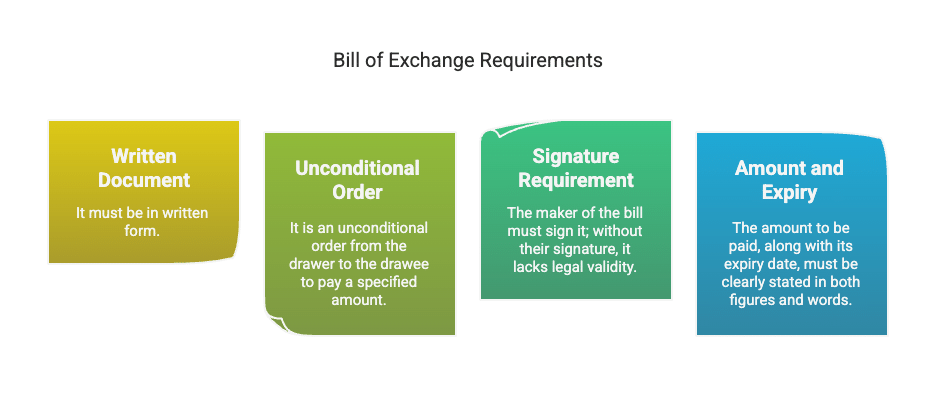
Q3: State any four essential features of bill of exchange.
Answer: The four essential features of a bill of exchange are:
- Written document: It must be in written form.
- Unconditional order: It is an unconditional order from the drawer to the drawee to pay a specified amount.
- Signature requirement: The maker of the bill must sign it; without their signature, it lacks legal validity.
- Amount and expiry: The amount to be paid, along with its expiry date, must be clearly stated in both figures and words.
Q4: State the three parties involved in a bill of exchange.
Answer: The following three parties are involved in a bill of exchange:
- Drawer: The person who creates and makes the bill.
- Drawee: The person who accepts the bill and is obligated to pay.
- Payee: The person who receives the payment specified in the bill.
Q5: What is meant by the maturity of a bill of exchange?
Answer: The Maturity of a bill of exchange refers to the date on which the bill is due for payment. The maturity date varies based on the terms and conditions specified in the bill. There are three types of bills: after-date bill, after sight bill, and at sight bill.
- After date bill: For an after-date bill, payment is made on the maturity date. This date is determined by adding a three-day grace period to the specified period of the bill, which begins from the date of drawing. For example, if a bill is drawn on 1st March 2011 and payable after one month, its maturity date is 4th April 2011. If the maturity date falls on a gazetted holiday, the bill is due for payment one day earlier. Conversely, if it is a casual holiday, the bill is due for payment one day later.
- After sight bill: In the case of an after-sight bill, payment is made on the maturity date, which is determined by adding a three-day grace period to the specified period starting from the date the drawee accepts the bill. For instance, if a one-month bill is drawn on 1st March 2011 and accepted by the drawee on 5th March 2011, its maturity date is 8th April 2011. Here, the period starts from 5th March and not 1st March. Similar to the after date bill, if the maturity date is a gazetted holiday, it is payable one day before, and if it is a casual holiday, it is payable one day after.
- At sight bill: For an at sight bill, the due date is when the bill is presented for payment by the holder. In this case, there is no grace period; the bill becomes due immediately upon presentation.
Q6: What is meant by dishonour of a bill of exchange?
Answer: The dishonour of a bill occurs when the acceptor fails to make the payment on the bill's maturity date. As a result, the acceptor's liability is reinstated. To record the dishonour of a bill of exchange, the entries are the reverse of those made when the bill was drawn.
In the books of drawer
Q7: Name the parties to a promissory note
Answer: The parties to a promissory note are as follows:
- Promisor: The person who makes the note and agrees to pay the amount specified in the promissory note.
- Payee: The individual or entity that receives the payment.
Q8: What is meant by the acceptance of a bill of exchange?
Answer: A bill of exchange is a financial document drawn in favour of a person from whom an amount is due. In simpler terms, it is created by creditors for their debtors to facilitate the payment of a specific amount on a specified date. Typically, a bill is issued by a seller to a purchaser. The purchaser accepts the bill for the amount owed due to credit sales. Additionally, a bill may be accepted for amounts due from other sources, such as commission payments, outstanding salaries, etc. Importantly, a bill cannot exist without the acceptance of the debtor.
Q9: What is Noting of a bill of exchange.
Answer: When a bill is presented for payment and the acceptor fails to make the payment, the bill is considered dishonoured. To maintain a legal proof of dishonour, the bill is noted by a Notary Public, who is authorised by the government. In return for this service, the Notary Public charges a fee known as noting charges. The Notary Public records the following facts:
- Date and amount of the bill
- Reasons for dishonour
- Amount of noting charges
Q10: What is meant by renewal of a bill of exchange?
Answer: When the acceptor of a bill of exchange does not have sufficient funds to meet the obligations of the bill on time, he or she may request an extension from the drawer for payment. If the drawer agrees, a new bill is drawn, which is referred to as the renewal of the bill. Typically, a bill is renewed on the condition that the drawee pays interest for the extended period.
Q11: Give the performa of a Bills Receivable Book.
Answer: The Bills Receivable Book is a crucial financial document used to record all the bills that a business has received and is due for payment. This document helps in tracking outstanding payments and managing cash flow effectively. Below is a typical format for a Bills Receivable Book:
- Date: The date on which the bill is received.
- Bill Number: A unique identifier for each bill.
- Party Name: The name of the person or company from whom the bill is received.
- Amount: The total amount specified in the bill.
- Due Date: The date by which the payment is expected.
- Status: The current status of the bill (e.g., paid, unpaid, overdue).

Q12: Give the performa of a Bills Payable Book.
Answer:

Q13: What is retirement of a bill of exchange?
Answer: When a holder receives the amount of a bill before the maturity date on the request of the acceptor, then it is called retirement of the bill of exchange. Holder of the bill may give discount for such earlier payment. This discount is termed as 'rebate'.
Entry in the books of the holder of the bill
Q14: Give the meaning of rebate.
Answer: If the drawee expresses his/her wish to pay the bill before the due date to the holder, and if the holder accepts his/her request, then on account of the early payment, the
holder may give some discount. This discount is termed as rebate. In other words, rebate is a discount given by the holder to the drawee (or acceptor) for his/her request of early payment of the bill before the due date. It is an expense for the drawer and hence, is debited to the drawer's books. On the other hand, as it is a gain for the acceptor of bill, so it is credited in the drawee's books.
Entry in the books of drawer of the bill:

Q15: Give the performa of a Bill of Exchange.
Answer: Performa of a Bill of exchange is given below.

Page Number: 332
Long answers:
Q1: A bill of exchange must contain an unconditional promise to pay. Do you agree with a statement?
Answer: According to the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1981, a bill of exchange is defined as an instrument in writing that contains an unconditional order, signed by the maker, directing a certain person to pay a certain sum of money only to, or to the order of, a specific person or to the bearer of the instrument. A bill of exchange contains an unconditional promise to pay a specific sum of money on an agreed date to the drawer or the bearer by the drawee of the bill.
An unconditional order to pay is one of the important characteristics of a negotiable instrument. This means that no conditions should be attached by the acceptor regarding the payment. For example, conditions such as "payment of the bill only in case of profit on sales" or "payment of the bill only if the prices of goods increase" should not be included. Additionally, the language of the bill should be clear and unambiguous.
Q2: Briefly explain the effects of dishonour and noting of a bill of exchange.
Answer:
When a bill is presented for payment and the acceptor fails to make the payment, the bill gets dishonoured. In this situation, liability of the acceptor is restored.
Entry in the books of drawer (if Noting charges are not paid):

Noting charges are charged by the notary public for keeping a proof that the bill is dishonoured. The noting charges are paid by the holder of the bill but are actually due on the drawee or the acceptor of the bill.
Notary public notes the below given facts.
1. Date and amount of bill
2. Reasons for dishonour
3. Amount of noting charges
Effect of Noting charges in the books of holder of bill (if Noting charges are paid):

Q3: Explain briefly the procedure of calculating the date of maturity of a bill of exchange? Give example.
Answer: The procedure to calculate the date of maturity of a bill of exchange is given below.
1. Ascertain the date on which the bill will be honoured.
2. Add three days of grace to the above date.
For example, a bill with maturity period of one month is drawn on 1st July and due date is 1st September. Then add 3 days of grace and payment will be made on 4th September.
Days of grace depend on the following situations:
1. Declared holidays: If the payment day happens to be a national holiday or Sunday, then the preceding day becomes the payment day.
For example,
1. If a bill is drawn on 12th July and its due date is 12th August, then after adding 3 days of grace the maturity day is 15th August. However, as 15th August is a national holiday; so, 14th August becomes the payment day.
2. If a bill is drawn on 1st May and the maturity period is of one month, then the due date is 1st June. After adding 3 days of grace, the payment date becomes 4th June. However, if 4th June happens to be a Sunday, then the payment will be made on 3rd June.
2. Undeclared holidays: If the payment day happens to be an emergency holiday, then the succeeding day becomes the payment day. For example, if a bill is drawn on 1st May and is payable after 15 days, then, after adding 3 days of grace period, the due date becomes 18th May. However, if a national strike is declared on 18th May, then 19th May becomes the due date of the bill.
Q4: Distinguish between bill of exchange and promissory note.
Answer:
Q5: Briefly explain the purpose and benefits of retiring a bill of exchange to the debtor and the creditor.
Answer: The retirement of a bill of exchange occurs when the holder receives the amount of the bill before its maturity date at the request of the acceptor. In this case, the holder may offer a discount for early payment, referred to as a 'rebate'. This rebate reflects a loss for the holder, as it is debited in their books upon receiving the payment. Conversely, the acceptor benefits from the rebate as it is recorded as a gain in their accounts. Thus, the retirement of a bill provides advantages to both parties involved:
- The holder receives immediate cash flow.
- The acceptor saves money by paying early.

Acceptor of the bill gets rebate for the payment made before the due date. The rebate is a gain for the drawee; so, it is credited in the books of the drawee.

(Bill paid before the due date and rebate received for early payment)
Q6: Explain briefly the purpose and advantages of maintaining of a Bills Receivable Book.
Answer: Bills Receivable Book is a special purpose book that is maintained to keep records of bills received from the debtors. It contains details such as acceptor's name, date of bill, due date, amount, etc. for future references. It is totalled periodically and its balance is transferred to the debit side of the bills receivable account.
Benefits of Maintaining the Bill Receivable Book
- Availability of Information: All information related to bills receivable, such as amounts and due dates, is recorded in one place, making it easily accessible.
- Minimised Fraud Risk: Since all bills are documented in one location, the likelihood of fraud is significantly reduced.
- Increased Accountability: The individual maintaining the Bills Receivable Book is responsible for any errors or omissions, ensuring a higher degree of accountability. If an error is detected, it can be rectified quickly.
- Time Efficiency: Recording bills receivable through this book takes less time than making journal entries, saving the accountant's time when handling numerous routine transactions.
Q7: Briefly explain the benefits of maintaining a Bills Payable Book and state how is its posting is done in the ledger?
Answer: A Bills Payable Book is a special purpose book, maintained to keep records of acceptance of bills, given to the creditors. It contains details of the amount, date of bill, due date, to whom acceptance is given, etc., for future references. It is totalled periodically and its balance is transferred to the credit side of the bills payable account.
Benefits of Maintaining Bills Payable Book
- Availability of Information: All information related to bills payable is recorded in one place, including the amount and due dates.
- Minimisation of Fraud: Since all bills are documented together, the possibility of fraud is reduced.
- Increased Responsibility: Transactions are recorded by the same individual, making it easier to detect and correct errors. This enhances the responsibility and accountability of the accountant.
Page Number: 333
Numerical questions:
Question 1: On Jan 01, 2016 Rao sold goods Rs 10,000 to Reddy. Half of the payment was made immediately and for the remaining half Rao drew a bill of exchange upon Reddy payable after 30 days. Reddy accepted the bill and returned it to Rao. On the due date Rao presented the bill to Reddy and received the payment Journalise the above transactions in the books Rao and prepare of Rao’s account in the books of Reddy.
Answer:
Books of Rao | ||||||
Journal |
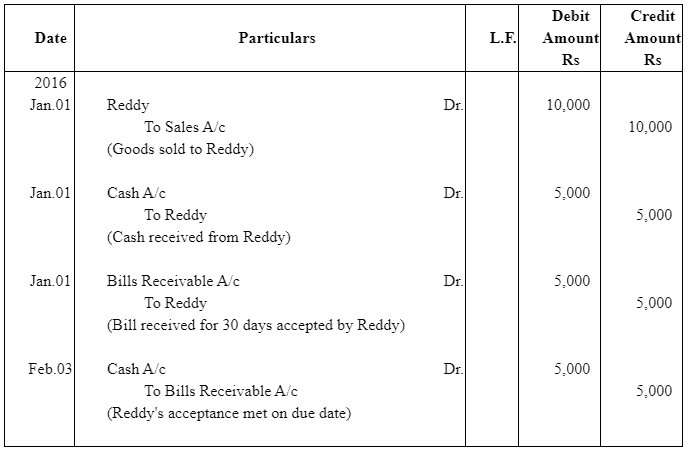

|
61 videos|220 docs|39 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solution (Part - 1) - Bills of Exchange - Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What is a bill of exchange? |  |
| 2. What are the types of bills of exchange? |  |
| 3. What are the parties involved in a bill of exchange? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between a bill of exchange and a promissory note? |  |
| 5. What is dishonor of a bill of exchange? |  |

















