UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Polity for UPSC CSE > Mind Map: Supreme Court
Mind Map: Supreme Court | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
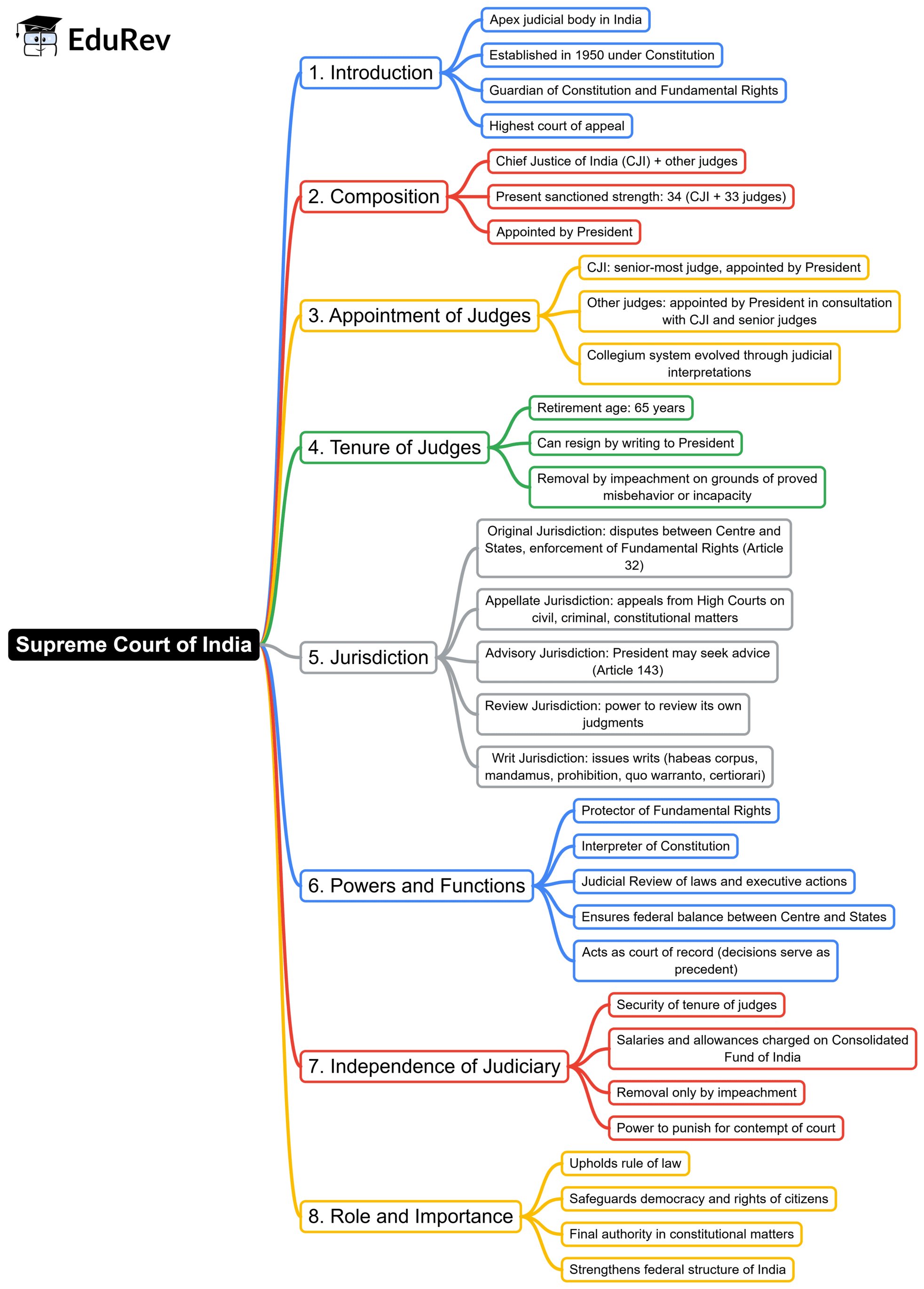
The document Mind Map: Supreme Court | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Polity for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
154 videos|973 docs|260 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Supreme Court - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the role of the Supreme Court in the Indian judicial system? |  |
Ans. The Supreme Court is the highest judicial forum and final court of appeal under the Constitution of India. It has the authority to interpret the Constitution, safeguard fundamental rights, and settle disputes between states or between the central government and states. The Court also has the power to review laws passed by the Parliament and can strike down any legislation that it finds unconstitutional.
| 2. How does the appointment process for Supreme Court judges work? |  |
Ans. Judges of the Supreme Court are appointed by the President of India, based on the recommendations of the Prime Minister and the Chief Justice of India. The appointment process involves consultation with other judges of the Supreme Court and High Courts to ensure a diverse and competent judiciary. The procedure aims to maintain judicial independence and integrity.
| 3. What are the different types of jurisdiction exercised by the Supreme Court? |  |
Ans. The Supreme Court exercises original, appellate, and advisory jurisdiction. Original jurisdiction pertains to cases involving the enforcement of fundamental rights and federal disputes. Appellate jurisdiction allows the Court to hear appeals against decisions from lower courts and tribunals. Advisory jurisdiction permits the Court to provide legal advice to the President on constitutional matters when requested.
| 4. What is the significance of Public Interest Litigation (PIL) in the Supreme Court? |  |
Ans. Public Interest Litigation (PIL) is a tool that allows individuals or groups to seek judicial intervention in matters of public interest. The Supreme Court has broadened access to justice through PIL, enabling citizens to address issues such as environmental protection, social justice, and human rights violations. This mechanism has empowered marginalized communities and has played a crucial role in societal reform.
| 5. How does the Supreme Court ensure the protection of fundamental rights? |  |
Ans. The Supreme Court plays a vital role in protecting fundamental rights by acting as the guardian of the Constitution. It has the power to issue writs for the enforcement of these rights under Article 32 of the Constitution. The Court hears cases of rights violations and can provide remedies such as injunctions or compensations to ensure justice is served, thereby upholding the rule of law.
Related Searches





















