CTET & State TET Exam > CTET & State TET Notes > English Language & Pedagogy for CTET & TET Exams > Mind Map: Noun
Mind Map: Noun | English Language & Pedagogy for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET PDF Download
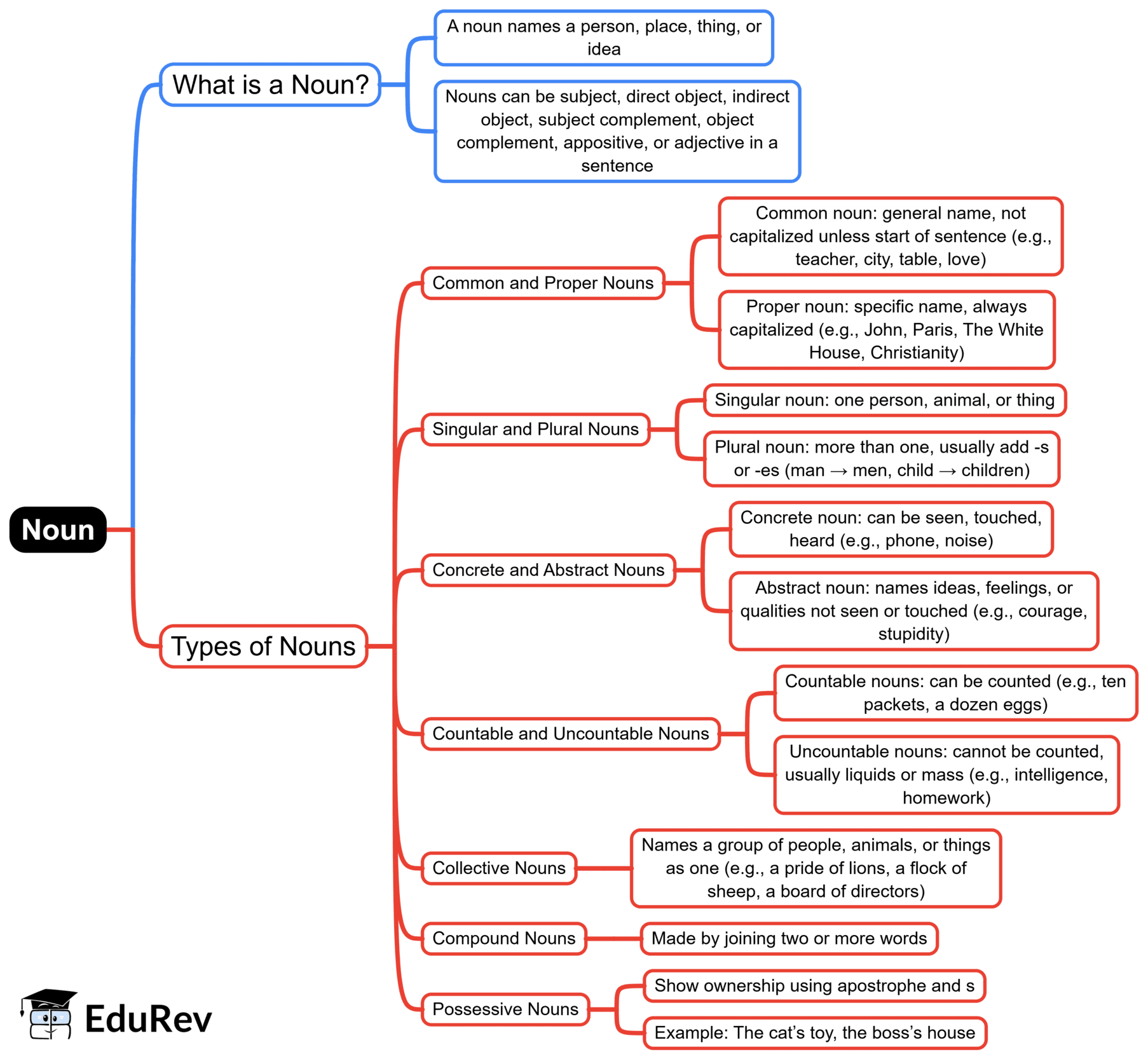
The document Mind Map: Noun | English Language & Pedagogy for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET is a part of the CTET & State TET Course English Language & Pedagogy for CTET & TET Exams.
All you need of CTET & State TET at this link: CTET & State TET
|
47 videos|208 docs|47 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Noun - English Language & Pedagogy for CTET & TET Exams - CTET & State TET
| 1. What is a noun, and what are its different types? |  |
Ans. A noun is a word that identifies a person, place, thing, or idea. Nouns can be categorized into several types:
1. <b>Common Nouns</b>: General names for a class of objects (e.g., cat, city).
2. <b>Proper Nouns</b>: Specific names for individual entities (e.g., John, New York).
3. <b>Collective Nouns</b>: Names that refer to a group of individuals or things (e.g., team, flock).
4. <b>Abstract Nouns</b>: Names for ideas, qualities, or conditions that cannot be seen or touched (e.g., love, freedom).
5. <b>Concrete Nouns</b>: Names for things that can be perceived through the senses (e.g., apple, car).
| 2. How do nouns function in a sentence? |  |
Ans. Nouns function as the subject or object within a sentence. The subject is the noun performing the action of the verb, while the object receives the action. For example, in the sentence "The dog (subject) chased the ball (object)," "dog" is the subject noun and "ball" is the object noun. Additionally, nouns can also act as the complement, describing or identifying the subject, as in "She is a teacher," where "teacher" is a noun complement.
| 3. Can nouns be pluralized, and what are the rules for pluralization? |  |
Ans. Yes, nouns can be pluralized to indicate more than one. The general rule is to add an "s" to the end of the noun (e.g., cat → cats). However, there are exceptions:
1. For nouns ending in "s," "x," "z," "ch," or "sh," "es" is added (e.g., bus → buses).
2. For nouns ending in a consonant followed by "y," the "y" is changed to "i" and "es" is added (e.g., baby → babies).
3. Irregular nouns have unique plural forms (e.g., child → children, mouse → mice).
| 4. What is the difference between countable and uncountable nouns? |  |
Ans. Countable nouns are items that can be counted and have both singular and plural forms (e.g., one apple, two apples). Uncountable nouns represent substances or concepts that cannot be counted individually and do not typically have a plural form (e.g., water, information). When quantifying uncountable nouns, terms like "some," "much," or "a little" are used instead of numbers.
| 5. How do nouns relate to adjectives in a sentence? |  |
Ans. Nouns and adjectives work together to provide more detail in a sentence. Adjectives describe or modify nouns, giving additional information such as quality, quantity, or state. For example, in the phrase "the red apple," "red" is the adjective describing the noun "apple." Adjectives typically precede the nouns they modify in English, although they can also follow linking verbs in certain contexts (e.g., "The apple is red").
Related Searches
















