UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > PSIR Optional for UPSC > Mind Map: India and South Asia
Mind Map: India and South Asia | PSIR Optional for UPSC PDF Download
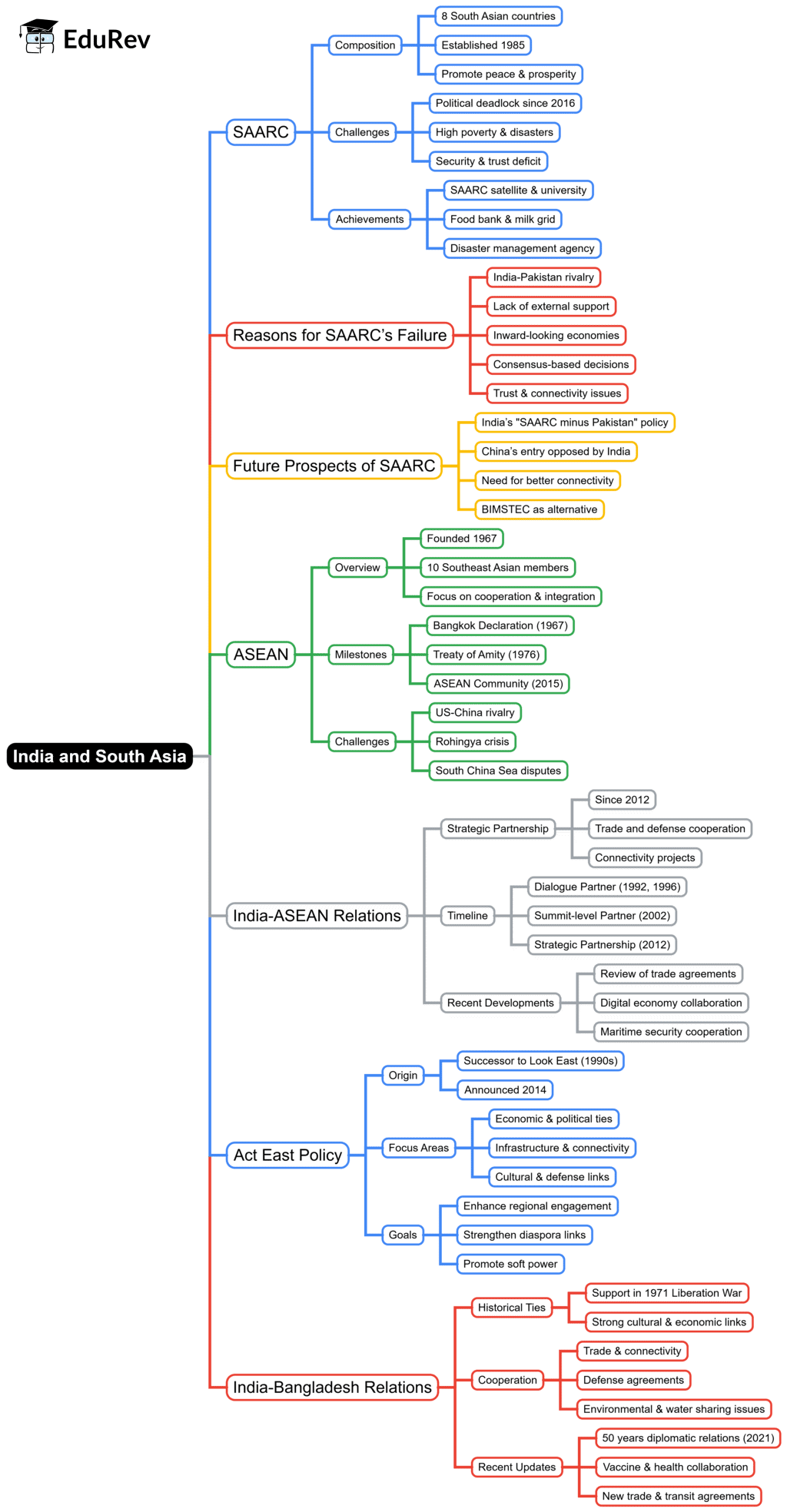
The document Mind Map: India and South Asia | PSIR Optional for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course PSIR Optional for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
177 videos|665 docs|152 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: India and South Asia - PSIR Optional for UPSC
| 1. What are the key geographical features of India and South Asia? |  |
Ans. India and South Asia are characterized by diverse geographical features, including the Himalayas in the north, the Indo-Gangetic Plain, the Thar Desert in the west, and the Deccan Plateau in the south. The region also includes significant rivers like the Ganges, Indus, and Brahmaputra, which are crucial for agriculture and settlement.
| 2. What is the significance of India's cultural diversity in South Asia? |  |
Ans. India's cultural diversity is a reflection of its rich history and multitude of ethnic groups, languages, religions, and traditions. This diversity contributes to a vibrant social fabric and fosters mutual respect and coexistence among different communities. It also plays a crucial role in the country's soft power and international relations.
| 3. How does India's political system function within South Asia? |  |
Ans. India operates as a federal parliamentary democratic republic, where the President is the head of state and the Prime Minister is the head of government. This system allows for a separation of powers among the executive, legislature, and judiciary. India's political structure influences governance across South Asia, setting a model for democratic processes in neighboring countries.
| 4. What are the major economic challenges faced by India and South Asia? |  |
Ans. Major economic challenges in India and South Asia include high levels of poverty, unemployment, and income inequality. Additionally, the region faces issues such as inadequate infrastructure, agricultural dependency, and the need for sustainable development to combat climate change and ensure long-term economic stability.
| 5. How does India engage with its South Asian neighbors? |  |
Ans. India engages with its South Asian neighbors through various means, including regional organizations like the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC), trade agreements, and bilateral relations. India aims to strengthen economic ties, enhance security cooperation, and address common challenges such as terrorism and climate change with its neighbors.
Related Searches





















