Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Subject-Wise Mind Maps for Class 10 > Mind Map: Carbon & its compounds
Mind Map: Carbon & its compounds | Subject-Wise Mind Maps for Class 10 PDF Download
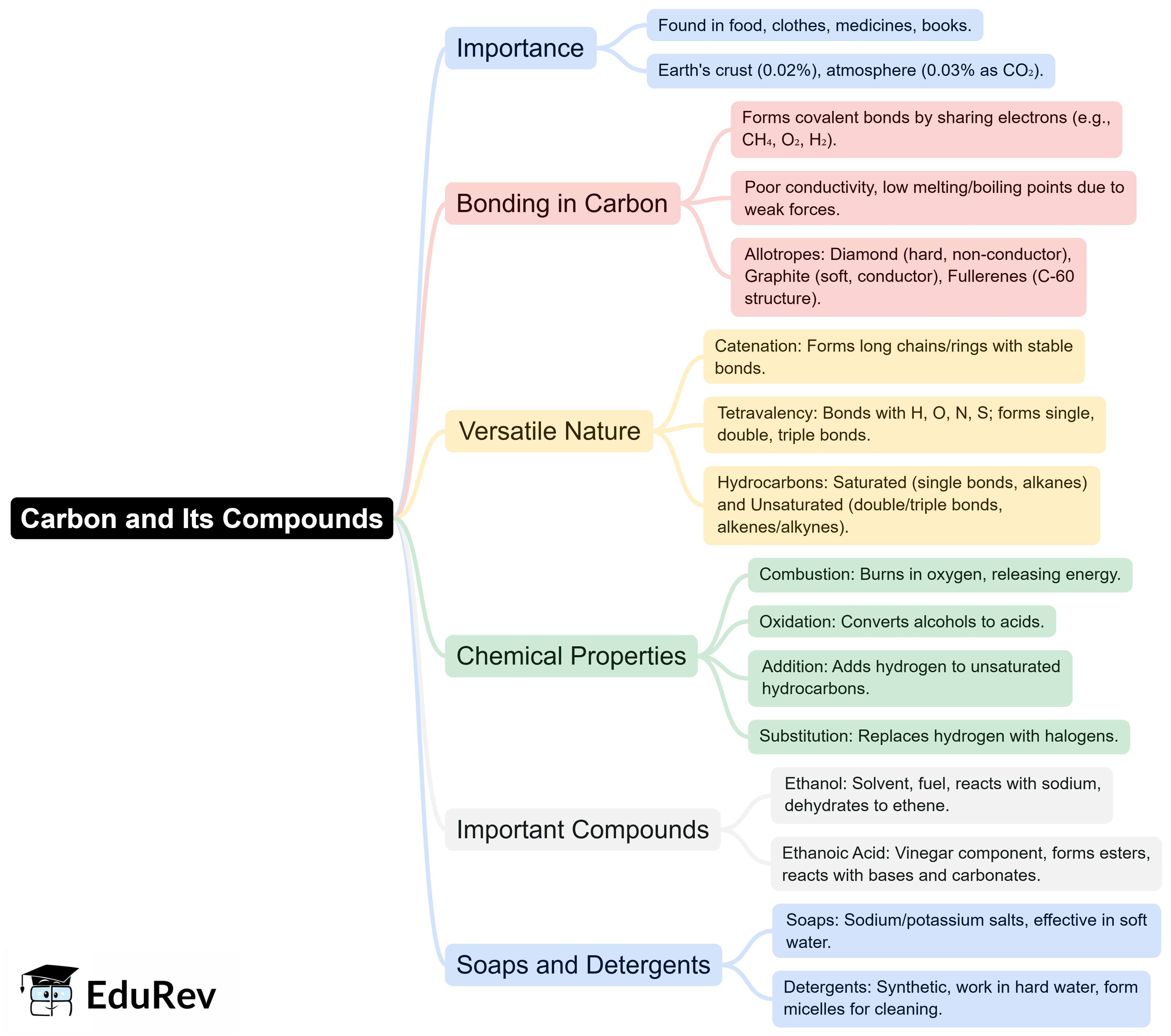
The document Mind Map: Carbon & its compounds | Subject-Wise Mind Maps for Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Subject-Wise Mind Maps for Class 10.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
FAQs on Mind Map: Carbon & its compounds - Subject-Wise Mind Maps for Class 10
| 1. What are the main forms of carbon and their significance in nature? |  |
Ans. The main forms of carbon include graphite, diamond, and amorphous carbon. Graphite is known for its electrical conductivity and is used in batteries and lubricants. Diamond is valued for its hardness and optical properties, making it ideal for cutting tools and jewelry. Amorphous carbon, such as soot, is often used as a black pigment in inks and paints. Each form of carbon plays a crucial role in various natural processes and industrial applications.
| 2. How do carbon compounds contribute to the greenhouse effect? |  |
Ans. Carbon compounds, particularly carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4), are significant contributors to the greenhouse effect. These gases trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere, leading to global warming. CO2 is primarily released through burning fossil fuels, while methane is emitted during agricultural practices and the decomposition of organic matter. Reducing emissions of these carbon compounds is essential for mitigating climate change.
| 3. What are the differences between organic and inorganic carbon compounds? |  |
Ans. Organic carbon compounds primarily contain carbon and hydrogen, often in combination with other elements such as oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur. They are typically associated with living organisms and include substances like carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. In contrast, inorganic carbon compounds, such as carbon dioxide and carbonates, do not primarily contain carbon-hydrogen bonds and are often found in non-living systems. The distinction is vital for understanding biochemical processes and material sciences.
| 4. What role does carbon play in biological systems? |  |
Ans. Carbon is a fundamental building block of life, forming the backbone of organic molecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. These compounds are essential for cellular structure, energy storage, and genetic information. Carbon's ability to form stable bonds with various elements allows for the complexity and diversity of biological molecules, making it crucial for life processes.
| 5. How do carbon compounds affect human health? |  |
Ans. Certain carbon compounds, such as carbon monoxide (CO) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), can pose health risks to humans. Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless gas that can cause poisoning by interfering with the blood's ability to carry oxygen. VOCs, found in many household products, can lead to respiratory issues and long-term health problems. Understanding the health impacts of these compounds is essential for environmental safety and public health.
Related Searches






















