UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > History for UPSC CSE > Mind Map: Calendars in India
Mind Map: Calendars in India | History for UPSC CSE PDF Download
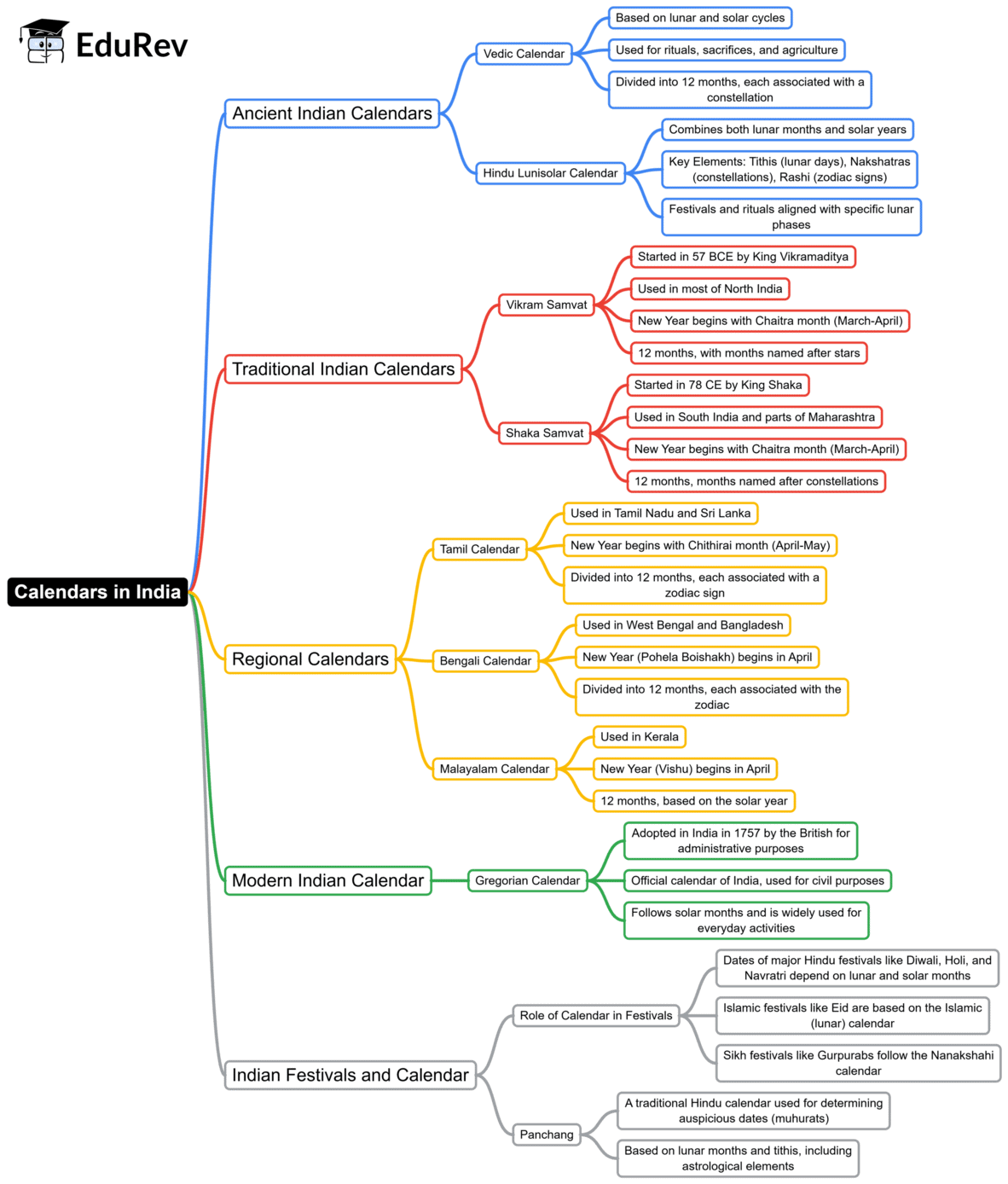
The document Mind Map: Calendars in India | History for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course History for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
216 videos|856 docs|219 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Calendars in India - History for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the major types of calendars used in India? |  |
Ans. In India, the major types of calendars include the Gregorian calendar, which is widely used for civil purposes; the Hindu calendar, which has several regional variations and is used for religious and cultural observances; the Islamic calendar, which is lunar-based and used by the Muslim community; and the Sikh calendar, known as the Nanakshahi calendar. Each of these calendars has its own significance and is used for different events and festivals throughout the year.
| 2. How do the Indian calendars differ from the Gregorian calendar? |  |
Ans. The Indian calendars differ from the Gregorian calendar primarily in their structure and base. The Gregorian calendar is solar-based, consisting of 12 months with a total of 365 days in a common year. In contrast, Hindu calendars may be lunisolar, with months based on lunar cycles, leading to variations in the number of days and months. For example, some Hindu calendars include an additional month (Adhik Maas) to synchronize with the solar year. This results in significant differences in the timing of festivals and auspicious days.
| 3. What is the significance of the Hindu calendar in Indian culture? |  |
Ans. The Hindu calendar holds immense cultural and religious significance in India. It dictates the dates of major festivals, religious observances, and rituals. For example, festivals like Diwali, Holi, and Navratri are based on specific dates in the Hindu calendar. Additionally, the calendar is used for determining auspicious timings (muhurat) for important life events such as weddings and housewarming ceremonies, making it central to the social fabric of Hindu culture.
| 4. What are the key features of the Islamic calendar followed in India? |  |
Ans. The Islamic calendar, or Hijri calendar, is a purely lunar calendar consisting of 12 months in a year of 354 or 355 days. Key features include its use in determining the dates of Islamic events and festivals, such as Ramadan, Eid al-Fitr, and Eid al-Adha. The Islamic calendar is significant for the Muslim community in India as it guides their religious practices and observances. Unlike the Gregorian calendar, the Islamic year shifts approximately 10 to 12 days earlier each year in relation to the solar year.
| 5. How do regional variations affect the use of calendars in India? |  |
Ans. Regional variations significantly affect the use of calendars in India due to the country's diverse cultural and religious landscape. Different states and communities may adopt specific versions of the Hindu calendar that align with local festivals and traditions. For instance, the Bengali calendar is different from the Tamil calendar, with unique New Year celebrations. Similarly, the use of the Islamic calendar may vary among different regions, affecting the timing of religious observances. These variations reflect the rich tapestry of India's cultural heritage, with each community having its own unique way of marking time.
Related Searches





















