UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Class 6 to 12 NCERT Mindmaps for UPSC Preparation > Mind Map: Ashoka: The Emperor Who gave up War
Mind Map: Ashoka: The Emperor Who gave up War | Class 6 to 12 NCERT Mindmaps for UPSC Preparation PDF Download
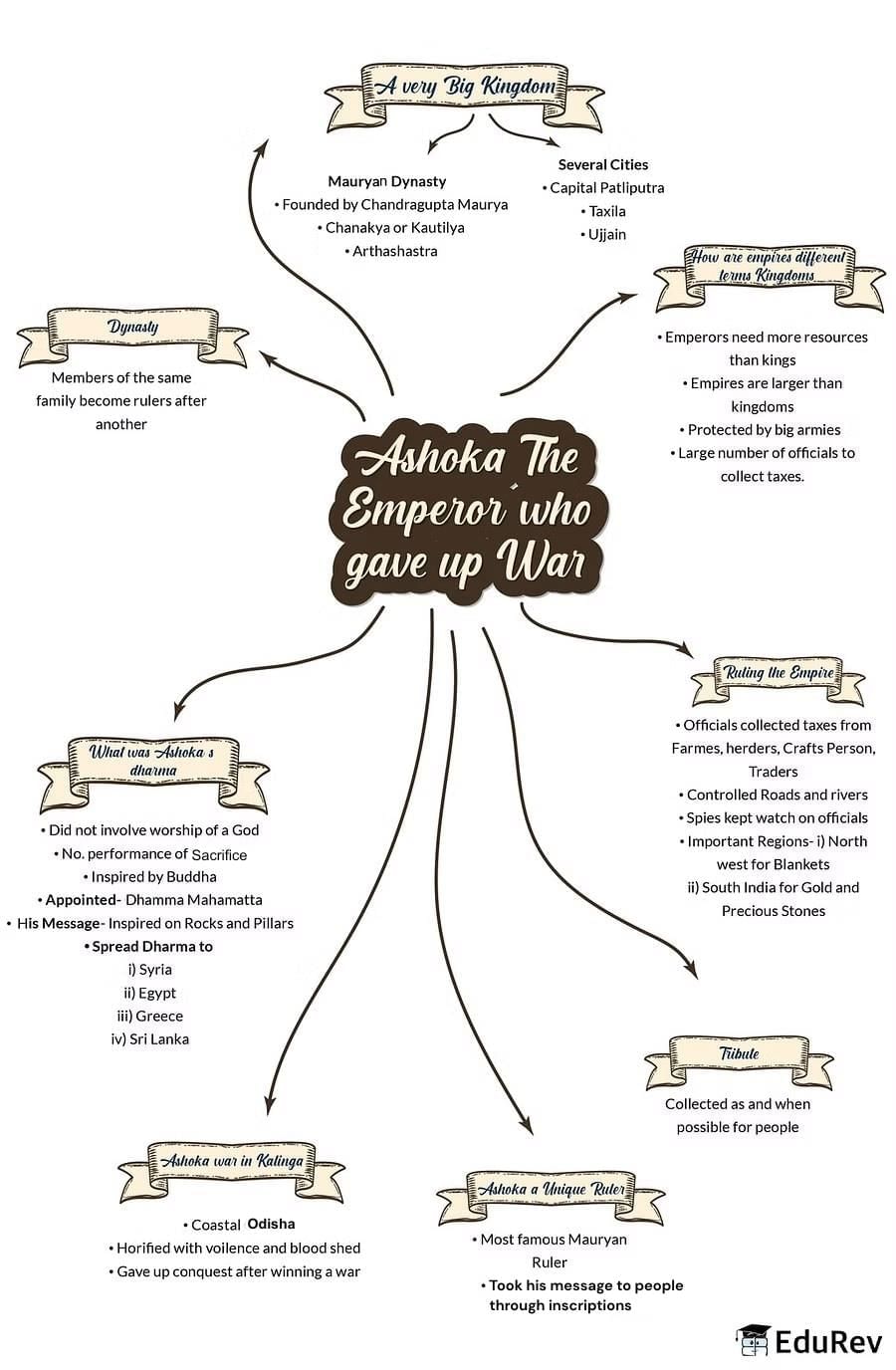
The document Mind Map: Ashoka: The Emperor Who gave up War | Class 6 to 12 NCERT Mindmaps for UPSC Preparation is a part of the UPSC Course Class 6 to 12 NCERT Mindmaps for UPSC Preparation.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
FAQs on Mind Map: Ashoka: The Emperor Who gave up War - Class 6 to 12 NCERT Mindmaps for UPSC Preparation
| 1. Who was Ashoka and why is he known as the Emperor Who gave up War? |  |
Ashoka was an Indian emperor who ruled the Maurya Dynasty from 268 to 232 BCE. He is known as the Emperor Who gave up War because after witnessing the brutality and suffering caused by his conquest of the Kalinga region, he experienced a change of heart. He renounced violence, embraced Buddhism, and dedicated his reign to promoting peace, harmony, and welfare of his subjects.
| 2. How did Ashoka's conversion to Buddhism influence his rule? |  |
Ashoka's conversion to Buddhism had a profound impact on his rule. It transformed him from a ruthless conqueror to a compassionate ruler. He adopted the principles of Buddhism, such as non-violence, tolerance, and compassion, as the guiding principles of his governance. He promoted religious tolerance, built numerous stupas and monasteries, and sent missionaries to spread Buddhism across his empire.
| 3. What were some of the major reforms introduced by Ashoka during his reign? |  |
Ashoka introduced several major reforms during his reign. He implemented a system of dhamma, which aimed to ensure justice, social welfare, and ethical conduct. He established hospitals, veterinary clinics, and rest houses for travelers. He encouraged the cultivation of medicinal plants and the protection of wildlife. Ashoka also promoted the welfare of his subjects through various measures, including the abolition of torture and the improvement of trade and infrastructure.
| 4. How did Ashoka's policy of Dhamma contribute to the stability of his empire? |  |
Ashoka's policy of Dhamma played a crucial role in maintaining the stability of his empire. By promoting principles such as non-violence, truthfulness, and compassion, he sought to create a just and harmonious society. This helped in reducing conflicts and upholding social order. His emphasis on religious tolerance also fostered a sense of unity among diverse religious communities within his empire. Additionally, his welfare policies and focus on public works projects contributed to the overall well-being of his subjects, further strengthening the stability of his rule.
| 5. How has Ashoka's legacy influenced subsequent rulers and societies? |  |
Ashoka's legacy has had a lasting impact on subsequent rulers and societies. His principles of non-violence, religious tolerance, and welfare governance continue to inspire leaders around the world. His edicts, which were inscribed on pillars and rocks, served as a model for later rulers in India and beyond. Ashoka's promotion of Buddhism helped in its spread across Asia, influencing the cultural and religious landscape of various regions. His emphasis on ethical governance and social welfare also laid the foundation for the development of welfare states in later periods.
Related Searches

















