Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Subject-Wise Mind Maps for Class 10 > Mind Map: Acids, Bases & Salts
Mind Map: Acids, Bases & Salts | Subject-Wise Mind Maps for Class 10 PDF Download
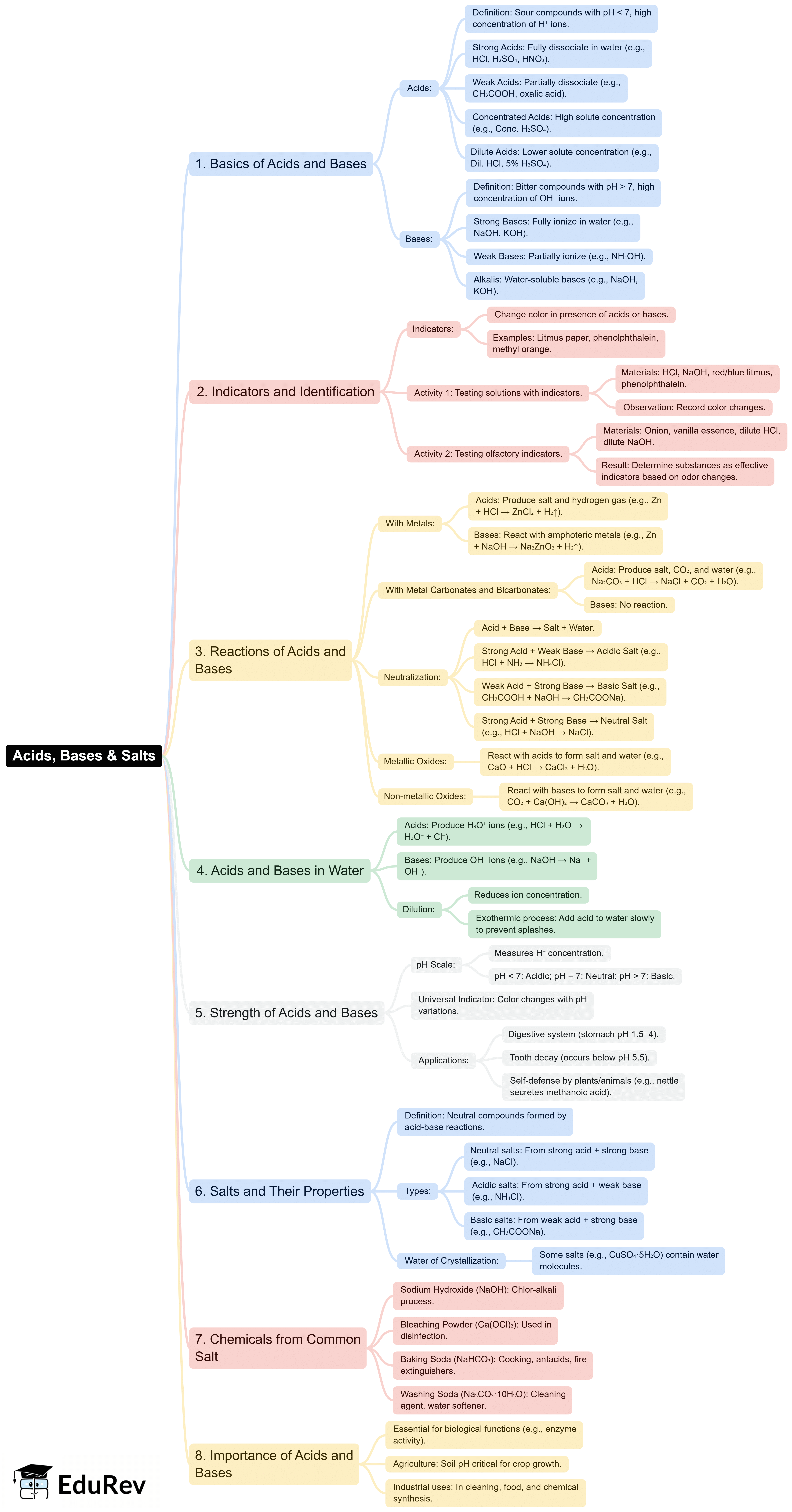
The document Mind Map: Acids, Bases & Salts | Subject-Wise Mind Maps for Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Subject-Wise Mind Maps for Class 10.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
FAQs on Mind Map: Acids, Bases & Salts - Subject-Wise Mind Maps for Class 10
| 1. What are the main properties of acids and bases? |  |
Ans. Acids typically have a sour taste, can conduct electricity in solution, and turn blue litmus paper red. They release hydrogen ions (H⁺) in solution. Bases, on the other hand, have a bitter taste, feel slippery, can also conduct electricity, and turn red litmus paper blue. They produce hydroxide ions (OH⁻) when dissolved in water.
| 2. How do acids and bases react with each other? |  |
Ans. Acids and bases undergo a chemical reaction known as neutralization. In this process, the hydrogen ions from the acid react with the hydroxide ions from the base to form water. This reaction often produces a salt as a byproduct. For example, hydrochloric acid (HCl) reacts with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to produce sodium chloride (NaCl) and water (H₂O).
| 3. What are some common examples of acids, bases, and salts? |  |
Ans. Common examples of acids include hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), and acetic acid (CH₃COOH). Examples of bases include sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), and calcium carbonate (CaCO₃). Salts are formed from the neutralization of an acid and a base; examples include sodium chloride (NaCl), magnesium sulfate (MgSO₄), and potassium nitrate (KNO₃).
| 4. What is the pH scale and how does it relate to acids and bases? |  |
Ans. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14 and is used to measure the acidity or basicity of a solution. A pH of 7 is considered neutral, which is the pH of pure water. A pH less than 7 indicates an acidic solution, with lower values representing stronger acids. Conversely, a pH greater than 7 indicates a basic (alkaline) solution, with higher values representing stronger bases.
| 5. How are salts formed, and what are their uses? |  |
Ans. Salts are formed through the reaction of an acid with a base during neutralization. They have various uses, such as flavoring food (e.g., table salt), preserving food (e.g., sodium nitrate), and in industrial applications (e.g., sodium carbonate in glass manufacturing). Additionally, salts play essential roles in biological processes and can be important in chemical reactions.
Related Searches

















