UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Polity for UPSC CSE > Mind Map: Working of the Constitution
Mind Map: Working of the Constitution | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
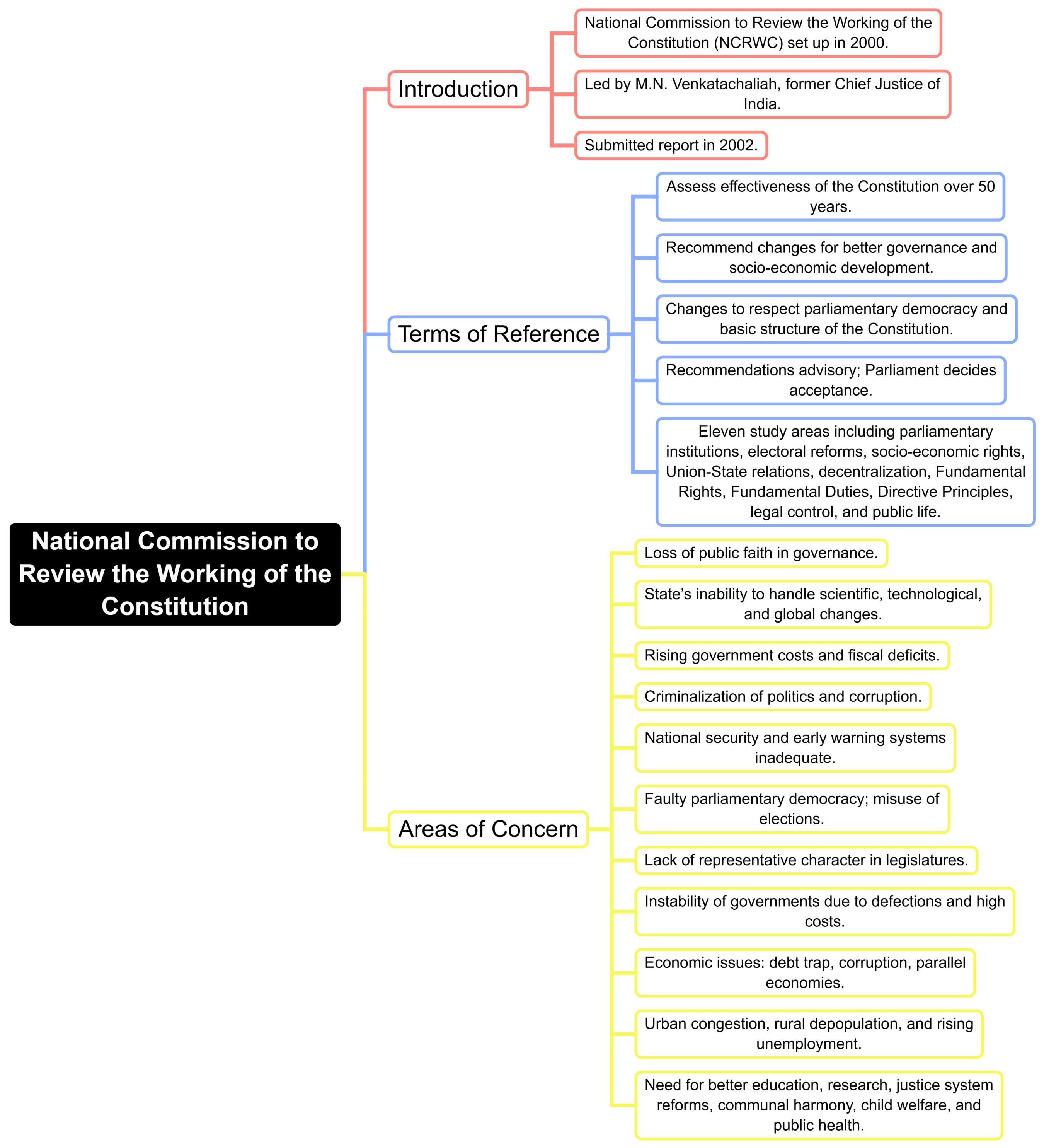
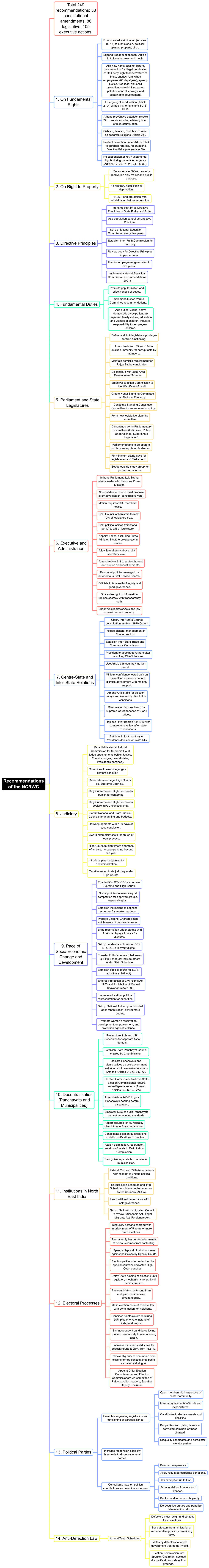
The document Mind Map: Working of the Constitution | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Polity for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
162 videos|992 docs|260 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Working of the Constitution - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the key features of the Constitution of India? |  |
Ans. The Constitution of India is characterized by several key features, including a written document that provides the framework for governance, a federal structure that divides powers between the central and state governments, and a parliamentary system that emphasizes the role of the legislature. It also enshrines fundamental rights and duties, ensuring the protection of individual freedoms, and establishes the directive principles of state policy to guide the governance towards social justice and welfare.
| 2. How does the Constitution of India ensure the separation of powers? |  |
Ans. The Constitution of India establishes the separation of powers among the three branches of government: the Executive, the Legislature, and the Judiciary. Each branch has distinct functions and responsibilities, with the Legislature responsible for making laws, the Executive for implementing them, and the Judiciary for interpreting and upholding them. This system is designed to prevent the concentration of power in one branch and to provide a system of checks and balances.
| 3. What is the significance of Fundamental Rights in the Indian Constitution? |  |
Ans. Fundamental Rights are essential provisions in the Indian Constitution that guarantee individual freedoms and rights to all citizens. They include the right to equality, freedom of speech and expression, protection against discrimination, and the right to constitutional remedies. These rights not only protect individuals from state action but also ensure the promotion of human dignity and the rule of law, making them a cornerstone of democracy in India.
| 4. How can amendments be made to the Constitution of India? |  |
Ans. Amendments to the Constitution of India can be made by following a specific procedure outlined in Article 368. There are three types of amendments: simple majority amendments, which require a simple majority of members present and voting; special majority amendments, which require a majority of the total membership of the House and a majority of those present and voting; and amendments requiring ratification by half of the state legislatures. This process ensures that changes to the Constitution are deliberate and reflective of a broad consensus.
| 5. What role does the Judiciary play in upholding the Constitution? |  |
Ans. The Judiciary in India plays a crucial role in upholding the Constitution by interpreting its provisions, protecting fundamental rights, and ensuring that laws enacted by the Legislature conform to constitutional mandates. The Supreme Court and High Courts have the power of judicial review, allowing them to invalidate laws and executive actions that are unconstitutional. This function of the Judiciary acts as a guardian of the Constitution, maintaining the rule of law and the balance of power among the various branches of government.
Related Searches





















