NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Chemistry Class 11 > Mind Map: Thermodynamics
Mind Map: Thermodynamics | Chemistry Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
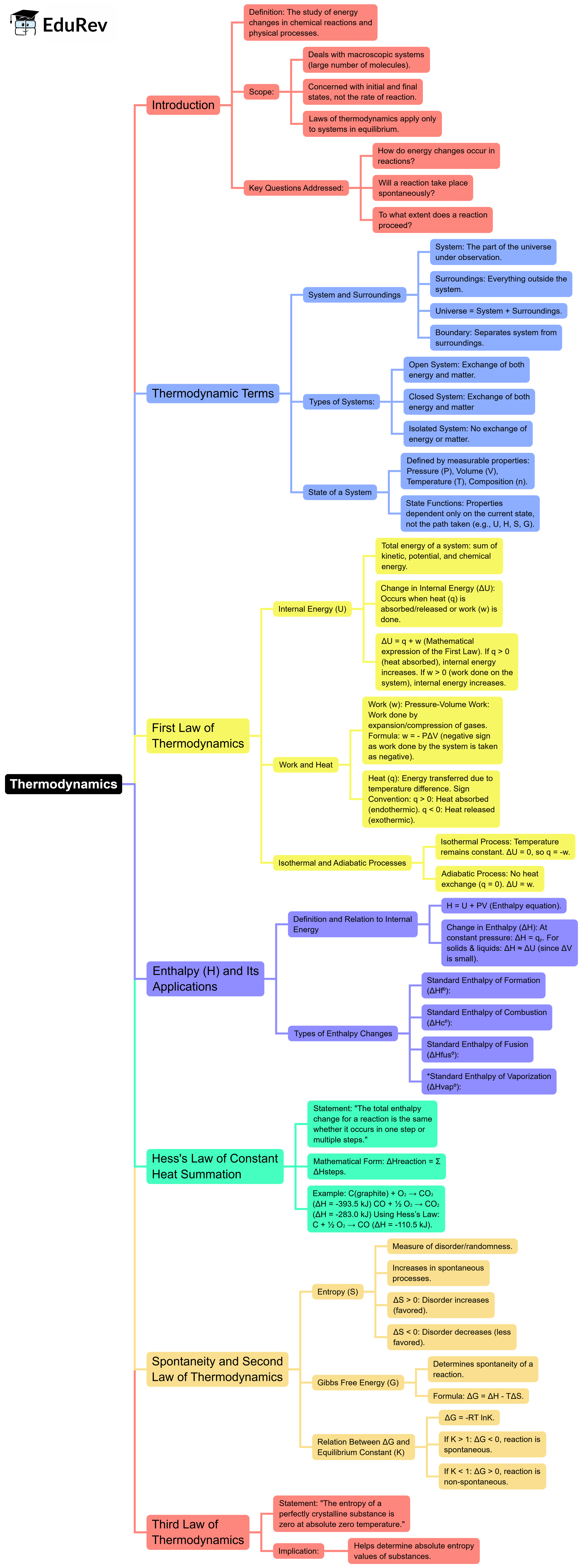
The document Mind Map: Thermodynamics | Chemistry Class 11 - NEET is a part of the NEET Course Chemistry Class 11.
All you need of NEET at this link: NEET
|
119 videos|338 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Thermodynamics - Chemistry Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What are the laws of thermodynamics? |  |
Ans. The laws of thermodynamics are fundamental principles that describe how energy is transferred and transformed. There are four main laws:
1. The Zeroth Law establishes thermal equilibrium.
2. The First Law (Law of Energy Conservation) states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed.
3. The Second Law states that the entropy of an isolated system always increases, implying that energy transformations are not 100% efficient.
4. The Third Law states that as temperature approaches absolute zero, the entropy of a perfect crystal approaches zero.
| 2. What is the difference between heat and temperature? |  |
Ans. Heat refers to the transfer of energy between systems or objects due to a temperature difference, while temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. In simpler terms, heat is energy in transit, and temperature is a property of a substance that reflects its thermal state.
| 3. What is entropy and why is it important in thermodynamics? |  |
Ans. Entropy is a measure of the disorder or randomness in a system. It is important in thermodynamics because it helps predict the direction of spontaneous processes and the feasibility of energy transformations. Higher entropy typically indicates a greater degree of disorder and less usable energy available for work.
| 4. Can you explain the concept of thermal equilibrium? |  |
Ans. Thermal equilibrium occurs when two or more systems in thermal contact no longer exchange heat energy because they are at the same temperature. At this state, the macroscopic properties of the systems become stable and there is no net flow of thermal energy between them.
| 5. How does the Carnot cycle demonstrate the principles of thermodynamics? |  |
Ans. The Carnot cycle is an idealized thermodynamic cycle that demonstrates how engines can operate between two heat reservoirs. It outlines the maximum possible efficiency of a heat engine operating between a hot and a cold reservoir, illustrating the Second Law of Thermodynamics. The efficiency of a Carnot engine depends on the temperatures of the reservoirs and shows that no real engine can be more efficient than a Carnot engine operating between the same temperatures.
Related Searches






















