Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Mathematics (Maths) Class 10 > Mind Map: Probability
Mind Map: Probability | Mathematics (Maths) Class 10 PDF Download
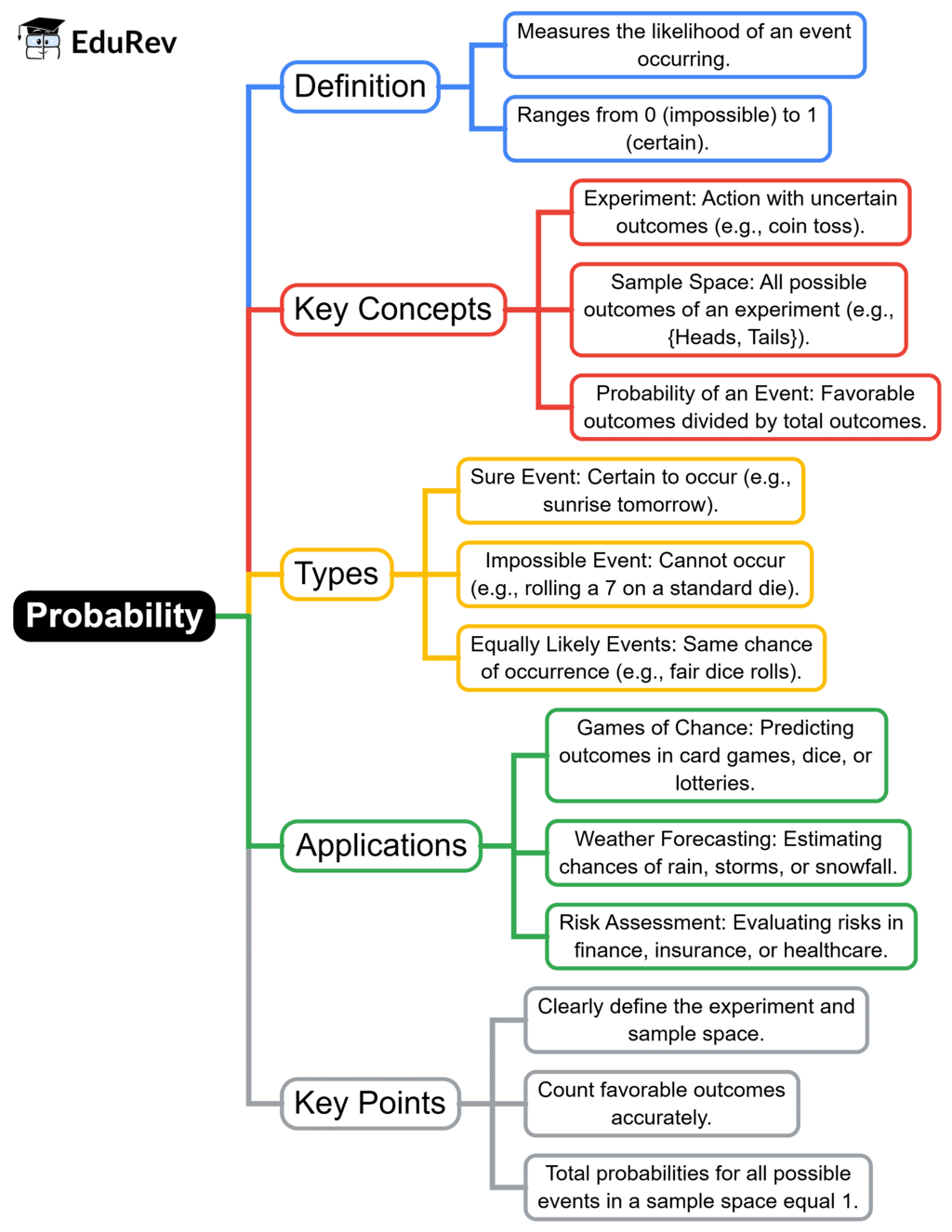
The document Mind Map: Probability | Mathematics (Maths) Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Mathematics (Maths) Class 10.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
127 videos|692 docs|84 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Probability - Mathematics (Maths) Class 10
| 1. What is the definition of probability in statistics? |  |
Ans. Probability is a branch of mathematics that deals with the likelihood or chance of different outcomes occurring in uncertain situations. It is quantified as a number between 0 and 1, where 0 indicates impossibility and 1 indicates certainty.
| 2. How do you calculate the probability of a single event? |  |
Ans. The probability of a single event can be calculated using the formula: P(E) = Number of favorable outcomes / Total number of possible outcomes. For example, if you roll a die, the probability of rolling a 3 is 1 (favorable outcome) divided by 6 (total outcomes), so P(3) = 1/6.
| 3. What is the difference between independent and dependent events in probability? |  |
Ans. Independent events are those whose outcomes do not affect each other, meaning the occurrence of one event does not influence the probability of the other. For instance, flipping a coin and rolling a die are independent. Dependent events, on the other hand, are those where the outcome of one event affects the outcome of another, such as drawing cards from a deck without replacement.
| 4. What is a probability distribution and why is it important? |  |
Ans. A probability distribution is a mathematical function that describes the likelihood of obtaining the possible values that a random variable can take. It is important because it provides a comprehensive picture of the outcomes of a random experiment and allows researchers to make informed predictions about future events.
| 5. Can you explain the Law of Large Numbers in probability? |  |
Ans. The Law of Large Numbers states that as the number of trials or experiments increases, the average of the results will get closer to the expected value or the theoretical probability. This principle assures that with a significant number of trials, the empirical probability will converge towards the theoretical probability.
Related Searches
















