Macronutrients: Carbohydrates | Food & Nutrition for Year 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Sources of Carbohydrates |

|
| Carbohydrate Deficiency and Excess |

|
| Dietary Reference Values |

|
| Forms of Carbohydrates |

|
Introduction
Carbohydrates are biological molecules encompassing simple sugars, starches, and dietary fiber, serving primarily as the body’s energy source. They contain glucose, released during digestion and utilized in cellular respiration. As the preferred energy source for cells, carbohydrates help preserve other energy sources, such as proteins, by reducing the need to break them down.
Sources of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are found in foods rich in sugars, starches, or fiber, including:
- Fruits
- Cakes
- Breads
- Potatoes
- Vegetables
Carbohydrate Deficiency and Excess
Carbohydrates are vital for energy production, and imbalances in intake can lead to health issues. A diet low in carbohydrates may cause:
- Symptoms of low blood sugar, such as tiredness, hunger, and dizziness
- Breakdown of muscle proteins to produce glucose, leading to muscle loss even in protein-rich diets
- Insufficient dietary fiber, increasing risks of constipation and bowel cancer
Excessive carbohydrate consumption can also be problematic, leading to:
- Weight gain and obesity from high sugar intake, which elevates heart disease risk
- Blood sugar fluctuations, potentially causing type 2 diabetes
- Tooth decay linked to excessive sugar
- Overconsumption of fiber, which may hinder iron and calcium absorption, causing mineral deficiencies
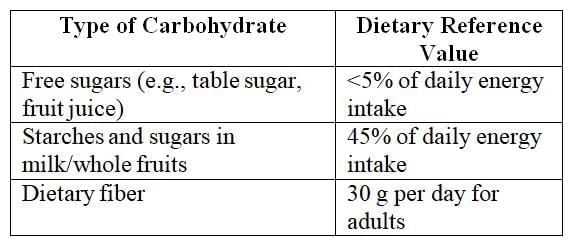
Dietary Reference Values
According to dietary reference values, half of the body's energy intake should come from carbohydrates. The majority of this 50% should be from starchy foods, with free sugars (such as those in refined sugar and fruit juice) contributing no more than 5%.
Forms of Carbohydrates
Sugars
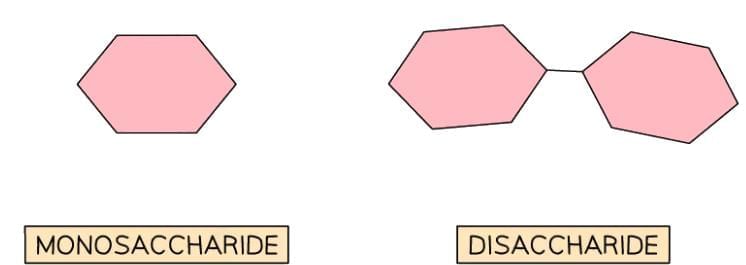
Sugars, or simple carbohydrates, include monosaccharides and disaccharides. Monosaccharides, single sugar molecules, are quickly absorbed without digestion. Examples include:
- Glucose
- Fructose
Disaccharides, composed of two monosaccharides, require digestion to break down into absorbable forms. Examples include:
- Sucrose (found in table sugar varieties like caster and granulated)
- Lactose (in milk)
- Maltose (in cereals)
Monosaccharides and disaccharides diagram
Due to their rapid absorption, sugars can spike blood sugar levels, which may be beneficial during activities like sports but can cause health issues if frequent. Dietary sugar sources include:
- Fruits and fruit juices
- Honey
- Refined sugar products (e.g., granulated sugar, golden syrup)
- Dairy products (e.g., milk, yogurt)
- Cereals
- Confectionery (e.g., biscuits, chocolate)
- Jams
- Soft drinks
- Sauces (e.g., ketchup)
- Soups
Starches
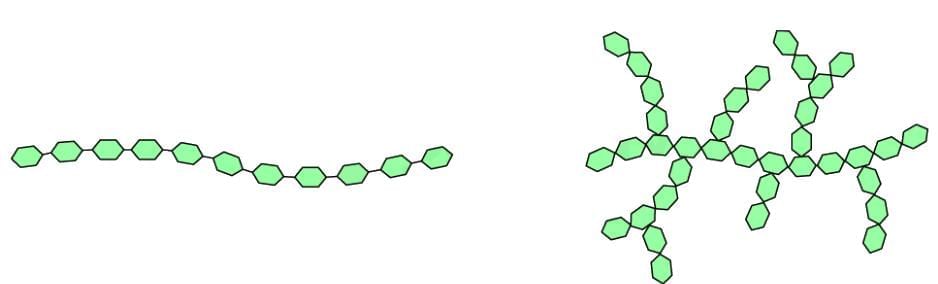
Starches, classified as polysaccharides, consist of long glucose chains linked by chemical bonds. These bonds require breakdown during digestion, slowing the release of glucose into the bloodstream. Hence, starch is considered a slow-release carbohydrate.
Polysaccharide diagram
Starches are derived solely from plant sources, as plants store their sugars as starch. Examples include:
- Root vegetables, such as potatoes and sweet potatoes
- Bread
- Pasta
- Cereals
- Lentils and beans
Dietary Fiber
Dietary fiber, a polysaccharide called cellulose, is found in plant cell walls and is indigestible by humans. It provides benefits such as:
- Slowing digestion, promoting fullness, and reducing snacking
- Absorbing water to ease food movement through the intestines, preventing constipation
- Lowering the risk of bowel cancer
High-fiber foods include:
- Wholegrain products (e.g., bran cereal, wholegrain bread)
- Fruits and vegetables
- Brown rice
- Oats
- Nuts
- Legumes (e.g., beans, lentils)
FAQs on Macronutrients: Carbohydrates - Food & Nutrition for Year 6
| 1. What are the main sources of carbohydrates in our diet? |  |
| 2. What happens if there is a deficiency of carbohydrates in the body? |  |
| 3. What are the consequences of excess carbohydrate intake? |  |
| 4. What are dietary reference values for carbohydrates? |  |
| 5. What are the different forms of carbohydrates? |  |














