MCQ (Solution) - Nature of Matter: Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures | Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Question 1:
Which description correctly defines a mixture in scientific terms?
Option A: A combination of substances where each component retains its own properties and no chemical reaction occurs
Option B: A single substance with a fixed composition that cannot be separated physically
Option C: Any item labeled “pure” in shops
Option D: A substance formed only when elements react in fixed ratios
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option A
Solution:
- A mixture forms when two or more pure substances are combined without chemical change, so each component keeps its identity and can often be separated by physical methods.
- Examples include air, seawater, sprout salad, sugar solution, and alloys like brass and stainless steel.
- Why others are incorrect: B describes pure substances (elements/compounds); C is marketing language and may still be a mixture (e.g., “pure” milk); D describes compounds, not mixtures.
Question 2:
Air is best classified as:
Option A: A pure compound because nitrogen and oxygen are bonded
Option B: A uniform (homogeneous) mixture of gases with variable pollutants
Option C: A non-uniform (heterogeneous) mixture because dust is visible
Option D: A single element because it is mostly nitrogen
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- The main gaseous components (N₂, O₂, Ar, CO₂, water vapour) are uniformly mixed, making air a homogeneous mixture; suspended dust/soot are pollutants, not integral parts.
- Composition can vary with humidity and pollution, consistent with a mixture rather than a compound.
- Why others are incorrect: A requires chemical bonding and fixed composition; C confuses transient particulates with the underlying uniform gas mixture; D confuses predominance with purity.
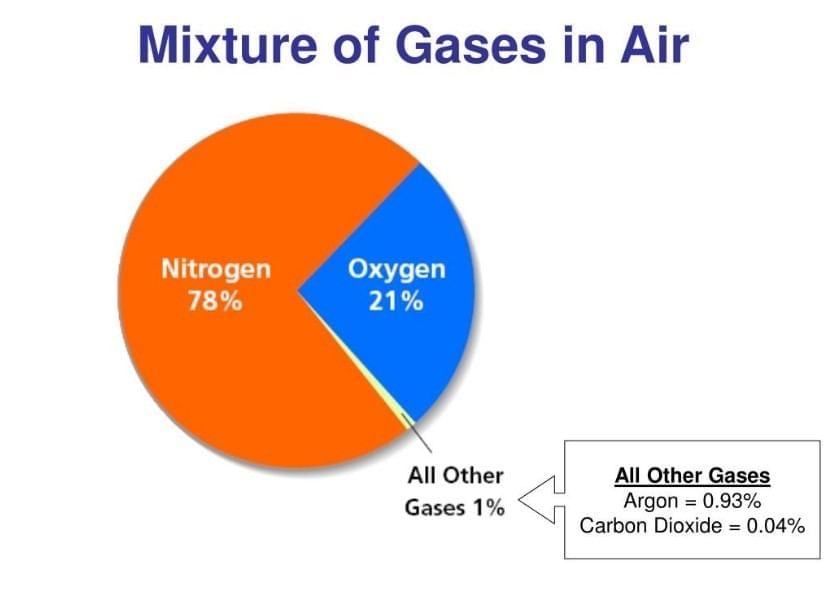
Question 3:
Which set contains only pure substances as defined in science?
Option A: Milk, seawater, air, soil
Option B: Fruit juice, muddy water, deodorant spray, soil
Option C: Brass, bronze, stainless steel, baking powder
Option D: Iron, oxygen, carbon dioxide, sodium chloride
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option D
Solution:
- Iron and oxygen are elements; carbon dioxide and sodium chloride are compounds—each has fixed composition throughout and cannot be separated by physical methods.
- Why others are incorrect: A, B, and C list mixtures (solutions, alloys, suspensions, propellant+solute systems).
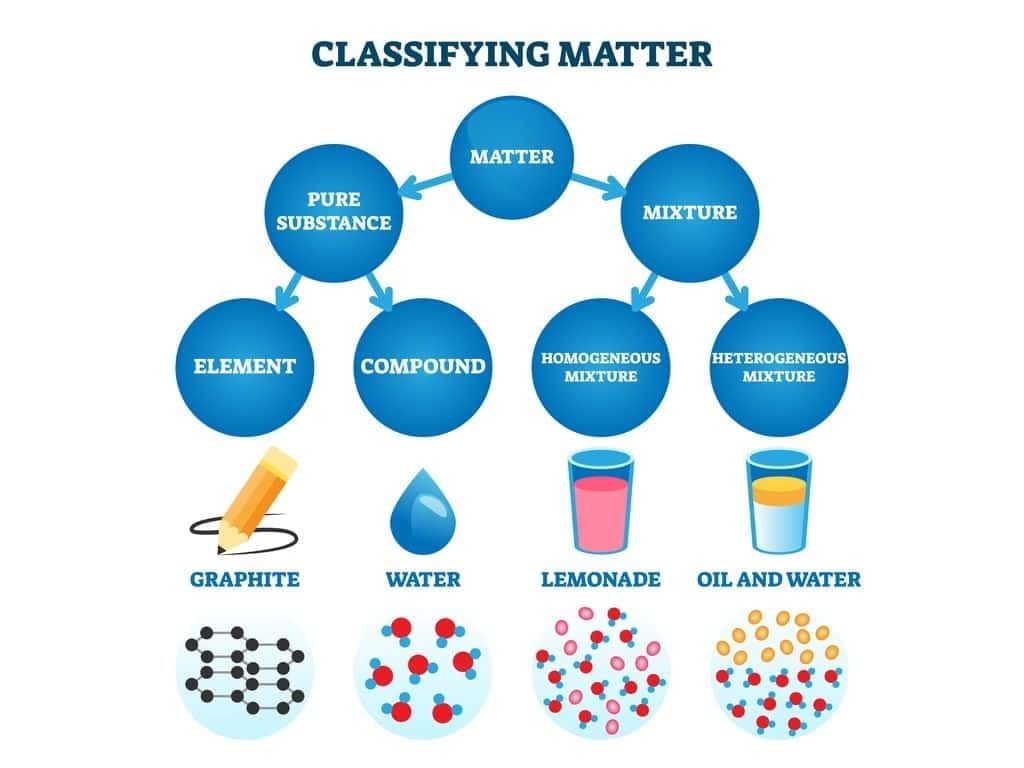
Question 4:
During electrolysis of water, the gases collected at the electrodes are in the volume ratio:
Option A: 1:1 hydrogen:oxygen
Option B: 2:1 hydrogen:oxygen
Option C: 1:2 hydrogen:oxygen
Option D: Only water vapour is formed
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Water (H₂O) decomposes to hydrogen and oxygen; twice as much hydrogen forms compared to oxygen by volume, reflecting the 2:1 atomic ratio.
- Hydrogen gives a ‘pop’ with a flame; oxygen supports brightening of a glowing splint/ flame.
- Why others are incorrect: A/C contradict stoichiometry; D is false—electrolysis yields H₂ and O₂, not vapour condensation.
Question 5:
Which statement best distinguishes an element from a compound?
Option A: Elements contain identical atoms; compounds contain fixed ratios of different elements chemically combined
Option B: Elements are separated by filtration; compounds by evaporation
Option C: Elements and compounds are both mixtures
Option D: Compounds always resemble their constituent elements
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option A
Solution:
- An element is made of one kind of atom; compounds form when different elements combine in fixed ratios with new properties and need chemical methods for decomposition.
- Why others are incorrect: B confuses physical separations; C misclassifies; D is false (e.g., NaCl vs metallic sodium and chlorine gas).
Question 6:
Stainless steel is classified as a mixture (alloy) because:
Option A: It has a fixed chemical formula of FeCrNiC
Option B: It is a homogeneous solid solution of metals (Fe, Cr, Ni) with small carbon, not a single compound
Option C: It is 100% iron with better polishing
Option D: It is a non-metallic ceramic
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Alloys are homogeneous mixtures whose composition can vary to tune properties; components are uniformly distributed without forming a single fixed-stoichiometry compound.
- Why others are incorrect: A implies fixed stoichiometry; C and D misidentify the material.
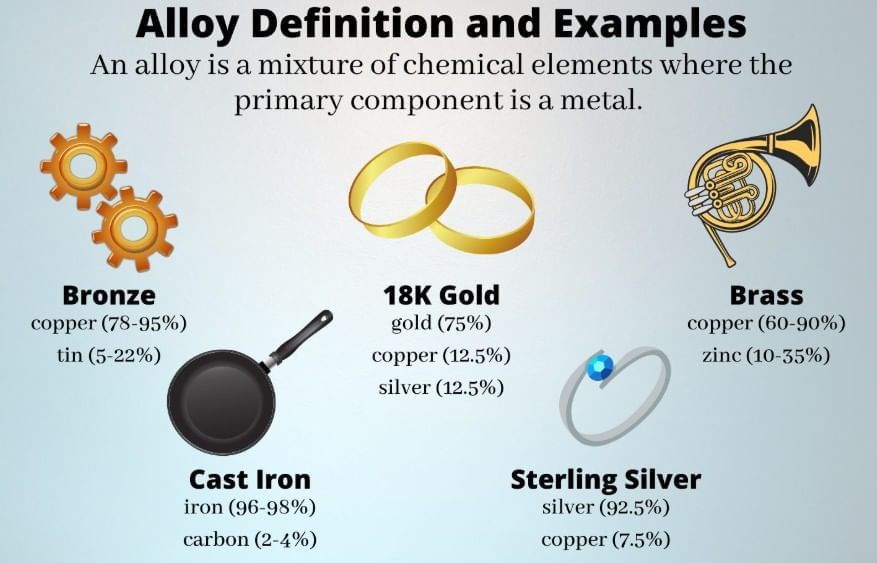
Question 7:
Which pairing correctly matches the mixture type, an example, and its uniformity?
Option A: Solid–solid mixture → brass → uniform
Option B: Liquid–liquid mixture → oil and water → uniform
Option C: Gas–liquid mixture → muddy water → uniform
Option D: Solid–gas mixture → smoke-free air → non-uniform
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option A
Solution:
- Brass (Cu+Zn) is a homogeneous solid solution (uniform alloy).
- Why others are incorrect: B oil and water are heterogeneous; C muddy water is solid–liquid heterogeneous; D smoke-free air is gas–gas homogeneous.
Question 8:
Which statement about “pure” on food labels vs scientific purity is correct?
Option A: “Pure” always means a single substance scientifically
Option B: In science, pure means one kind of particle only; “pure” milk or ghee can still be mixtures of many substances
Option C: Science does not classify foods
Option D: All edible products are elements
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Scientific purity requires one substance with identical particles; everyday “pure” often means unadulterated but may contain multiple components (e.g., fats, proteins, water).
- Why others are incorrect: A is not generally true for consumer labels; C/D are incorrect generalizations.
Question 9:
Why is water a compound whereas an unreacted blend of hydrogen and oxygen would be a mixture?
Option A: Water can be filtered into hydrogen and oxygen easily
Option B: Water has chemically bonded elements in a fixed 2:1 ratio and new properties; an unreacted blend lacks bonding and retains component properties
Option C: Hydrogen and oxygen are solids at room temperature
Option D: Mixtures always share the same properties as water
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Compounds form via chemical combination with fixed ratios and unique properties; physical mixing does not create bonds, so the blend remains gases with original properties.
- Why others are incorrect: A is false; C is wrong at room conditions; D contradicts definitions.
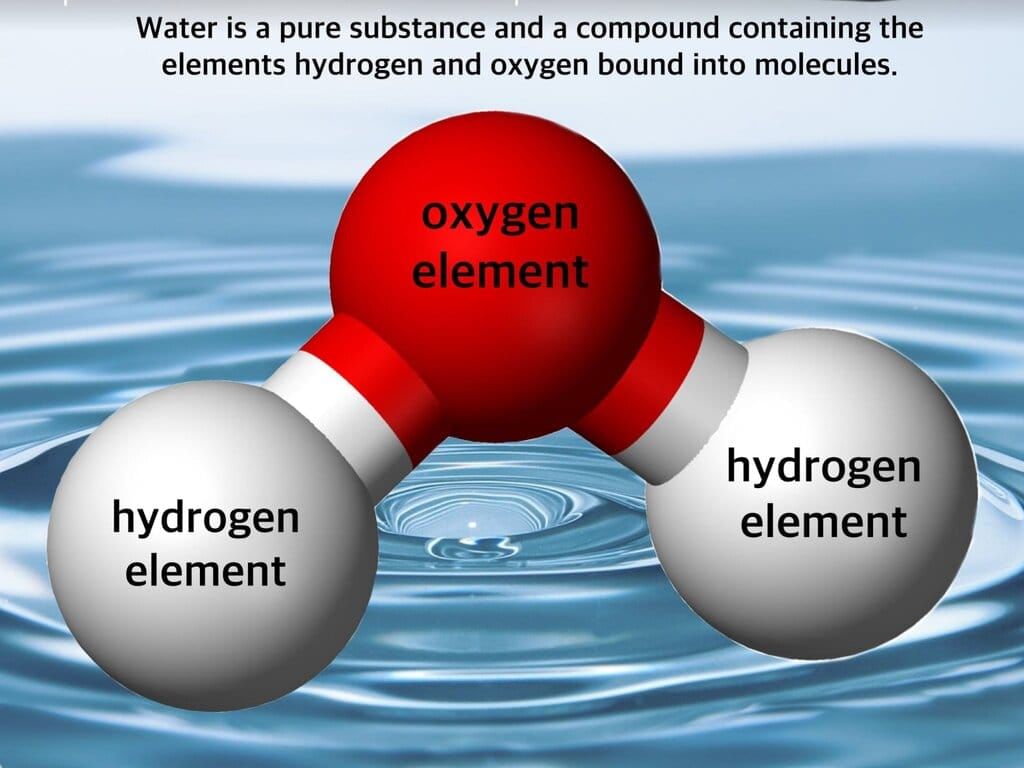
Question 10:
Which observation proves Sample B (from heating iron + sulfur) is a compound, not a mixture?
Option A: It is uniformly black
Option B: It is still attracted to a magnet
Option C: It is not attracted to a magnet and releases a rotten-egg smelling gas with dilute HCl
Option D: Iron and sulfur can be separated by sieving
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option C
Solution:
- Formation of iron sulfide (FeS) yields new properties: non-magnetic and evolves H₂S (rotten egg odour) with dilute HCl—evidence of a new chemical substance.
- Why others are incorrect: A alone is insufficient; B matches the mixture (iron magnetic), not the compound; D applies to mixtures, not compounds.
Question 11:
Which list correctly classifies items as elements, compounds, or mixtures?
Option A: Elements—water, nitrogen, iron, air
Option B: Pure substances—CO₂, iron, oxygen, sugar
Option C: Uniform mixtures—minerals, seawater, bronze, air
Option D: Non-uniform mixtures—air, sand, brass, muddy water
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- CO₂ (compound), iron (element), oxygen (element), sugar (compound) are pure substances in the scientific sense.
- Why others are incorrect: A wrongly lists water/air as elements; C “minerals” are mostly compounds/mixtures, not necessarily uniform; D air and brass are homogeneous, not non-uniform.
Question 12:
Which statement accurately describes minerals?
Option A: Minerals are only pure elements found in rocks
Option B: Minerals are natural solids with fixed composition; most are compounds, some are native elements
Option C: Minerals are man-made alloys
Option D: Minerals are any dissolved substances in water
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option B
Solution:
- Minerals like quartz, calcite, mica are compounds; native minerals like gold/sulfur are pure elements; all are naturally occurring solids with definite composition.
- Why others are incorrect: A ignores compound minerals; C/D misdefine minerals.

Question 13:
Which row shows a correct “type → example → separation possibility (physical)”?
Option A: Mixture → seawater → can separate salt by evaporation
Option B: Compound → sodium chloride → separate Na and Cl by filtration
Option C: Element → oxygen → separate into smaller substances by decantation
Option D: Compound → water → separate into H₂ and O₂ by sieving
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option A
Solution:
- Mixtures can be separated by physical methods (e.g., evaporating water from seawater leaves salt).
- Why others are incorrect: Compounds need chemical methods (not filtration/decantation/sieving) to break into elements; elements cannot be broken down chemically.
Question 14:
Which scenario aligns with using matter to address environmental challenges as highlighted?
Option A: Developing a carbon-based aerogel that absorbs oil efficiently due to high porosity
Option B: Mixing random elements for instant medicines
Option C: Replacing water with H₂/O₂ gas mix for safety
Option D: Calling air a compound to regulate emissions
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option A
Solution:
- Graphene aerogel is an engineered material with extreme lightness and porosity, suitable for cleaning oil spills—an example of applying compounds/mixtures to environmental problems.
- Why others are incorrect: B is unscientific; C is hazardous; D misclassifies air and offers no practical control mechanism.
Question 15:
Which conclusion about the iron–sulfur system is correct?
Option A: The unheated mixture (Sample A) is non-magnetic
Option B: The heated product (Sample B) shows the same properties as iron and sulfur
Option C: Sample A is a mixture whose components retain properties; Sample B is a compound with new properties and fixed composition
Option D: Both A and B can be separated by magnets
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer: Option C
Solution:
- Sample A (iron + sulfur) is heterogeneous; iron is separable by magnet and reacts with dilute HCl to give H₂; sulfur remains unreacted in HCl; Sample B (FeS) is non-magnetic and gives H₂S with dilute HCl—clear new properties and fixed composition.
- Why others are incorrect: A false—iron in A is magnetic; B false—properties change; D only A is separable by magnet, B is not.
|
54 videos|234 docs|13 tests
|
FAQs on MCQ (Solution) - Nature of Matter: Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures - Science Curiosity Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What is the difference between an element, a compound, and a mixture? |  |
| 2. How are compounds formed from elements? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of mixtures, and how can they be separated? |  |
| 4. What role do elements play in forming compounds? |  |
| 5. Can mixtures have varying compositions, and what does this mean for their properties? |  |
















