Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Question Answers - Atoms and Molecules
Q1: Glucose has the molecular formula C6H12O6. Calculate :
(a) Its molecular mass.
(b) The number of atoms in one molecule of glucose.
(c) The number of gram molecules in 18 g of glucose.
Ans: The molecular mass of a compound is the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms present in its molecular formula.
(a) Molecular mass of C6H12O6
= (6 × 12u) + (12 × 1u) + (6 × 16u)
= 72u + 12u + 96u = 180u
(b) The number of atoms in one molecule of C6H12O6
= 6 atoms of C + 12 atoms of H + 6 atoms of O
= 6 + 12 + 6 = 24 atoms
(c) Number of gram molecules
= Mass of glucose (g) / Molecular mass of glucose (g)
= 18 g / 180 g/mol
= 0.1 mol
Q2: What is the use of the mole concept in chemistry?
Ans: The mole concept is extremely useful in chemistry for quantitative analysis:
- It allows chemists to count atoms, molecules, or ions using mass.
- One mole of any substance contains 6.022 × 1023 particles (Avogadro's number).
- One mole of any gas occupies 22.4 litres at standard temperature and pressure (STP).
- It helps in calculating reactants and products in chemical reactions through balanced equations.
- It is used to determine molar mass and establish relationships between mass, volume, and number of particles.
Q3: Give symbol and valency of: Potassium, Barium, Aluminium, Calcium, Cobalt, Fluorine, Lead, Zinc, Iodine, Sulphide.
Ans: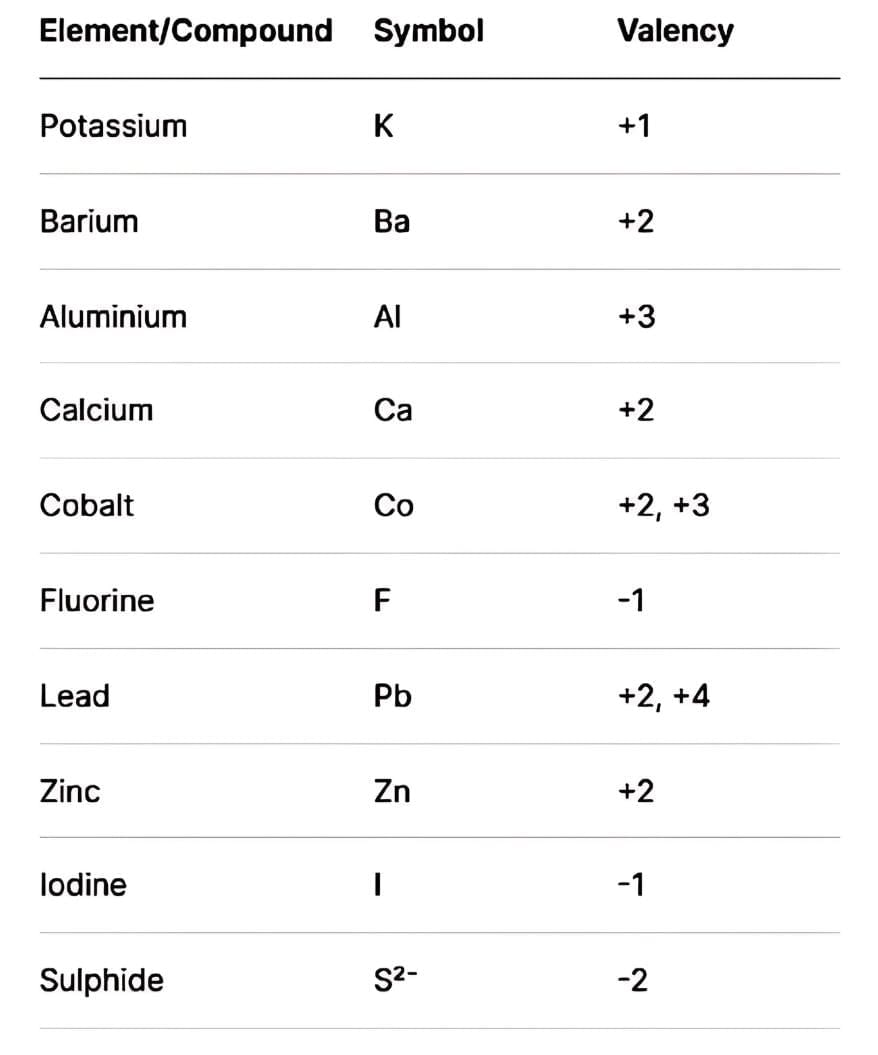
Q4: In a reaction, 6.83 g of lead chloride precipitated. The initial solution had 5 g each of lead nitrate and sodium chloride. What is the amount of sodium nitrate formed?
Ans: Initially, we have:
50 g of 10% lead nitrate solution = 5 g Pb(NO3)2 + 45 g water
50 g of 10% sodium chloride solution = 5 g NaCl + 45 g water Total mass before reaction = 5 g + 5 g + 90 g water = 100 g
After reaction, 6.83 g of lead chloride (PbCl2) precipitates out. Assuming no mass is lost, Total mass after = 100 g Remaining components (water and NaNO3) = 100 – 6.83 = 93.17 g
Water is 90 g, so: Mass of sodium nitrate formed = 93.17 – 90 = 3.17 g
Q5: Write a formula for the following :
(a) Zinc sulphate,
(b) Methane,
(c) Ammonium carbonate.
Ans:
(a) Zinc sulphate 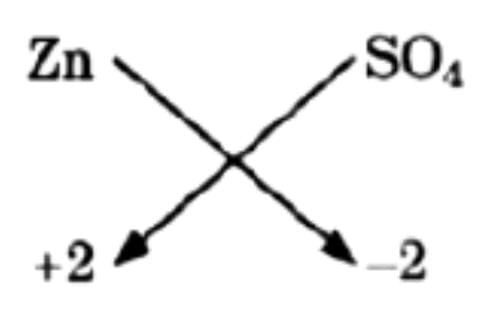
Thus, Zn2(SO4)2 and finally = ZnSO4
(b) Methane
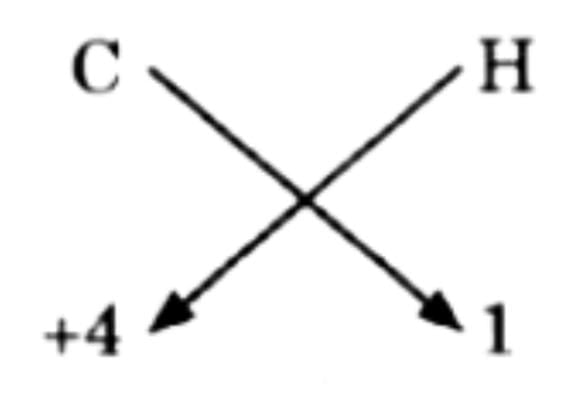
Thus, finally = CH4
(c) Ammonium carbonate
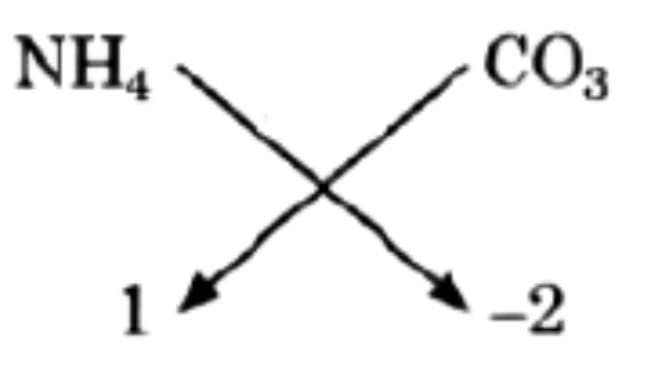 Thus, finally = (NH4)2CO3
Thus, finally = (NH4)2CO3
Q6: Explain the law of multiple proportions.
Ans: According to the law of multiple proportions, when two elements combine to make one or more compounds, then the ratio of weights of these elements remains in a fixed ratio to one another.
For example: Hydrogen and oxygen combine to form water (H2O) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) under different conditions. 2 grams of hydrogen combine with 16 grams of oxygen in the case of water, while 2 grams of hydrogen combine with 32 grams of oxygen to form hydrogen peroxide. Now, the weights of oxygen combine with a fixed weight of hydrogen in water and hydrogen peroxide, respectively ,are 16 and 32, which are in a simple ratio of 16: 32 or 1 : 2.
Q7: What are molecules? Give a brief explanation of the arrangement of the constituent atoms in the molecules.
Ans: A molecule is the smallest particle of an element or compound which is stable under normal conditions. And it can freely show all the properties of that element or compound. It may be made up of one, two or more atoms. A molecule with one atom is called a monoatomic molecule.
E.g. helium, neon, etc.
A molecule with two atoms is called a diatomic molecule. E.g. Cl2, O2.
Similarly, there are molecules containing three atoms (CO2), four atoms (P4) and so on.
Q8: The mass of one molecule of a substance is 4.65 × 10-23 grams. What is its molecular mass?
Ans: Mass of 1 molecule of a substance = 4.65 × 10-23 grams
Mass of 6.023 × 1023 molecules of a substance
= 4.65 × 10-23 × 6.023 × 1023
= 28 g/mol
Molecular mass of the substance = 28 g/mol
Q9: An element 12X24 loses two electrons to form a cation, which combines with the anion of element 17Y35 formed by gaining an electron.
(a) Write the electronic configuration of element X.
(b) Write the electronic configuration of the anion of element Y.
(c) Write the formula for the compound formed by the combination of X and Y.
Ans:
(a) X = 2, 8, 2
(b) Y– = 2, 8, 8
(c) XY2
Q10: Calculate the formula unit masses of ZnO, Na2O, K2CO3 given atomic masses of Zn = 65u, Na = 23u, K = 39u, C = 12u, and 0 = 16u.
Ans: Formula unit mass of ZnO = 1 × 65u + 1 × 16u = 81u
Formula unit mass of Na2O = 2 × 23u + 1 × 16u = 62u
Formula unit mass of K2CO3 = 2 × 39u + 1 × 12u + 3 × 16u = 138u
Q11: What is the mass of :
(a) 1 mole of nitrogen atoms?
(b) 4 moles of aluminium atoms (atomic mass of aluminium = 27)?
(c) 10 moles of sodium sulphite (Na2SO3)?
Ans:
(a) 1 mole of nitrogen atoms
= 1 × gram atomic mass of nitrogen atom
= 1 × 14 g = 14 g
(b) 4 moles of aluminium atoms
= 4 × gram atomic mass of aluminium atoms
= 4 × 27 g = 108 g
(c) 10 moles of sodium sulphite (Na2SO3)
= 10 (2 × gram atomic mass of Na + 1 × gram atomic mass of sulphur + 3 × gram atomic mass of oxygen)
= 10 (2 × 23 g + 1 × 32 g + 3 × 16g)
= 10 (46 g + 32 g + 48 g)
= 10 × 126 g = 1260 g
Q12: Give the postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory.
Ans: John Dalton proposed his atomic theory in 1808. It explains the nature of matter in terms of atoms. The main postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory are:
- All matter is made up of indivisible particles called atoms.
- Atoms of a given element are identical in mass and properties.
- Atoms of different elements have different masses and chemical properties.
- Atoms combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds.
- Atoms can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
- The relative number and types of atoms in a given compound remain constant.
These postulates laid the foundation for modern chemistry, although some parts were later modified with the discovery of subatomic particles.
Q13: (a) Give one point of difference between an atom and an ion.
(b) Give one example each of a polyatomic cation and an anion.
(c) Identify the correct chemical name of FeSO3: Ferrous sulphate, Ferrous sulphide, Ferrous sulphite.
(d) Write the chemical formula for the chloride of magnesium.
Ans:
(a) An atom is a neutral particle containing equal numbers of protons and electrons. An ion is a charged particle formed when an atom loses or gains electrons. Positive ions are called cations, and negative ions are called anions.
(b) (i) Polyatomic cation: Ammonium ion, (NH4)+
(ii) Polyatomic anion: Sulphate ion, (SO4)2–
(c) FeSO3 contains Fe²⁺ and SO3²⁻ (sulphite ion), so the correct name is Ferrous sulphite.
(d) Magnesium has a valency of 2, and chlorine has a valency of 1. Therefore, the formula is MgCl2 (Magnesium chloride).
Q14: When 3.0 g of magnesium is burnt in 2.00 g of oxygen, 5.00 g of magnesium oxide is produced. What mass of magnesium oxide will be formed when 3.00 g of magnesium is burnt in 5.00 g of oxygen? Which law of chemical combination will govern your answer? State the law.
Ans: According to the given reaction: 3.00 g magnesium + 2.00 g oxygen → 5.00 g magnesium oxide. This shows that 3 g of magnesium reacts completely with 2 g of oxygen.
Now, when 3.00 g magnesium is burnt in 5.00 g oxygen, only 2 g of oxygen will be used (as per the fixed ratio), and 3 g of oxygen will remain unused.
So, mass of magnesium oxide formed = 3 + 2 = 5.00 g
Law involved: This illustrates the Law of Definite Proportions, which states that a chemical compound always contains the same elements in the same fixed ratio by mass.
Q15: (a) Calculate the number of molecules of SO2 present in 44 g of it.
(b) If one mole of oxygen atoms weighs 16 grams, find the mass of one atom of oxygen in grams.
Ans:
(a) Molecular mass of SO2 = Atomic mass of S + 2 × Atomic mass of O
= 32 + 2 × 16
= 64u
Molar mass = 64 g
Number of molecules, N = 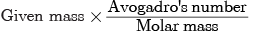
= 44/64 x 6.022 x 1023
= 4.14 × 1023 molecules
(b) One mole of oxygen contains 6.022 × 1023 atoms of oxygen
Mass of one atom of oxygen = 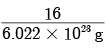
= 2.66 × 10–23 g
Q16: Sodium is represented as 23Na11.
(a) What is its atomic mass?
(b) Write its gram atomic mass.
(c) How many atoms of Na will be there in 11.5 g of the sample?
Ans:
(a) Atomic mass = 23u
(b) Gram atomic mass = 23 g
(c) Given mass = 11.5 g
Molar mass = 23 g Number of atoms (N) = 
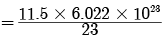
= 3.011 × 1023 atoms
|
84 videos|544 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Question Answers - Atoms and Molecules
| 1. What are atoms and how do they differ from molecules? |  |
| 2. How are elements organized in the periodic table? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of chemical bonds in the formation of molecules? |  |
| 4. What role do valence electrons play in chemical reactions? |  |
| 5. Can you explain the concept of isotopes and their significance? |  |





















