Laxmikant Summary: Goods and Services Tax Council | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Establishment |

|
| Vision and Mission |

|
| Composition |

|
| Working |

|
| Functions |

|
| Other Functions |

|
Establishment
 Goods And Services Tax Council
Goods And Services Tax Council Article 279-A of Indian Constitution
Article 279-A of Indian Constitution
- The Joint Amendment Act of 2016 allowed for a new tax system, known as the Goods and Services Tax (GST), to be implemented in the country.
- To ensure the proper management of this tax, there needs to be strong cooperation and coordination between the central government and the individual states.
- The amendment created a way for this consultation process by establishing a Goods and Services Tax Council, which is often referred to as the GST Council.
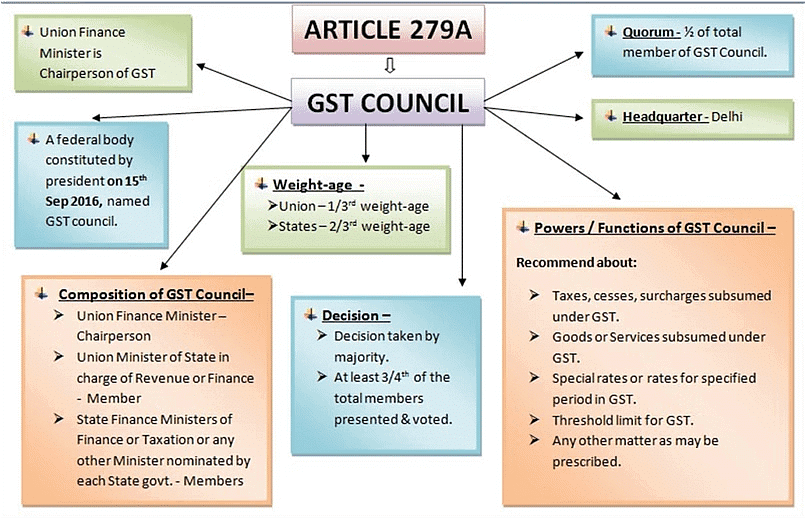
- This amendment added a new Article 279-A to the Constitution.
- This Article gives the President the power to form the GST Council by issuing an order.
- In 2016, the President used this authority to set up the Council.
- The Secretariat for the Council is based in New Delhi.
- The Union Revenue Secretary serves as the ex-officio Secretary to the Council.
Vision and Mission
- The Council, while performing its duties, should focus on creating a consistent structure for CST and developing a unified national market for goods and services.
- Additionally, the Council is responsible for setting the procedures for how it carries out its functions.
- The vision of the Council is to:
- Establish the highest standards of cooperative federation in how the Council operates.
- Serve as the first constitutional federal body with the authority to make all significant decisions related to CST.
- The mission of the Council is to:
- Develop a CST structure through extensive consultations.
- Create a framework that is driven by information technology and is user-friendly.
Composition
The Council is a group that includes members from both the central government and the states. Here are the key members:
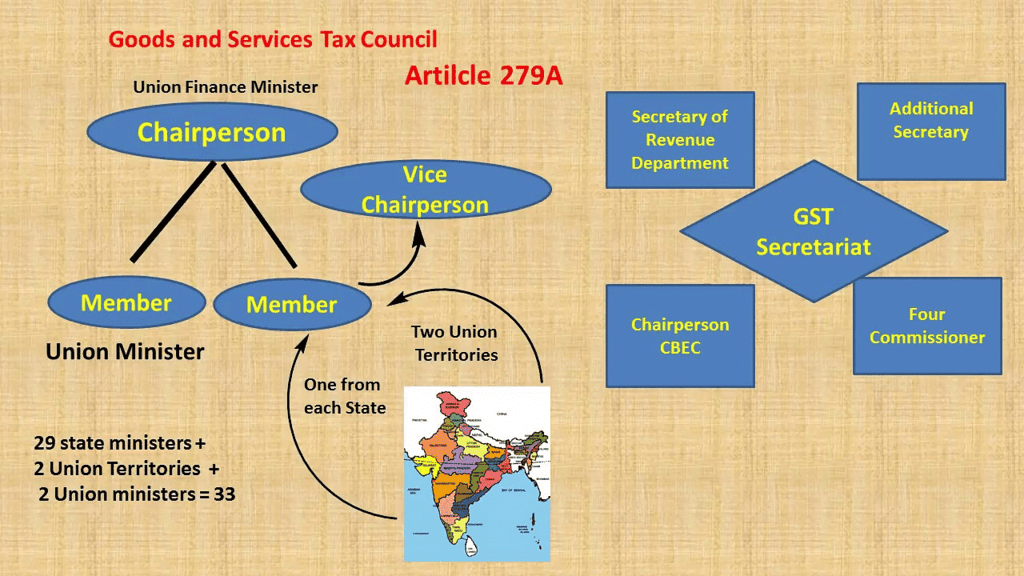
- Chairperson: The Union Finance Minister will serve as the Chairperson of the Council.
- Member: The Union Minister of State responsible for Revenue or Finance will also be a member.
- State Representation: Each state government will nominate a Minister responsible for Finance or Taxation, or any other Minister of their choice to be part of the Council.
- Vice-Chairperson: Members from the states will select one of their own to be the Vice-Chairperson of the Council.
- Term Decision: The members can decide on the term duration for the Vice-Chairperson.
- Permanent Invitee: The Union Cabinet has also decided that the Chairperson of the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) will be a permanent invitee (non-voting) to all Council meetings.
Working

- The decisions made by the Council occur during its meetings.
- A meeting requires a quorum, which is half of the total members of the Council.
- For any decision to be valid, it must be approved by a majority of at least three-fourths of the weighted votes from the members who are present and voting.
- The voting follows these principles:
- The vote from the central government carries a weight of one-third of the total votes cast during that meeting.
- The votes from all the state governments combined account for two-thirds of the total votes cast at that meeting.
- Any actions or proceedings of the Council remain valid despite the following issues:
- Any vacancy or issue in the Council's formation.
- Any problem related to the appointment of a member of the Council.
- Any procedural mistakes made by the Council that do not impact the essence of the case.
Functions
- The Council needs to provide suggestions to the central and state governments on several important topics:
- Determine the taxes, cesses, and surcharges imposed by the central government, state governments, and local authorities that should be included in the Goods and Services Tax (GST).
- Identify which goods and services will be subject to GST and which ones will be exempt from it.
- Develop Model GST Laws and establish the rules for how GST is applied, shared in cases of interstate trade, and the criteria for defining the place of supply.
- Set the threshold limit for turnover, below which certain goods and services may be exempt from GST.
- Decide on the GST rates, including minimum rates and bands for GST.
- Establish any special rate or rates for a specific time to gather extra funds during natural disasters or emergencies.
- Make special provisions for the states of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Jammu and Kashmir, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura, Himachal Pradesh, and Uttarakhand.
- Address any other issues related to GST that the Council may choose to discuss.
Other Functions
In addition to its main responsibilities, the Council has some other important functions:
- The Council will suggest a date for when GST can be applied to petroleum crude, high-speed diesel, motor spirit (petrol), natural gas, and aviation turbine fuel.
- If there is a disagreement regarding the recommendations or how they are carried out, the Councilwill set up a way to resolve the issue:
- Between the central government and one or more states.
- Between the central government and any state or states on one side and one or more other states on the other side.
- Between two or more states.
- The Council must also suggest how to provide compensation to the states for any loss of revenue due to the introduction of GST for a period of five years.
- Based on this suggestion, the Parliament will decide on the compensation.
- As a result, the Parliament created the law in 2017.
|
154 videos|973 docs|260 tests
|
FAQs on Laxmikant Summary: Goods and Services Tax Council - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the main purpose of the Goods and Services Tax Council? |  |
| 2. Who are the members of the Goods and Services Tax Council? |  |
| 3. How does the Goods and Services Tax Council function? |  |
| 4. What are the key functions of the Goods and Services Tax Council? |  |
| 5. What role does the Goods and Services Tax Council play in resolving disputes related to GST? |  |




















