Important Questions: Diversity in the Living World | Science for Class 6 PDF Download
Q1: What is biodiversity?
a) The variety of rocks in an area
b) The variety of plants, animals, and living organisms in a region
c) The variety of weather patterns
d) The variety of soils
Answer: b
Q2: Which type of venation is common in monocot plants like grass?
a) Reticulate venation
b) Parallel venation
c) Spiral venation
d) Circular venation
Answer: b
Q3: Which animal is an amphibian that lives both on land and in water?
a) Lion
b) Frog
c) Eagle
d) Snake
Answer: b
Q4: What is the main function of a plant’s stem?
a) To produce seeds
b) To provide structure and support
c) To absorb water
d) To attract pollinators
Answer: b
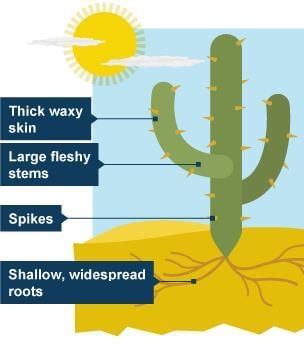
Q5: Which plant adaptation helps cacti survive in deserts?
a) Broad leaves
b) Thick, fleshy stems to store water
c) Long, thin roots
d) Bright flowers
Answer: b
Q6: Which animal is a herbivore?
a) Lion
b) Crow
c) Cow
d) Snake
Answer: c
Q7: What type of root system is typically found in dicot plants like chickpeas?
a) Fibrous roots
b) Taproots
c) Aerial roots
d) Prop roots
Answer: b
Q8: Which project was launched in 1973 to protect Bengal tigers?
a) Cheetah Reintroduction Project
b) Project Tiger
c) Sacred Groves Initiative
d) Great Indian Bustard Conservation
Answer: b
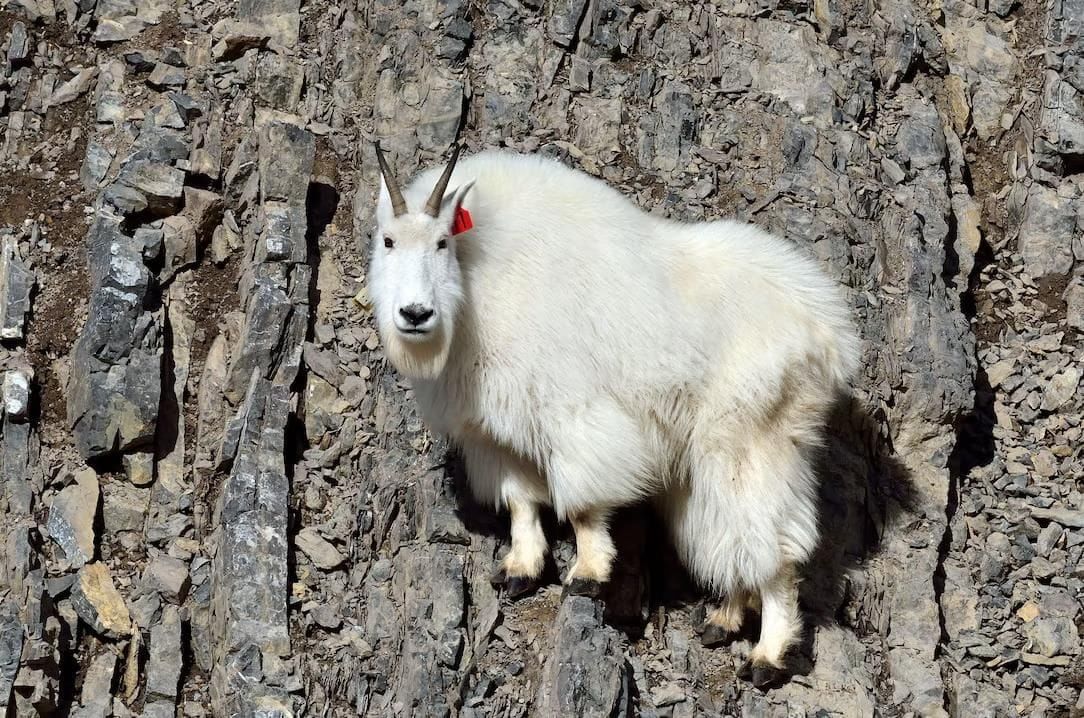
Q9: What is the habitat of a mountain goat?
a) Desert
b) Ocean
c) Mountain
d) Grassland
Answer: c
Q10: Which flower is known for its bright colors and grows in the Nilgiris and Sikkim?
a) Hibiscus
b) Jasmine
c) Rhododendron
d) Rose
Answer: c
Q11: Define biodiversity and give one example of it.
Answer: Biodiversity is the variety of plants, animals, and other living organisms in a region. An example is a forest with different trees, birds, and insects living together.
Q12: What is the difference between reticulate and parallel venation in leaves?
Answer: Reticulate venation has veins forming a net-like pattern, common in dicot plants like mango. Parallel venation has veins running parallel to each other, common in monocot plants like grass.
Q13: Name two types of plant roots and give one example for each.
Answer: 1. Taproots: Carrot.
2. Fibrous roots: Wheat.
Q14: What are adaptations, and give one example for a plant and an animal.
Answer: Adaptations are special features or behaviors that help living things survive in their environment. Example: Cactus has thick stems to store water (plant); camels have humps to store fat (animal).
Q15: What is a sacred grove, and why is it important?
Answer: A sacred grove is a forest patch protected by local communities, preserving diverse plants and animals. It is important for conserving biodiversity and medicinal plants.
Q16: Describe how plants are grouped based on their height and stems, with examples.
Answer: Plants are grouped based on height and stems to understand their characteristics:
- Height and Stems:
- Trees: Tall plants with hard, woody stems and branches starting high, e.g., mango, banyan.
- Shrubs: Shorter than trees with multiple woody stems branching near the ground, e.g., rose, lemon.
- Herbs: Small plants with soft, green stems, e.g., coriander, wheat.
- Climbers: Plants with weak stems that climb using tendrils, e.g., grapevine, pea plant.
- Creepers: Plants with fragile stems that creep on the ground, e.g., watermelon, pumpkin.
These groupings help identify plants’ growth patterns and their roles in ecosystems, like providing shade (trees) or ground cover (creepers).
Q17: Explain how animals adapt to different habitats, with examples from deserts and oceans.
Answer: Animals adapt to their habitats with special features or behaviors to survive:
- Deserts: Camels have humps to store fat for energy, long legs to walk on hot sand, and wide hooves to prevent sinking, allowing them to survive without water for days.
- Oceans: Fish have streamlined bodies for easy swimming, fins for movement, and gills to breathe underwater, enabling them to thrive in aquatic environments.
These adaptations ensure animals can find food, stay safe, and live in their specific habitats, like the dry desert or watery ocean, contributing to biodiversity.
Q18: Discuss the importance of protecting biodiversity and mention two government initiatives in India for conservation.
Answer: Protecting biodiversity is crucial because it maintains ecosystem balance, providing food, shelter, and resources for plants, animals, and humans. For example, trees offer homes for birds, and animals like bees pollinate crops. Loss of biodiversity due to habitat destruction reduces these benefits, threatening species like the Bengal tiger. In India, two government initiatives for conservation are:
- Project Tiger (1973): Protects Bengal tigers by preserving their forest habitats.
- Cheetah Reintroduction Project (2022): Aims to restore cheetah populations by reintroducing them to suitable habitats.
These efforts, along with protecting areas like sacred groves, help conserve biodiversity for future generations.
|
70 videos|334 docs|27 tests
|
FAQs on Important Questions: Diversity in the Living World - Science for Class 6
| 1. What is biodiversity and why is it important in the living world? |  |
| 2. How do scientists classify living organisms? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of ecosystems and their significance? |  |
| 4. What is the role of conservation in maintaining biodiversity? |  |
| 5. How do human activities impact biodiversity? |  |