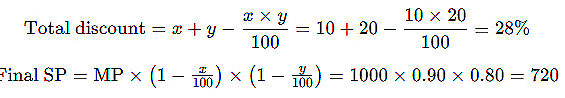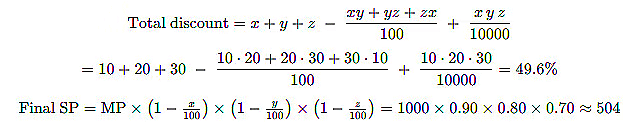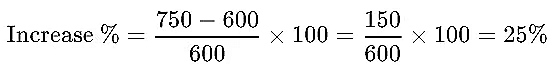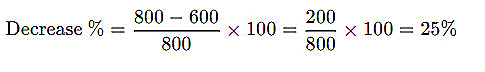Important Formulas: Profit and Loss | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Formulas for Profit and Loss |

|
| Successive Discount Formula |

|
| Increase and Decrease Percentage Problem |

|
| Solved Examples |

|
This document provides essential formulas for calculating profit and loss in transactions. It covers the basics of Cost Price, Selling Price, and the conditions for profit or loss.
Key formulas include those for calculating profit percentage, loss percentage, selling price, and cost price. Additionally, it explains how to calculate successive discounts and handle percentage increase and decrease problems.
These formulas are useful for anyone dealing with pricing, business transactions, or financial calculations.

Formulas for Profit and Loss
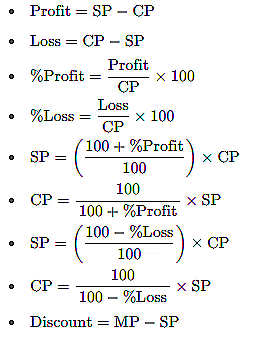
Cost Price – It is basically the price at which a commodity or object is bought at. e.g. Shopkeeper buying Sugar from a Farmer to sell in his grocery store. In its short form, it is denoted as C.P.
Selling Price – The price at which the commodity is sold at. e.g. Shopkeeper selling sugar to his customer. In its short form is denoted as S.P.
Gain or Profit – If the Cost Price is less than the Selling Price, gain is made.
Loss – If the Cost price is greater than the Selling price, Loss is incurred.
1. C.P in case of gain: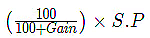
2. C.P in case of Loss: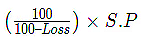 3. S.P in case of Gain:
3. S.P in case of Gain: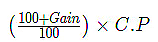
4. S.P in case of Loss: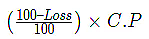
Important Formulas for Profit and Loss
Successive Discount Formula
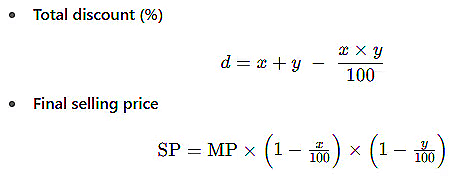
For three successive discounts of x%, y% and z% :
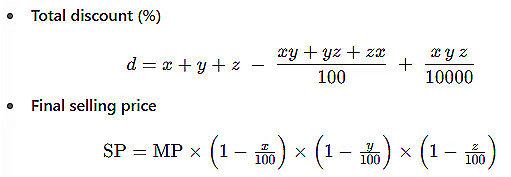
Example: The marked price of a shirt is Rs.1000. A shopkeeper offers 10% discount on this shirt and then again offers 20% discount on the new price. How much will you have to pay, finally?
Sol:
Case 2: If there are three discounts:
It means a discount on the discount on the discount. (Analogous to Compound Interest rate, which signifies interest on interest)
If there are three discounts, x%, y% and z%, then find the total discount of x % and y % first and, using it find the total discount with z %
Example: The marked price of a shirt is Rs.1000. A shopkeeper offers 10% discount on this shirt and then again offers 20% discount on the new price, and then and then again offers 30% discount on the new price . How much will you have to pay, finally?
Sol:
Increase and Decrease Percentage Problem
1. Percentage Increase
If a value rises from A to B, the percentage increase is 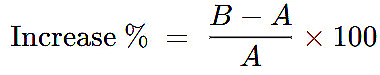
Example: A product’s price goes from $600 to $750. What is the percentage increase?
Ans:
Percentage Decrease
If a value falls from A to C, the percentage decrease is 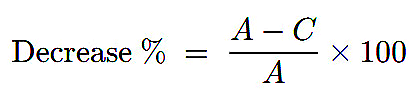
Example: A gadget’s price drops from $800 to $600. What is the percentage decrease?
Ans:
Solved Examples
Q1: A farmer buys 240 cows. He sells some of them at a gain of 20% and the remaining at a gain of 30%. If he gains 28% on the whole, then how many did he sell at a gain of 20%?
A. 40
B. 48
C. 54
D. 28
Sol: B
Ans:
Let him sell x cows at the gain of 20% and y cows at a gain of 30%.
Therefore, 0.2x + 0.3y = -0.28(x+y)
=> y=4x,
Therefore, x+4x=240
=>x=48.
Q2: I buy two horses, A and B. A costs Rs.50 more than B. I sell A at a profit of 16% and 13 at a profit of 7%. My total gain is Rs.100. What was the original price of 8?
A. Rs.450
B, Rs.400
C. Rs.350
D. Rs.500
Sol: B
Ans:
A = B + 50 ….(1)
1.16 A + 1.07 B = A + B + 100 …..(2)
=> A = Rs.450, B = Rs.400.
Q3: A shopkeeper purchases several articles at the rate of 11 for Rs.10 and sells them at the rate of 10 for Rs.11. What would be the profit earned by him?
A. 11%
B. 10%
C. 20%
D. 21%
Sol: D
Ans:
Cost Price for 11 articles = Rs.10 .... (I)
Sales Price for 10 articles = Rs.11 .... (II)
Sales Price for 11 articles = Rs.12.1 (III)
Thus, required profit = [(12.1-10)/10] x 100 = 21%.
Q4: Rakesh bought 20 chairs for Rs.1000. He repaired and sold them at the rate of Rs.500 per pair. He got profit of Rs.100 per chair. How much did he spend on repairs?
A. Rs.1500
B, Rs.2000
C. Rs.2500
D, Rs.1800
Ans:
Purchase price for 20 chairs=Rs. 1000
Repairs amount (to be determined) =Rs. X
Sales price for 20 chairs = Rs. 5000
Profit derived for 20 chairs = Rs. 2000
We have, (3) - [(1) + (2)] = (4).
? x 5000 - (1000 + X) = 2000
=> X = 2000
Q5: Kiran buys an article with 25% discount on the marked price. He makes a profit of 10% by selling it at Rs.660. What was the marked price?
A. Rs.900
B. Rs.60
C. Rs.700
D. Rs.800
Ans:
Let the marked price of the article be Rs. X
? Purchase Price (C.P) for Kiran = 0.75 X.
? S.P for Kiran = (0.75 X) + 10% of (0.75 X) = 660.
? 0.825 X = Rs.660
=> X = Rs.800
|
192 videos|840 docs|2223 tests
|
FAQs on Important Formulas: Profit and Loss - General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce
| 1. What is the formula for calculating profit? |  |
| 2. How can I calculate the loss percentage? |  |
| 3. What is the formula for calculating successive discounts? |  |
| 4. How do I calculate the increase percentage? |  |
| 5. How can I calculate the decrease percentage? |  |