Class 7 Social Science Chapter 7 HOTS Questions - The Gupta Era: An Age of Tireless Creativity
Q1: How did the decline of the Kushana Empire contribute to the rise of the Gupta Empire?
Ans:
- The decline of the Kushana Empire around the 3rd century CE created a power vacuum in the north and northwest of India.
- With the weakening of the Kushanas, the Gupta dynasty, originally a small local kingdom, had an opportunity to rise to power.
- By strategically conquering neighboring regions and forming alliances, the Guptas expanded their influence.
- The downfall of the Kushanas allowed the Guptas to establish a stable and prosperous empire, leading to the cultural and intellectual flourishing of the Gupta period.
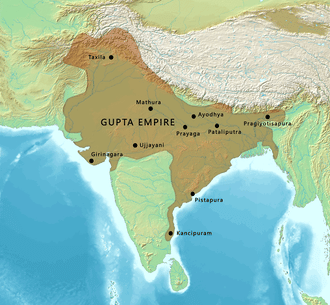 Gupta Empire
Gupta Empire
Q2: Compare the contributions of Samudragupta and Chandragupta II to the Gupta Empire in terms of military conquests and cultural achievements.
Ans:
- Samudragupta, the father of Chandragupta II, is known for his military conquests, which expanded the Gupta Empire through warfare and diplomacy.
- He unified a large portion of India, often allowing defeated kings to rule as tributaries.
- Chandragupta II, on the other hand, focused more on cultural achievements and consolidating the empire.
- While he continued his father’s military campaigns, he also promoted art, literature, and science.
- Under his reign, the empire saw the flourishing of Sanskrit literature, the construction of beautiful temples, and advancements in astronomy and mathematics.
Q3: How would you use the Gupta model of governance to address issues of central control and regional autonomy in a modern democratic state?
Ans:
- To apply the Gupta model of governance in a modern democratic state, I would focus on a strong central government that maintains overall control while allowing regional autonomy.
- Just as the Gupta emperors appointed local rulers as tributaries while maintaining political stability, modern leaders could use a decentralized approach, giving states or provinces more control over local affairs, such as education and healthcare, while ensuring national unity through a shared constitution and central policies.
- This approach balances centralization with local governance, fostering both unity and diversity.
Q4: If you were a Gupta ruler, how would you encourage both economic growth and cultural exchange between different regions of the empire?
Ans:
- As a Gupta ruler, I would promote economic growth by ensuring stable trade routes and fair tax policies, making trade between regions profitable.
- I would invest in infrastructure such as roads, ports, and marketplaces to facilitate the movement of goods like textiles, spices, and gems.
- Additionally, I would encourage cultural exchange by supporting scholars, artists, and craftsmen from different regions, allowing them to travel and share their knowledge.
- I would also fund educational institutions like Nālandā University, which could attract scholars from all parts of the empire and beyond, fostering intellectual and cultural growth.
Q5: Why do you think the Gupta Empire’s support of multiple schools of thought, such as Buddhism, Jainism, and Vedic traditions, was significant for its cultural unity?
Ans:
- The Gupta Empire’s support of multiple schools of thought helped promote cultural unity by fostering an environment of religious tolerance and intellectual diversity.
- By supporting Buddhism, Jainism, and Vedic traditions, Gupta rulers ensured that no single religion dominated, allowing people from various backgrounds to coexist peacefully.
- This approach encouraged cultural exchange, artistic developments, and philosophical discourse, contributing to the empire’s long-lasting cultural influence.
- The inclusive attitude promoted by the Gupta rulers also helped maintain political stability and unity in a diverse empire.
Q6: What might have happened to the Gupta Empire if they had not focused on trade and cultural development as key pillars of their economy?
Ans:
- If the Gupta Empire had not focused on trade and cultural development, the empire might have faced economic stagnation and social unrest.
- Trade was a major source of wealth for the Guptas, as they exported goods like spices, textiles, and gems, and also traded with foreign nations.
- Without a thriving trade network, the empire would have lacked the financial resources to maintain a strong military, fund infrastructure, or support the arts and sciences.
- Cultural development, including the support of Sanskrit literature and religious tolerance, also helped unify the empire’s diverse populations.
- Without these elements, the Gupta Empire would have likely faced a decline in both political power and cultural influence.
Q7: Design a public policy initiative that would have supported the Gupta Empire’s advancements in art and literature. What key features would the policy include?
Ans: The public policy initiative would focus on patronage of arts and education, encouraging creativity and intellectual growth.
Key features of the policy would include:
- Grants and Scholarships: Establishing state-funded scholarships for scholars and artists to pursue education in various fields, including literature, astronomy, and mathematics.
- Cultural Centers: Setting up institutions like Nālandā University across the empire to promote learning and the exchange of ideas, fostering an environment of intellectual development.
- Art Patronage: The state would commission the construction of temples, sculptures, and paintings, ensuring that artists and craftsmen receive the resources they need to showcase their talent.
- Promotion of Sanskrit: Encouraging the use of Sanskrit in literature, poetry, and philosophy, while also supporting other regional languages and cultures to maintain diversity.
- Trade of Artifacts: Facilitating the trade of art and literature with other kingdoms and empires, ensuring cultural exchange and the growth of the empire’s artistic reputation.
|
23 videos|272 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Class 7 Social Science Chapter 7 HOTS Questions - The Gupta Era: An Age of Tireless Creativity
| 1. What were some major achievements in art during the Gupta Era? |  |
| 2. How did literature flourish during the Gupta Era? |  |
| 3. What contributions did the Gupta Empire make to mathematics and science? |  |
| 4. How did religion influence culture during the Gupta Era? |  |
| 5. What was the significance of trade during the Gupta Era? |  |
















