Year 6 Exam > Year 6 Notes > Food & Nutrition for Year 6 > Food Choices
Food Choices | Food & Nutrition for Year 6 PDF Download
Understanding Food Choices
People choose foods based on various factors, including religious beliefs, cultural influences, ethical considerations, and medical needs.
Religious Reasons for Making Food Choices
Buddhism
- Most Buddhists follow a vegetarian or vegan diet.
- Alcohol is generally avoided.
- Monks and nuns may fast after midday.
- During Wesak, a key festival, only vegetarian food is consumed, and alcohol is avoided.
Christianity
- Many Christians observe Lent, abstaining from certain foods for 40 days and nights.
- Some Catholics fast on Fridays and before Lent.
- Christian festivals include:
- Christmas, celebrating Jesus' birth, with traditional foods like roast turkey and mince pies.
- Easter, marking Jesus’ resurrection, featuring foods like hot cross buns and simnel cake.
Hinduism
- Cows are sacred, so beef and beef products are prohibited, though milk is permitted as it involves no harm to animals.
- Emphasis on ahimsa (non-violence) leads many Hindus to adopt vegetarianism.
- Alcohol is often avoided.
- Hindu festivals include:
- Diwali, the festival of lights, celebrated with sweets.
- Navratri, involving a 24-hour fast.
Islam
- Pork and its byproducts are forbidden.
- Meat must be halal, prepared through specific slaughter methods.
- Alcohol is prohibited.
- Seafood is restricted, but fish with fins are allowed.
- Muslims celebrate Eid, marking the end of Ramadan, a month-long fast where no food or drink is consumed during daylight hours.
Judaism
- Jewish dietary laws prohibit shellfish and pork.
- Dairy and meat cannot be consumed together.
- Food must be kosher, with meat from animals slaughtered in a specific way and from species with split hooves that chew cud (e.g., cows, deer).
- Fish must have fins to be kosher.
- Jewish festivals with specific foods include:
- Passover, featuring unleavened bread and a special meal.
- Rosh Hashanah (Jewish New Year), with meals including apples dipped in honey.
- Yom Kippur, a 24-hour fast preceded by a meal and followed by prayers.
- Hanukkah, the festival of lights, with various traditional foods.
Rastafarianism
- Rastafarians follow an I-tal diet, focusing on natural, unprocessed foods.
- Chemically modified foods or those with artificial additives are avoided.
- The diet emphasizes fruits and vegetables, avoids salt, pork, and fish longer than 12 inches.
- Many Rastafarians are vegetarian or vegan.
- Alcohol, milk, and coffee are avoided, with herbal teas preferred.
- The birthday of Haile Selassie, a divine figure, is celebrated with community feasts.
Sikhism
- Kosher or halal meats are forbidden due to inhumane slaughter methods.
- Alcohol, tobacco, and intoxicants are avoided.
- Many Sikhs are vegetarian.
- The birthday of Guru Nanak Dev Ji, Sikhism’s founder, is celebrated with Karah Parshad, a sacred pudding.
Cultural Reasons for Making Food Choices
Culture includes beliefs, customs, practices, behaviors, and artifacts that shape societal identity, directly influencing food preferences and choices.
Ethical and Moral Reasons for Making Food Choices
Individuals’ ethical and moral views influence food choices, leading to avoidance of:
- Foods produced through inhumane practices that harm animal welfare.
- Products where producers are unfairly compensated; fairtrade products ensure ethical treatment of workers.
- Foods with high carbon footprints due to long-distance imports; choosing local produce reduces this impact.
- Products grown with harmful chemicals like pesticides or fertilizers; organic foods avoid these.
- Genetically modified (GM) foods, due to potential long-term health or environmental concerns.
Medical Reasons for Making Food Choices
Intolerances
- Gluten: Found in wheat, rye, and barley. Non-coeliac gluten sensitivity causes symptoms like bloating, diarrhea, abdominal pain, headaches, fatigue, and joint pain. Gluten-free alternatives allow recipe modifications.
- Lactose: A sugar in milk and dairy. Lactose intolerance leads to bloating, gas, and diarrhea. Affected individuals should avoid dairy or opt for lactose-free alternatives.

Allergies
People with food allergies need to steer clear of foods that cause allergic reactions. Common allergens include:
- Nuts (e.g., peanuts, tree nuts)
- Eggs
- Milk
- Wheat
- Fish
- Shellfish (e.g., prawns, crab)
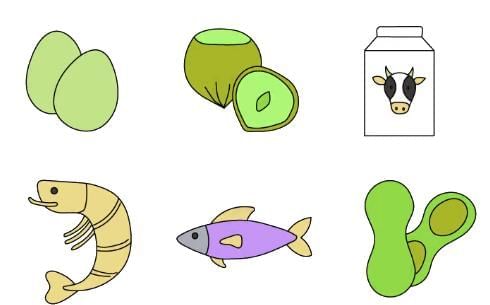
Consuming an allergen can trigger reactions such as:
- Skin rashes or hives
- Itching in the mouth, eyes, or skin
- Swelling of the lips, face, or eyes
- Trouble breathing
In severe cases, anaphylactic shock may occur, involving:
- Swelling in the mouth or throat
- Partial or complete airway blockage
- Difficulty speaking
If anaphylactic shock happens, an EpiPen should be used immediately to lower the risk of death.
The document Food Choices | Food & Nutrition for Year 6 is a part of the Year 6 Course Food & Nutrition for Year 6.
All you need of Year 6 at this link: Year 6
FAQs on Food Choices - Food & Nutrition for Year 6
| 1. What are some common religious dietary restrictions? |  |
Ans.Many religions have specific dietary laws that guide food choices. For instance, in Islam, followers adhere to halal dietary laws, which prohibit the consumption of pork and alcohol. In Judaism, kosher laws dictate what foods are permissible, including the separation of meat and dairy products. Hinduism often encourages vegetarianism, as many Hindus believe in Ahimsa, or non-violence towards animals. These practices reflect the deeper spiritual beliefs and values of each religion.
| 2. How does culture influence food choices? |  |
Ans.Culture plays a significant role in shaping food choices through traditional recipes, cooking methods, and communal eating practices. Different cultures have unique cuisines based on local ingredients, historical events, and environmental factors. For example, Mediterranean diets emphasize olive oil, fish, and vegetables, while Asian cuisines often incorporate rice and spices. Cultural celebrations and rituals also involve specific foods, reinforcing community identity and heritage.
| 3. What are ethical reasons for making food choices? |  |
Ans.Ethical reasons for food choices often revolve around animal welfare, environmental sustainability, and fair trade practices. Many individuals choose vegetarian or vegan diets to avoid contributing to animal suffering. Others may opt for organic or locally-sourced foods to support sustainable farming practices and reduce their carbon footprint. Additionally, some consumers prioritize purchasing products that ensure fair wages and safe working conditions for farmers and workers in the food supply chain.
| 4. How do medical conditions affect food choices? |  |
Ans.Medical conditions greatly influence food choices, as certain diets can help manage health issues. For instance, individuals with diabetes may need to monitor their carbohydrate intake to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Those with lactose intolerance often avoid dairy products, while individuals with celiac disease must adhere to a strict gluten-free diet. Consulting healthcare professionals or nutritionists is essential for creating a diet that supports health and well-being based on specific medical needs.
| 5. What role do personal beliefs play in food choices? |  |
Ans.Personal beliefs, including values about health, environmentalism, and social justice, significantly impact food choices. Many people choose to eat organic or non-GMO foods due to concerns about health and the environment. Others may advocate for food justice, focusing on equitable access to nutritious food for all communities. Personal beliefs about sustainability and animal rights can lead individuals to adopt specific diets, such as vegetarianism or flexitarianism, reflecting their commitment to these values.
Related Searches




















