Bank Exams Exam > Bank Exams Notes > IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation > Codes used in Banking Sectors
Codes used in Banking Sectors | IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation - Bank Exams PDF Download
Introduction
Here are some codes which were introduced to accelerate banking operations in the country.
1. IFSC (Indian Financial System Code)
- Generally IFSC is considered as the base of banking because it is essential part of money management in India.
- IFSC identifies the payer’s and payee’s bank branch and ensures that funds are transferred to the correct bank branch.
- It consists 11 character alpha numeric code, in which first 4 characters represents bank and last 6 characters represents the bank branch and 5th character (Zero) is kept for future usage.
- IFSC is generally printed on the front page of the passbook even on the cheque leaf.
2. MICR Code (Magnetic Ink Character Recognition Code)
- MICR technology is used for printing MICR Codes on cheques.
- It is the 9 digits code used to recognise the location of the bank branch which is participating in ECS (Electronic Clearing Service).
- Out of 9 digits the very first three digits represents the city, next three represents the bank and last three digits represents the bank branch.
3. SWIFT Code
- Society of worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) code is also known as BIC. It is a network that enables financial transactions across the world in a secure and systematic manner.
- Generally SWIFT Code is printed on the front page of the passbook.
- SWIFT Code contained 8 or 11 alpha numeric characters, in which first 4 characters represents city, next 2 characters represents Country, then 2 characters represents location of city, and then optional last three in 11 alpha numeric characters represents the bank branch.
4. MMID (Mobile Money Identifier)
- Mobile Money Identifier can be defined as a unique code which is used to facilitate immediate fund transfer via IMPS.
- One can simply log in to the mobile banking app of the bank and have to enter the receiver’s mobile number, the amount and MMID then the fund will be transferred easily.
- MMID is a combination of 7-digits.
5. Cheque Number
- A Cheque Number is 6 digit number that is used to identify a cheque. It contains the details including the date, account number, cheque amount, cheque number, etc thus it acts as a cheque identifier for banking operations.
- The cheque number is printed between inverted commas at the bottom of a cheque leaf; the cheque number shows the status of the cheque. Its position is at the bottom of a cheque leaf right to the MICR Code.
6. CIF Number (Customer Information Number)
- CIF Number contains all the details of the customer (Account holder) like the details related to loan and Demat account, KYC details (Know Your Customer), etc. A CIF number is a virtual file of an account holder issued by the bank at the time of account opening.
- CIF number is generally printed on the front page of the passbook along with other account details of an account holder.
- The account holder’s bank has the sole right to access the CIF Number of an account holder and retrieve his/her details if required. An account holder can check his number of bank accounts under on unique CIF Number.
- That’s why the CIF number is very important because it maintains the transparency between the bank and its customers thus further avoids any sort of fraudulent activities.
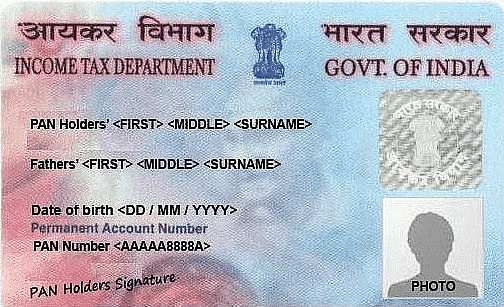
7. PAN Number (Permanent Account Number)
- PAN is a unique 10 alphanumeric character code that is allotted by the Income Tax department.
- PAN number acts as an electronic system wherein all the tax-related information of a taxpayer is sorted in a single place.
- PAN number is compulsory for paying income tax and it is identity proof of a person.
- PAN number is essential for major financial transactions like opening a bank account, sale or purchase of a property, investing in Mutual Funds, etc.
10 alphanumeric characters are designed as follows on PAN Card:
- First 3 alphabets between A to Z,
- 4th character represents the category of the taxpayer (Individual Category is ‘P’),
- 5th one represents the first character of Surname of the taxpayer,
- The next 4 characters contain numbers from 0001 to 9999 and
- The last 10th character contains the alphabet check number.
8. BSR Code (Basic Statistical Return Code)
- The unique BSR Code is assigned by RBI to all the registered banks in India.
- The code is used to track all the online payments which are made towards the tax by various banks and alerts the Income Tax Department.
- BSR Code is also used to upload the details of the challan after recording all the taxes paid by the banks.
- BSR Code contains 7 digits code wherein the first 3 numbers represent the bank then the next and last 4 numbers represent the branch of the corresponding bank.
The document Codes used in Banking Sectors | IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation - Bank Exams is a part of the Bank Exams Course IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation.
All you need of Bank Exams at this link: Bank Exams
|
675 videos|1082 docs|322 tests
|
Related Searches
















