Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Practice Question Answers - Control and Coordination
True or False
Q1. Thyroid gland is the largest endocrine gland of the body.
Ans: True
The thyroid gland is the largest endocrine gland and plays a vital role in regulating metabolism, growth, and development.
Q2. Endocrine part of pancreas is called islets of Langerhans.
Ans: True
The islets of Langerhans are clusters of cells in the pancreas that secrete hormones like insulin and glucagon.
Q3. Progesterone is also known as birth hormone.
Ans: False
Progesterone is a hormone involved in pregnancy and the menstrual cycle, but it is not referred to as the birth hormone.
Q4. Follicle stimulating hormone stimulates formation of corpus luteum.
Ans: False
The luteinizing hormone (LH), not follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), stimulates the formation of the corpus luteum.
Q5. Function of Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone in human is not known.
Ans: True
The exact function of melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) in humans is unclear, but it is believed to affect pigmentation.
Q6. Neurohypophysis is associated with Growth Hormone (GH).
Ans: False
Growth Hormone (GH) is secreted by the anterior pituitary (adenohypophysis), not the neurohypophysis.
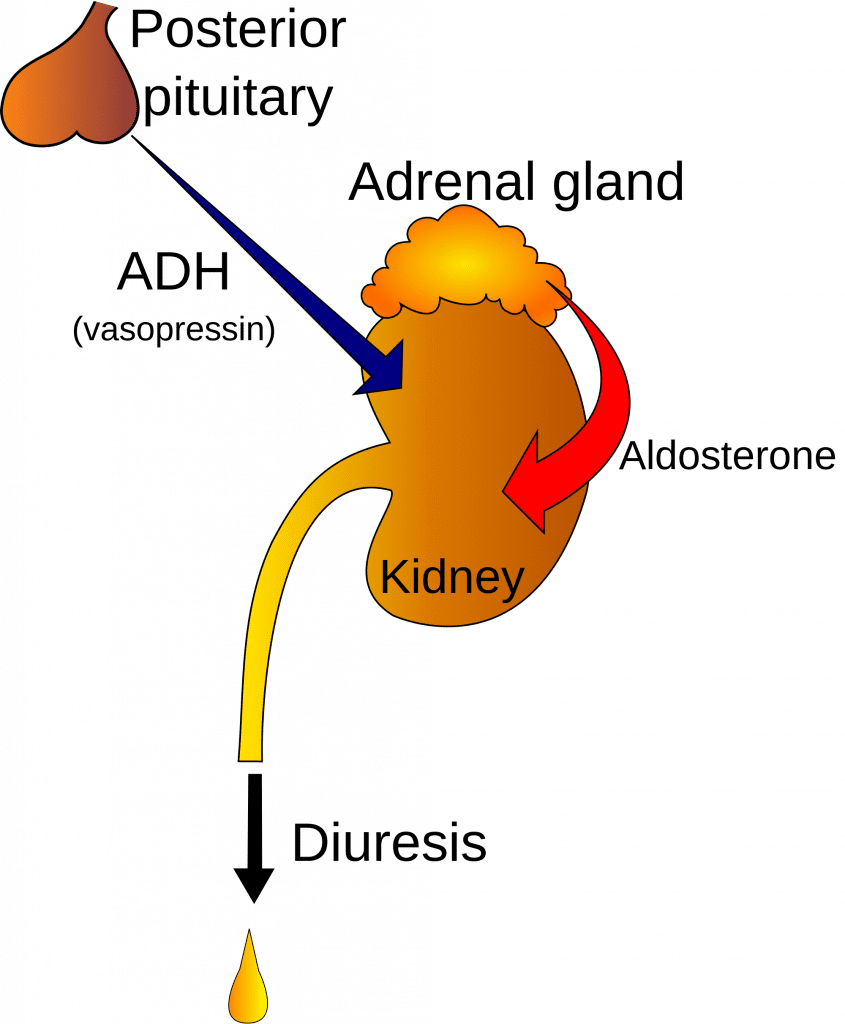
Q7. ADH helps in re-absorption of water from nephron.
Ans: True
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) increases water reabsorption in the kidneys, reducing water loss in urine.
Q8. Thyroid gland regulates the BMR of body.
Ans: True
The thyroid gland produces thyroxine, which regulates the basal metabolic rate (BMR) of the body.
Q9. Secretion of exocrine glands is known as hormone.
Ans: False
Exocrine glands secrete substances like enzymes and mucus, not hormones.
Q10. Hypothalamus regulates the secretion of pituitary hormones.
Ans: True
The hypothalamus controls the pituitary gland by releasing hormones that regulate its activity.
Fill in the blanks
Q1. Element ........................ is essential for the synthesis of thyroxine.
Ans: Iodine
Iodine is an essential element required by the thyroid gland for the synthesis of thyroxine.
Q2. A ........................ mechanism regulates the action of the hormones.
Ans: Feedback
The feedback mechanism controls hormone levels by increasing or decreasing their secretion based on the body's needs.
Q3. Secretion of ductless gland is called .......................
Ans: Hormone
Hormones are chemical messengers secreted by ductless endocrine glands into the bloodstream.
Q4. Deficiency of insulin hormone causes ........................
Ans: Diabetes mellitus
A lack of insulin leads to high blood sugar levels, causing diabetes.
Q5. Deficiency of ........................ causes cretinism in children.
Ans: Thyroxine
A deficiency of thyroxine in children causes cretinism, a condition marked by stunted growth and mental retardation.
Q6. ........................ hormone regulates growth and development of the body.
Ans: Growth
Growth hormone, secreted by the pituitary gland, regulates the growth and development of the body.
Q7. ........................ is the only hormone which stored in our body.
Ans: Thyroxine
Thyroxine is stored in the thyroid gland before being released into the bloodstream.
Q8. Spermatogenesis in males and oogenesis in females are stimulated by ........................ hormone.
Ans: Follicle-stimulating
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates spermatogenesis in males and oogenesis in females.
Q9. Hyposecretion of ........................ causes diabetes insipidus.
Ans: Vasopressin
A deficiency of vasopressin leads to diabetes insipidus, characterized by excessive urination and thirst.
Q10. Secretion of milk is stimulated by ........................ while ejection of milk is stimulated by ........................
Ans: Prolactin; Oxytocin
Prolactin stimulates milk production, and oxytocin triggers milk ejection during breastfeeding.
Q11. The hormone which controls secondary sexual characters in male is ........................
Ans: Testosterone
Testosterone, secreted by the testes, regulates the development of male secondary sexual characteristics.
Q12. Oxytocin hormone is released by ........................ and help in ........................
Ans: Posterior pituitary; Childbirth
Oxytocin, released by the posterior pituitary, induces uterine contractions during childbirth.
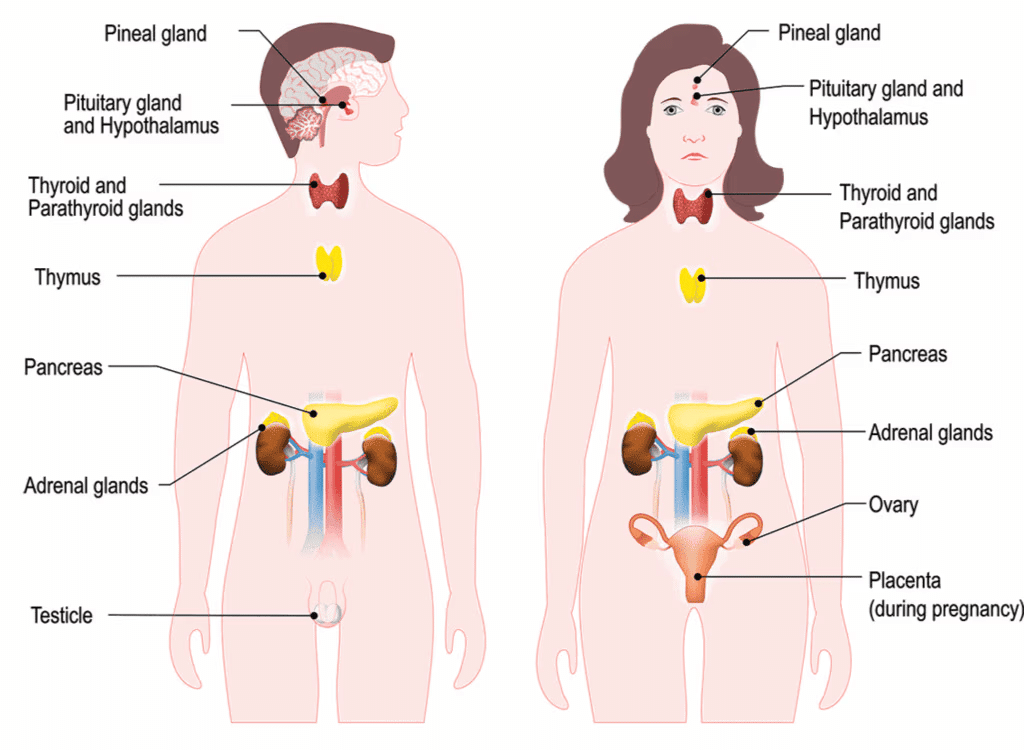
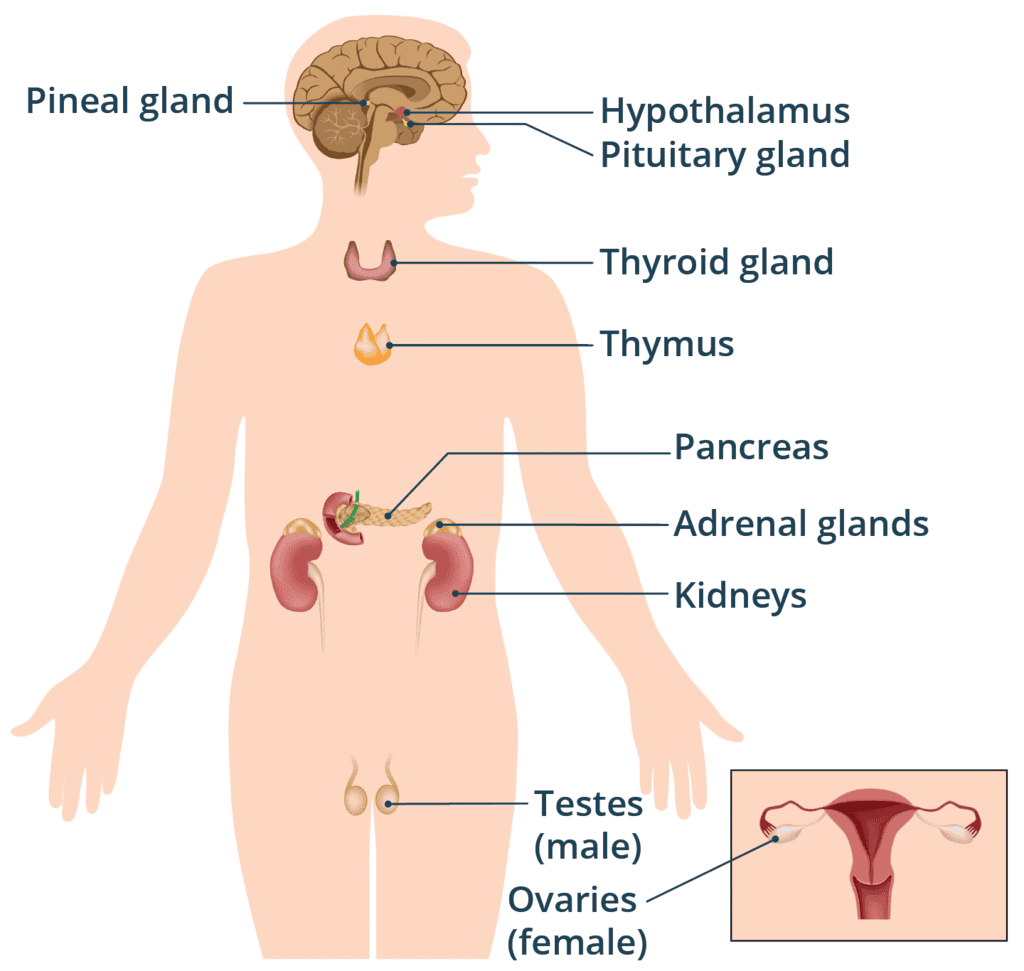
Q13. The master gland in human body is ........................
Ans: Pituitary
The pituitary gland is the master gland as it regulates other endocrine glands.
Q14. Hormones are ........................ substances secreted in ........................ quantities by ........................
Ans: Chemical; Small; Endocrine glands
Hormones are chemical messengers secreted in small quantities by endocrine glands to regulate body functions.
Q15. The movement of a plant in response to light is called __________.
Ans: Phototropism
Phototropism is the growth movement of a plant toward or away from light. Shoots show positive phototropism by growing toward the light, while roots may show negative phototropism by growing away from it. This helps the plant maximize photosynthesis.
Match the following:
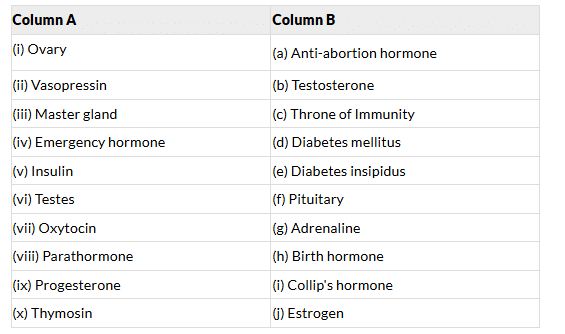
Answer:
(i) - (j), (ii) - (e), (iii) - (f), (iv) - (g), (v) - (d), (vi) - (b), (vii) - (h), (viii) - (i), (ix) - (a), (x) - (c)
|
80 videos|661 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Practice Question Answers - Control and Coordination
| 1. What is the role of the nervous system in control and coordination? |  |
| 2. How do hormones contribute to control and coordination in the body? |  |
| 3. What are the main components of the human nervous system? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between voluntary and involuntary actions? |  |
| 5. How do reflex actions work in terms of control and coordination? |  |