Cheat Sheet: Subordinate Courts | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Constitutional Provisions |

|
| Structure and Jurisdiction |

|
| Chronology for Quick Revision |

|
Introduction
This chapter covers the role and structure of Subordinate Courts in India, which operate below the High Courts and handle both civil and criminal cases at the local level. Led by district judges, these courts are crucial for delivering justice across districts, with their decisions subject to review by the High Courts. Understanding their constitutional provisions, organization, and jurisdiction is essential for grasping the functioning of India’s judiciary.
Constitutional Provisions
The Constitution of India, under Part VI, outlines the framework for appointing and managing judges in Subordinate Courts, ensuring a structured judicial system. These provisions define the roles of the state governor, High Court, and State Public Service Commission in maintaining judicial independence and efficiency.
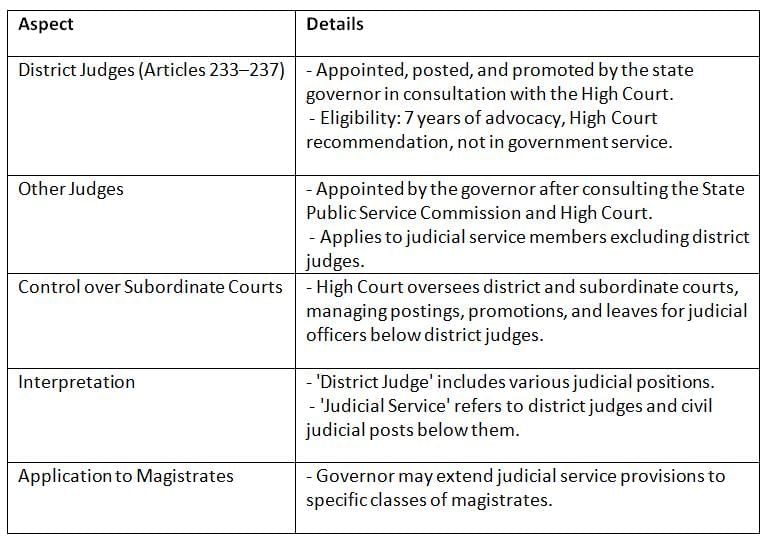
Key Points:
- The Constitution ensures High Court oversight and governor involvement in appointments, maintaining judicial integrity.
- The term 'district judge' is broad, and provisions can extend to magistrates, ensuring flexibility in judicial administration.
Structure and Jurisdiction
Subordinate Courts are organized in a three-tier structure below the High Court, with jurisdiction varying by state. This hierarchy ensures efficient handling of civil and criminal cases, from small disputes to serious matters, with the district judge as the top authority in a district.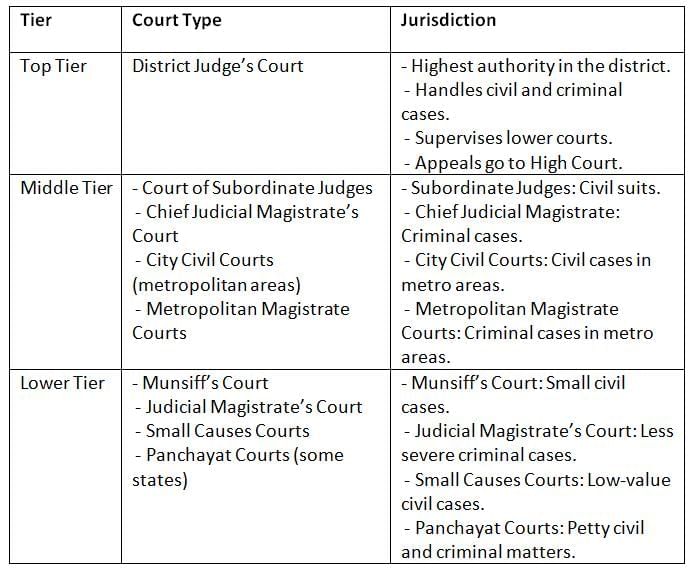
Key Points:
- The three-tier structure, led by the district judge, ensures comprehensive coverage of cases.
- Jurisdiction varies by case type and value, with specialized courts like Small Causes and Panchayat Courts addressing minor disputes.
- Appeals from the district judge go directly to the High Court.
Chronology for Quick Revision
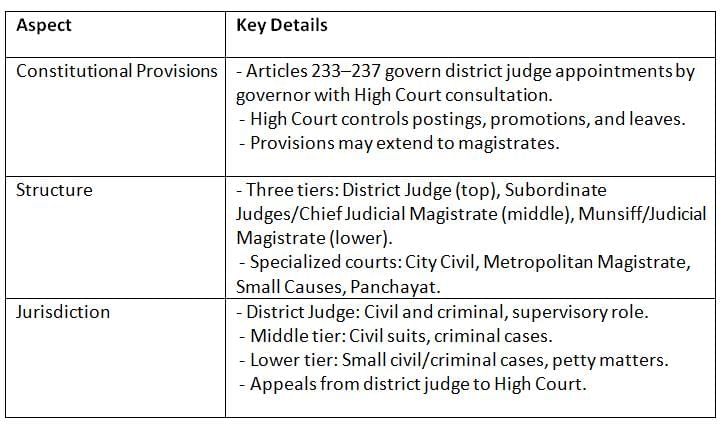
Conclusion
This chapter highlights the critical role of Subordinate Courts in India’s judicial system, ensuring justice at the grassroots level. By detailing their constitutional framework, structure, and jurisdiction, it underscores their importance in maintaining a fair and accessible judiciary. Understanding these courts is vital for appreciating how local-level justice connects to the broader judicial hierarchy under High Court supervision.
|
154 videos|985 docs|260 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Subordinate Courts - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the key constitutional provisions related to subordinate courts in India? |  |
| 2. What is the structure of subordinate courts in India? |  |
| 3. What is the jurisdiction of subordinate courts in India? |  |
| 4. How does one revise the chronology of subordinate courts for UPSC preparation? |  |
| 5. Why is the control of subordinate courts by High Courts significant? |  |















