Cheat Sheet: Political Parties | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
This chapter explains the role, types, and characteristics of political parties in India, along with their significance in the democratic framework. Political parties are voluntary groups sharing common political views, aiming to gain power through constitutional means to promote national interests. The chapter provides a clear overview of their classifications, the Indian party system, and conditions for recognition as national or state parties, serving as a concise reference for understanding India’s dynamic political landscape.
Meaning and Types of Political Parties
Political parties are organized groups that share political ideologies and seek power through democratic processes to advance national interests. They are classified based on their ideologies and goals, shaping the political system in democracies like India.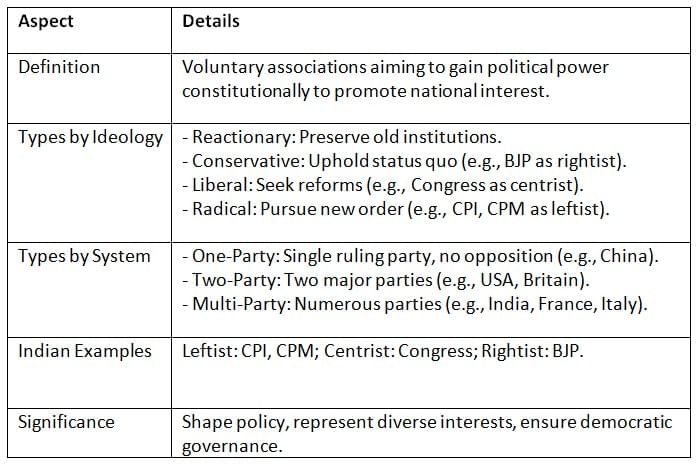
Key Points: Political parties drive democracy by representing ideologies and interests. India’s multi-party system reflects its diverse society, with parties ranging from leftist to rightist, though ideological clarity often blurs in practice.
Party System in India
India’s party system is characterized by its multi-party nature, shaped by the country’s diversity, universal adult franchise, and unique political dynamics. It has evolved from Congress dominance to a competitive multi-party landscape.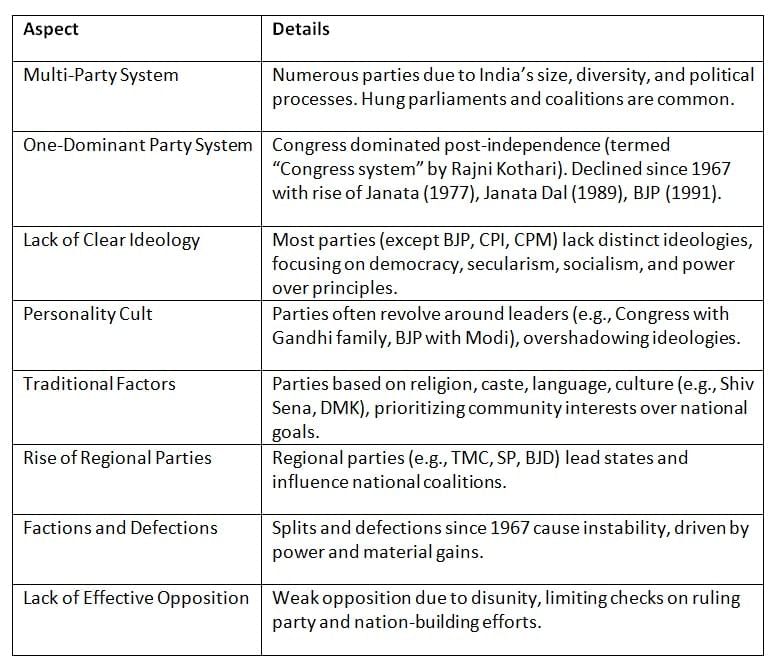
Key Points: India’s multi-party system reflects its diversity but faces challenges like ideological ambiguity, leader-centric politics, and weak opposition, impacting democratic stability.
Conditions for Recognition as a National Party
The Election Commission of India grants national party status based on specific electoral performance criteria, ensuring only significant parties receive recognition.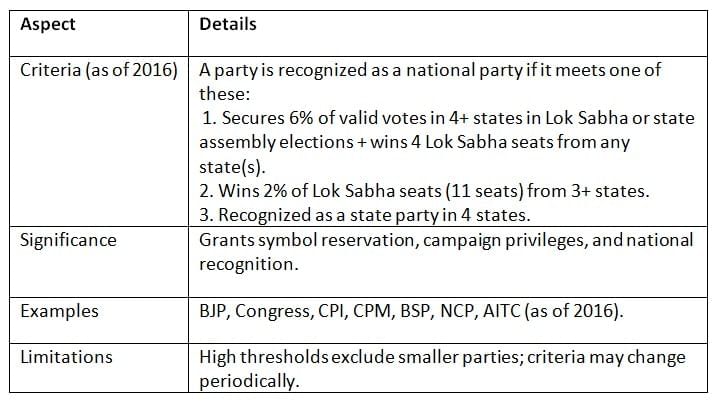
Key Points: National party status enhances a party’s influence but requires significant electoral success across states, favoring established parties.
Conditions for Recognition as a State Party
State party recognition by the Election Commission acknowledges parties with strong regional presence, granting them benefits like reserved symbols within the state.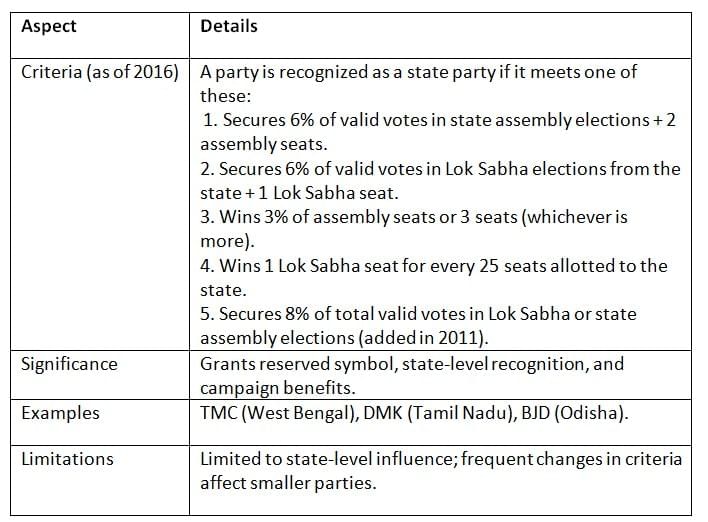
Key Points: State party recognition empowers regional parties but requires consistent electoral performance, reflecting their local influence.
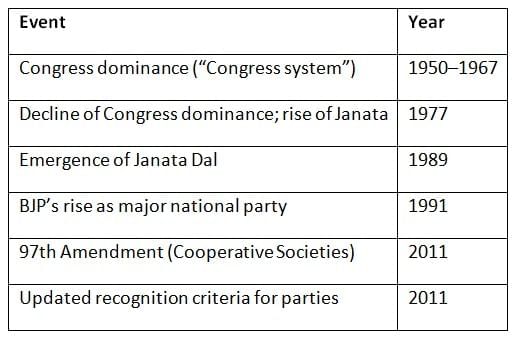
Chronology of Key Developments
Conclusion
This chapter highlights the role of political parties in shaping India’s democracy, from their ideological classifications to the unique multi-party system. Despite challenges like ideological ambiguity, personality-driven politics, and weak opposition, political parties remain central to governance and representation. Understanding their characteristics and recognition criteria is essential for appreciating India’s vibrant yet complex democratic framework.
|
154 videos|993 docs|260 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Political Parties - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the meaning of a political party? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of political parties? |  |
| 3. What are the conditions for recognition as a national party in India? |  |
| 4. What are the conditions for recognition as a state party in India? |  |
| 5. What is the party system in India? |  |
















