Humanities/Arts Exam > Humanities/Arts Notes > Psychology Class 11 > Cheat Sheet: Learning
Cheat Sheet: Learning | Psychology Class 11 - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
Definition of Learning
Learning is a long-lasting modification in behaviour or potential behaviour resulting from an individual’s experiences, demonstrated by relatively permanent changes due to practice and experience.
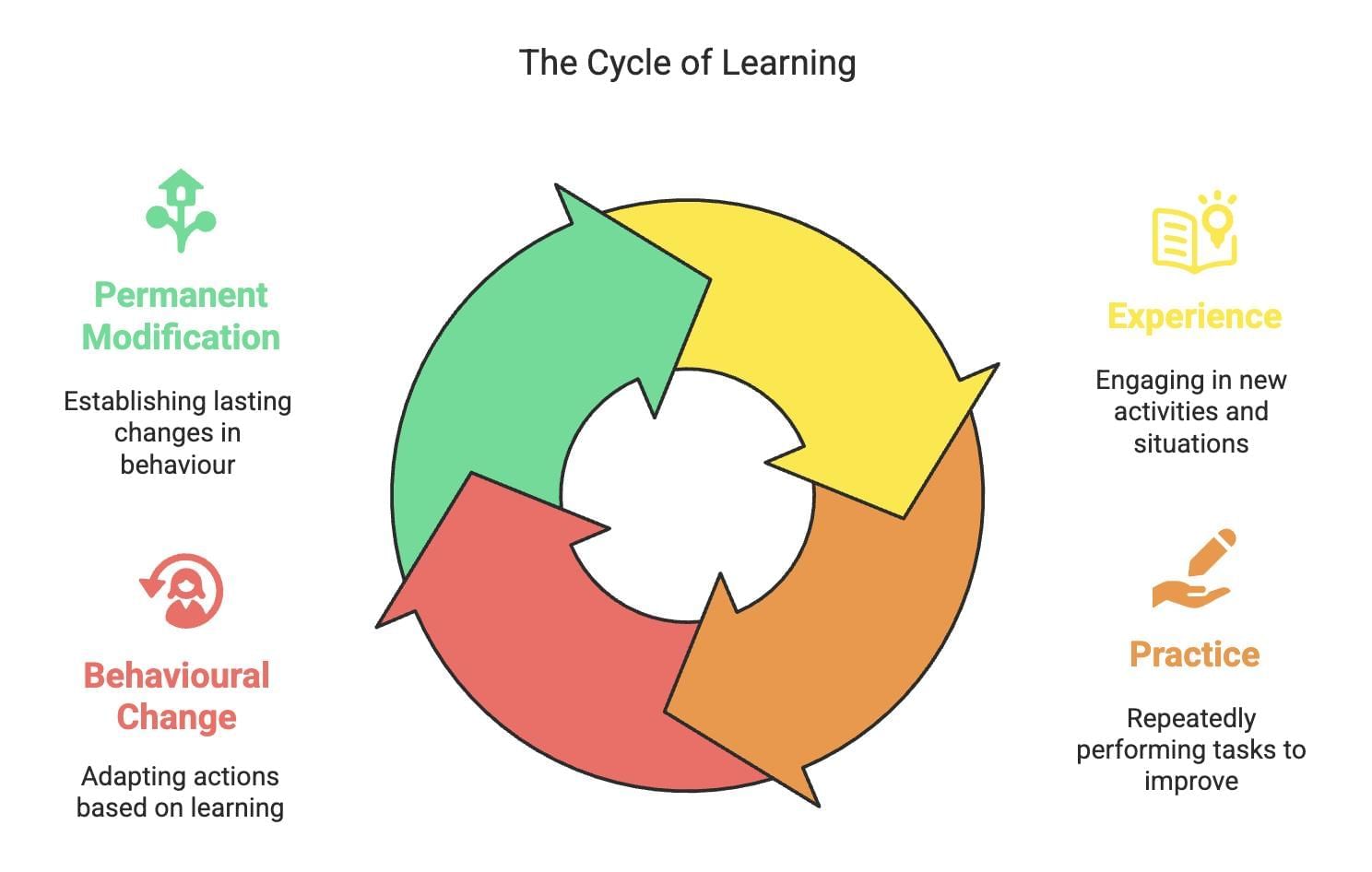
Features of Learning
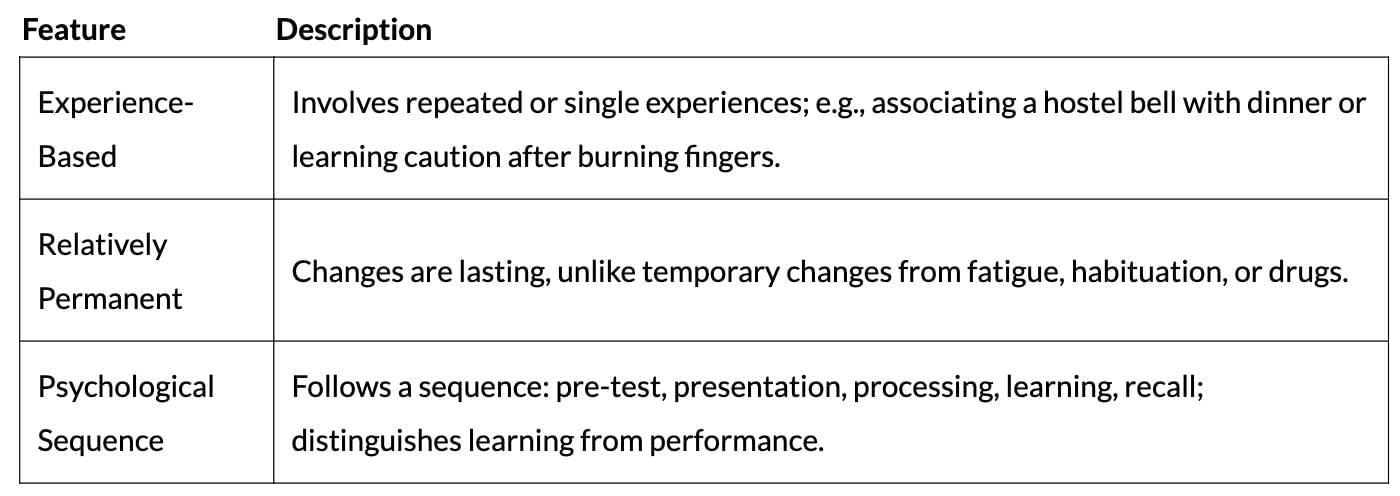
Paradigms of Learning
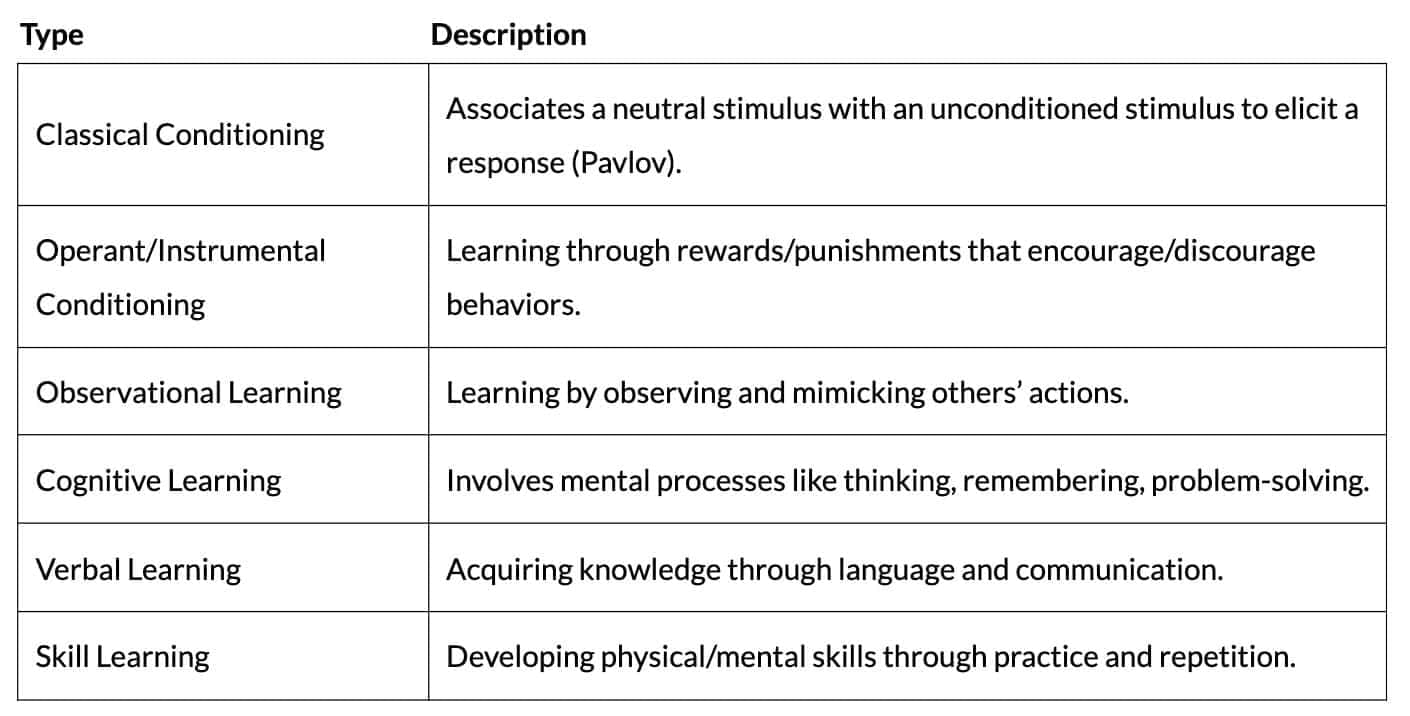
Classical Conditioning
- Mechanism: Neutral stimulus (CS) paired with unconditioned stimulus (US) elicits conditioned response (CR); CS predicts US (Pavlov’s dog experiments).
- Procedures:
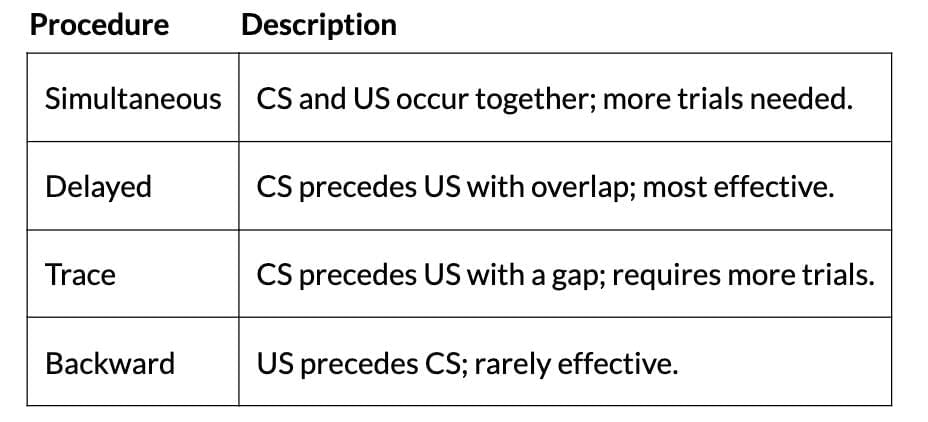
- Determinants:
- Appetitive Stimuli: Trigger approach behaviours (e.g., eating); take longer to condition.
- Aversive Stimuli: Trigger avoidance (e.g., shocks); condition faster (1-3 trials).
- CS Intensity: Stronger CS speeds up conditioning.
Operant/Instrumental Conditioning
- Mechanism: Behaviour shaped by consequences; positive/negative reinforcement increases behaviour likelihood, and punishment decreases it.
- Skinner Box (B.F. Skinner): Rat learns to press lever for food; voluntary behaviours (operants) are conditioned by rewards.
- Examples: Children learning to say “please” for favours, finding sweets jars, using devices.
- Reinforcement Types:

- Reinforcement Schedules:
- Continuous: Rewards every response; high response rate but low resistance to extinction.
- Partial: Rewards some responses; higher resistance to extinction (fixed/variable ratio, fixed/variable interval).
- Shaping: Reinforcing successive approximations to desired behaviour.
- Punishment: Introduces an unpleasant outcome to reduce behaviour.
- Determinants: Frequency, quality, amount of reinforcement; timing between behaviour and reinforcement.
Key Learning Processes
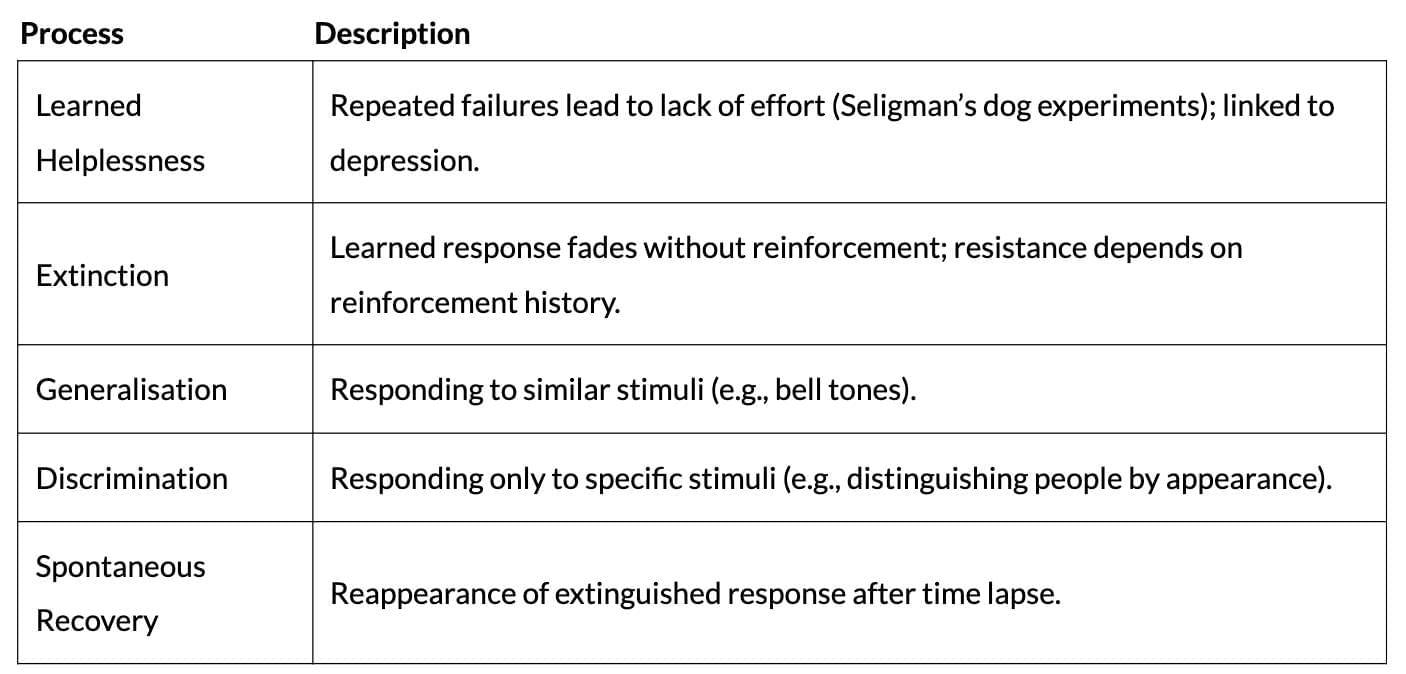
Observational Learning
- Definition: Learning by watching and imitating others (Bandura’s social learning/modelling).
- Examples:
- Fashion: Imitating the styles of attractive models.
- Social Situations: Emulating admired individuals.
- Children: Imitating adult behaviours in play (e.g., pretend games).
- Bandura’s Experiment: Children watched a film of a boy with a Bobo doll; aggression varied based on the reward/punishment of the model.
- Findings: Behaviour expression depends on the model’s consequences; shapes traits like aggression, kindness.
Cognitive Learning
- Definition: Involves mental processes; retains insights and mistakes from experience.
- Types:

- Factors: Motivation, learner readiness.
Verbal Learning
- Definition: Gaining knowledge through words; methods include paired-associate, serial, and free recall.
- Methods:

- Material meaningfulness (associations, familiarity, word relationships).
- List length (longer lists take more time).
- Category clustering (organising by subjective categories).
- Natural: Ill-defined, harder to learn.
- Artificial: Well-defined, easier to learn.
Skill Learning
- Definition: Performing complex tasks smoothly through practice; involves stimulus-response chains.
- Examples: Driving, piloting, shorthand, reading.
- Phases:
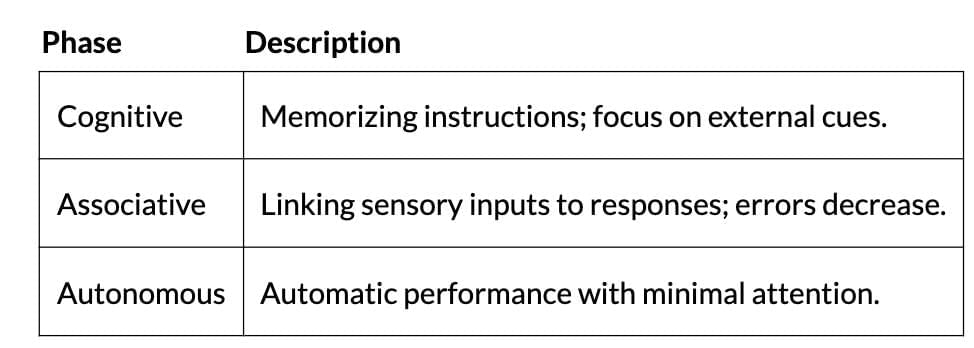
- Key Factor: Practice drives improvement and automaticity.
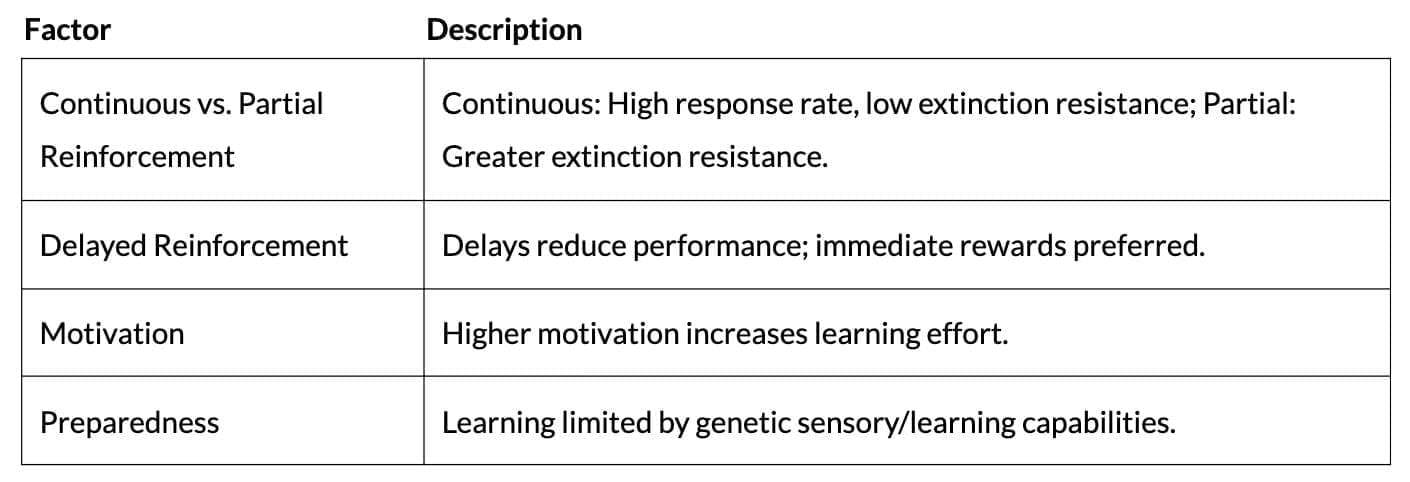
Factors Facilitating Learning
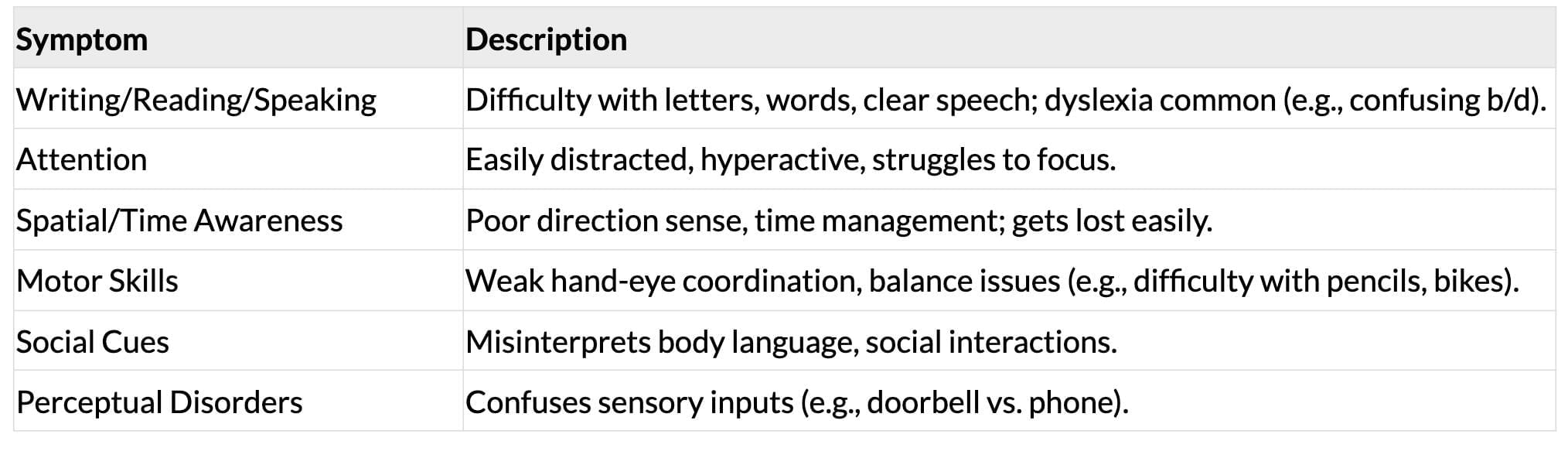
Learning Disabilities
- Definition: Disorders causing challenges in reading, writing, speaking, reasoning, and mathematics due to central nervous system issues; treatable with remedial strategies.
- Symptoms:
- Note: Can occur with or without physical/sensory/intellectual disabilities; observable in children with average/high intelligence.
The document Cheat Sheet: Learning | Psychology Class 11 - Humanities/Arts is a part of the Humanities/Arts Course Psychology Class 11.
All you need of Humanities/Arts at this link: Humanities/Arts
|
43 videos|110 docs|18 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Learning - Psychology Class 11 - Humanities/Arts
| 1. What is the definition of learning in the context of psychology? |  |
Ans.Learning is a relatively permanent change in behavior or knowledge that occurs as a result of experience or practice. It involves the acquisition of new skills, knowledge, or attitudes through various processes such as conditioning, observation, and cognitive understanding.
| 2. What are the key features of learning? |  |
Ans.The key features of learning include the following: it is a process that results in a change in behavior, it is influenced by both internal factors (like motivation and cognition) and external factors (like environment and social interactions), it is often goal-directed, and it can be intentional or unintentional.
| 3. What are the main paradigms of learning? |  |
Ans.The main paradigms of learning include behaviorism, which focuses on observable behaviors and the responses to environmental stimuli; cognitive theory, which emphasizes the role of mental processes; and constructivism, which posits that learners construct knowledge through experiences and interactions.
| 4. How does classical conditioning differ from operant conditioning? |  |
Ans.Classical conditioning involves learning through association, where a neutral stimulus becomes associated with a meaningful stimulus, leading to a conditioned response. Operant conditioning, on the other hand, involves learning through consequences, where behaviors are strengthened or weakened based on reinforcement or punishment following the behavior.
| 5. What is observational learning and how does it occur? |  |
Ans.Observational learning, also known as social learning, occurs when individuals learn by watching others and imitating their behaviors. This process involves attention to the model, retention of the behavior, reproduction of the behavior, and motivation to perform the observed behavior, often influenced by the perceived rewards or consequences associated with it.
Related Searches





















