Cheat Sheet: Goods and Services Tax Council | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
This chapter explains the Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council, a constitutional body established to ensure cooperation between the Centre and states for effective GST implementation. It covers the Council’s establishment, composition, functions, vision, and working mechanism, highlighting its role in fostering cooperative federalism and a unified national market.
Establishment of the GST Council
The GST Council was created under Article 279-A by the 101st Constitutional Amendment Act of 2016 to manage the Goods and Services Tax, ensuring coordination between the Centre and states.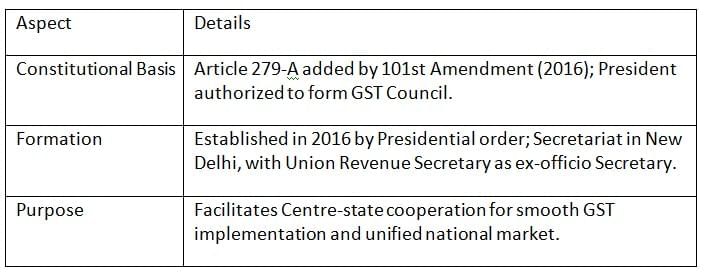
Key Points: The GST Council, set up in 2016, is a constitutional body designed to streamline GST administration through collaborative federal governance.
Vision and Mission of the GST Council
The GST Council aims to create a consistent, user-friendly GST framework, promoting cooperative federalism and a unified market.
Key Points: The Council’s vision and mission focus on cooperative federalism, stakeholder consultation, and technology-driven GST administration.
Composition of the GST Council
The GST Council includes representatives from both the Centre and states, ensuring balanced decision-making for GST policies.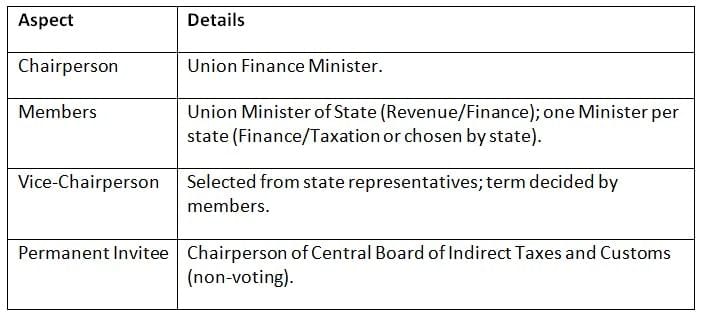
Key Points: The GST Council’s diverse composition ensures representation of both Centre and states, fostering collaborative GST governance.
Working of the GST Council
The GST Council operates through meetings, with decisions requiring a high majority to ensure consensus, and its proceedings remain valid despite procedural issues.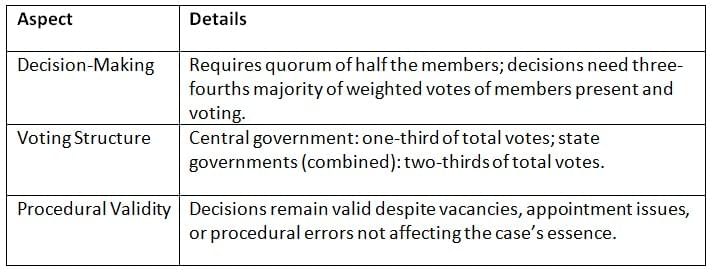
Key Points: The GST Council’s decision-making process emphasizes consensus through weighted voting, ensuring robust and valid outcomes.
Functions of the GST Council
The GST Council advises on key GST aspects, from tax inclusion to compensation, ensuring a uniform and effective tax system.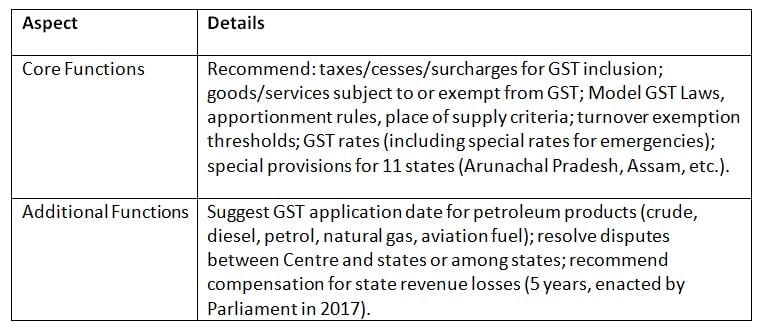 Key Points: The GST Council’s recommendations cover tax structures, exemptions, and dispute resolution, ensuring a cohesive GST framework and state support.
Key Points: The GST Council’s recommendations cover tax structures, exemptions, and dispute resolution, ensuring a cohesive GST framework and state support.
Advantages of the GST Council
The GST Council’s structure and functions offer significant benefits for India’s tax system and federal cooperation.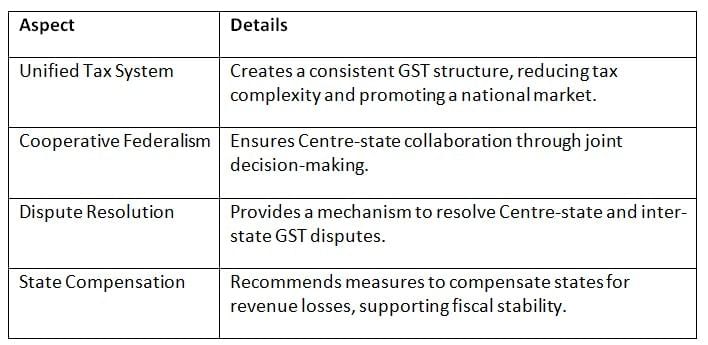 Key Points: The GST Council fosters a unified, cooperative tax system, addressing disputes and supporting states for effective GST implementation.
Key Points: The GST Council fosters a unified, cooperative tax system, addressing disputes and supporting states for effective GST implementation.
Chronology for Quick Revision
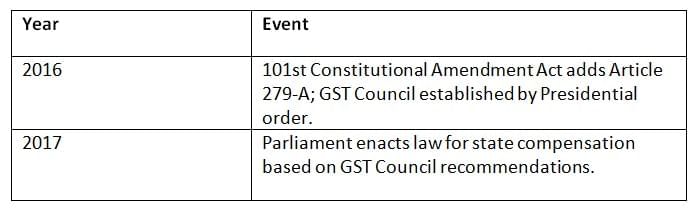
Conclusion
This chapter highlights the Goods and Services Tax Council’s critical role in India’s tax system, established under Article 279-A to foster Centre-state cooperation. Through its diverse composition, consensus-driven decisions, and comprehensive functions, the Council ensures a unified, user-friendly GST framework. Its vision of cooperative federalism and mission to create an IT-driven system support a national market while addressing state needs through compensation and dispute resolution. The GST Council remains a cornerstone of India’s fiscal federalism, promoting equitable and efficient tax governance.
|
154 videos|985 docs|260 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Goods and Services Tax Council - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the GST Council and when was it established? |  |
| 2. What are the vision and mission of the GST Council? |  |
| 3. Who are the members of the GST Council? |  |
| 4. What are the primary functions of the GST Council? |  |
| 5. What are the advantages of having a GST Council? |  |
















