UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Economy for UPSC CSE > Cheat Sheet: Food Security & Public Distribution System
Cheat Sheet: Food Security & Public Distribution System | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Concept of Food Security
- Ensures availability, accessibility, and affordability of food to all people at all times.
- Recognised as a legal right under the National Food Security Act (NFSA), 2013.
- Food security also includes nutrition security, especially for vulnerable sections.
Dimensions of Food Security
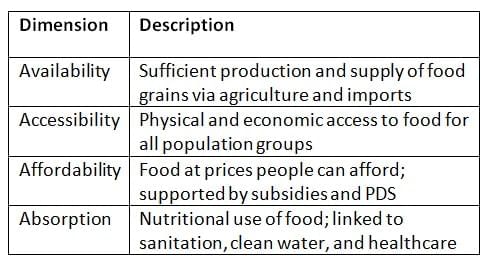
Key Components of India's Food Security System
- Buffer Stock Policy: Maintained by Food Corporation of India (FCI).
- Minimum Support Price (MSP): Incentivizes production by guaranteeing price to farmers.
- Public Distribution System (PDS): Distributes subsidized food grains to eligible families.
- NFSA 2013: Legally entitles 75% rural & 50% urban population to food security.
Public Distribution System (PDS)
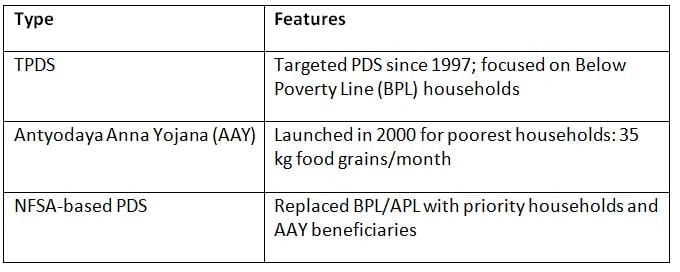
Foodgrains under NFSA
- Rice @ ₹3/kg
- Wheat @ ₹2/kg
- Coarse grains @ ₹1/kg
(These prices are now fixed across India post-2023 reforms)
Nutritional Support Programs
- Mid-Day Meal Scheme: Cooked meals for children in schools (now under PM POSHAN).
- Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS): Nutrition and preschool education for children (0–6 yrs).
- Poshan Tracker: Real-time monitoring of ICDS since 2021.
PDS Reforms and Digitisation
One Nation One Ration Card (ONORC):
- Launched 2019, fully implemented by 2023.
- Enables migrant beneficiaries to access PDS anywhere in India.
Digitisation Measures:
- Aadhaar seeding of ration cards.
- Electronic Point of Sale (ePoS) machines in fair price shops.
- Online allocation and grievance redressal.
Performance and Coverage
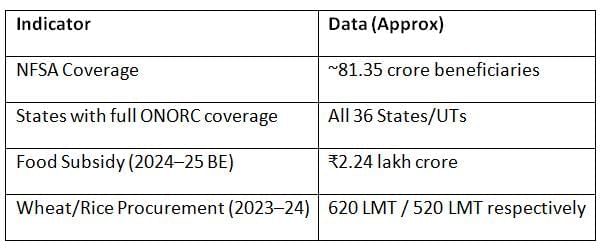
Contemporary Issues in PDS & Food Security
- Leakages & Diversion in PDS despite digitisation.
- Exclusion Errors due to Aadhaar-related mismatches.
- Nutritional Security lagging behind calorie security.
- Climate Variability impacting food production and price stability.
- Cereal-centric approach criticized; lacks pulses, millets, and oilseeds.
- Buffer Stock Mismanagement: Often exceeds norms, leading to storage and fiscal costs.
The document Cheat Sheet: Food Security & Public Distribution System | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Economy for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
145 videos|485 docs|159 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Food Security & Public Distribution System - Indian Economy for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the concept of food security and its importance for a nation? |  |
Ans.Food security refers to the condition in which all individuals have access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food to meet their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life. It is crucial for a nation as it directly affects the health, productivity, and overall well-being of its population. Ensuring food security helps in reducing poverty, enhancing economic stability, and promoting social cohesion.
| 2. What are the main dimensions of food security? |  |
Ans.The main dimensions of food security include availability, access, utilization, and stability. Availability refers to the physical supply of food, access involves the economic and physical ability to obtain food, utilization is about the nutritional quality and safety of food, and stability ensures that these three dimensions are maintained over time, even in the face of shocks such as natural disasters or economic downturns.
| 3. What are the key components of India's food security system? |  |
Ans.India's food security system is primarily composed of the Public Distribution System (PDS), nutritional support programs, and various agricultural policies aimed at increasing food production. The PDS plays a critical role in distributing food grains at subsidized rates to the needy, while nutritional support programs ensure that vulnerable groups receive essential nutrients for their health.
| 4. How does the Public Distribution System (PDS) function in India? |  |
Ans.The Public Distribution System (PDS) in India distributes food grains and other essential commodities to the economically weaker sections of society at subsidized prices. It operates through a network of fair price shops across the country, which are responsible for delivering food items to beneficiaries based on their eligibility. The system aims to improve food security and reduce hunger.
| 5. What are the recent reforms and digitization efforts in the PDS? |  |
Ans.Recent reforms in the PDS include the introduction of direct benefit transfer (DBT) to eliminate leakages and ensure that subsidies reach the intended beneficiaries. Digitization efforts involve the use of technology to improve the transparency and efficiency of the system, such as the implementation of online monitoring systems, e-PDS platforms, and biometric authentication for beneficiaries, thereby enhancing accountability and reducing corruption.
Related Searches





















