Cheat Sheet: Directive Principles of State Policy | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Overview of Directive Principles of State Policy
Part IV of the Indian Constitution outlines the Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP), which guide the government in making laws and policies. These principles are not enforceable by courts but are essential for good governance, aiming to create a welfare state focused on justice, liberty, equality, and fraternity.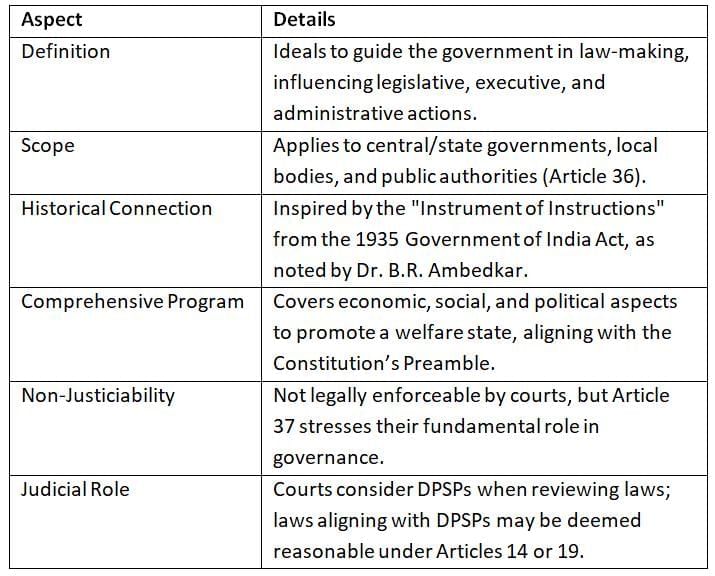
The Directive Principles provide a roadmap for achieving a welfare state, emphasizing social and economic justice. Though not legally binding, their importance in governance is undeniable, reflecting the Constitution’s core values.
Classification of Directive Principles
The Constitution does not classify DPSPs, but they can be grouped into three categories based on their content: Socialistic, Gandhian, and Liberal-Intellectual. Each category reflects distinct goals for India’s development.
Socialistic Principles
These principles aim to establish a democratic socialist state by promoting social and economic justice and reducing inequalities.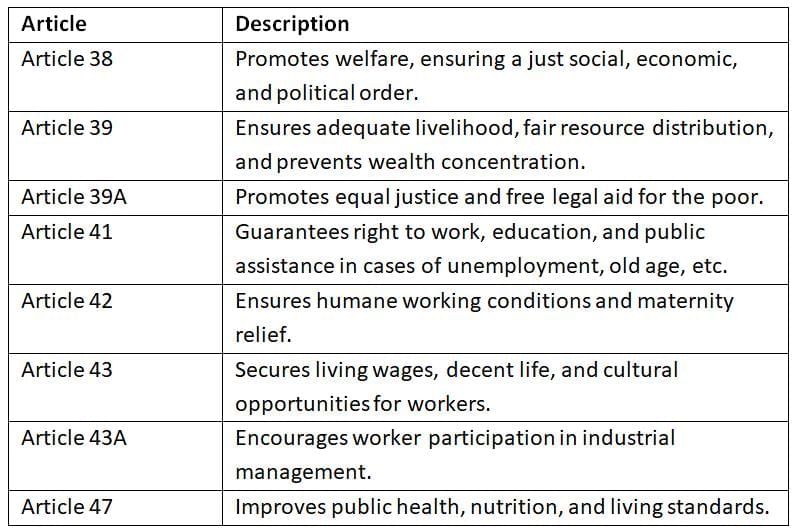
Socialistic principles focus on reducing inequalities and uplifting the disadvantaged, laying the foundation for a welfare-oriented society.
Gandhian Principles
These principles reflect Mahatma Gandhi’s vision, emphasizing rural development, self-governance, and social harmony.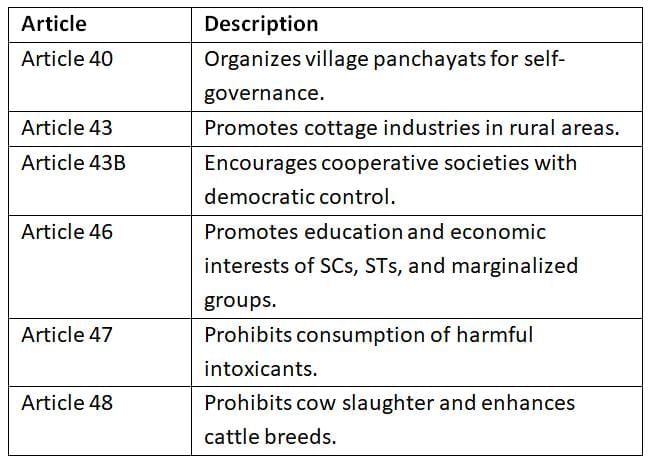
Gandhian principles highlight the importance of rural empowerment and sustainable development, aligning with Gandhi’s vision of self-reliant villages.
Liberal-Intellectual Principles
These principles promote individual rights, modern governance, and progressive ideas for national development.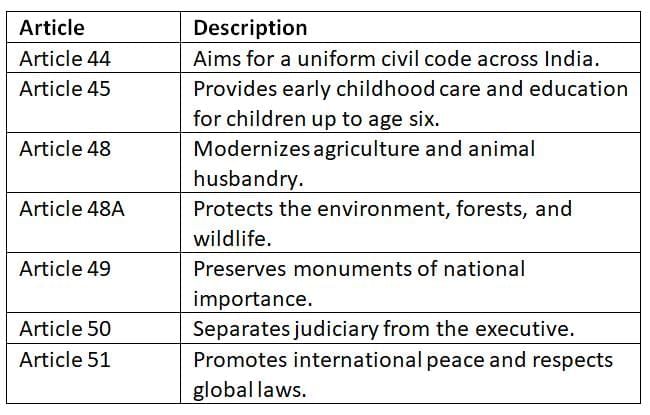
Liberal-Intellectual principles encourage modernity, equality, and global harmony, shaping India’s progressive outlook.
New Directive Principles Added by Amendments
Constitutional amendments have added new DPSPs to address evolving needs, strengthening the framework for governance.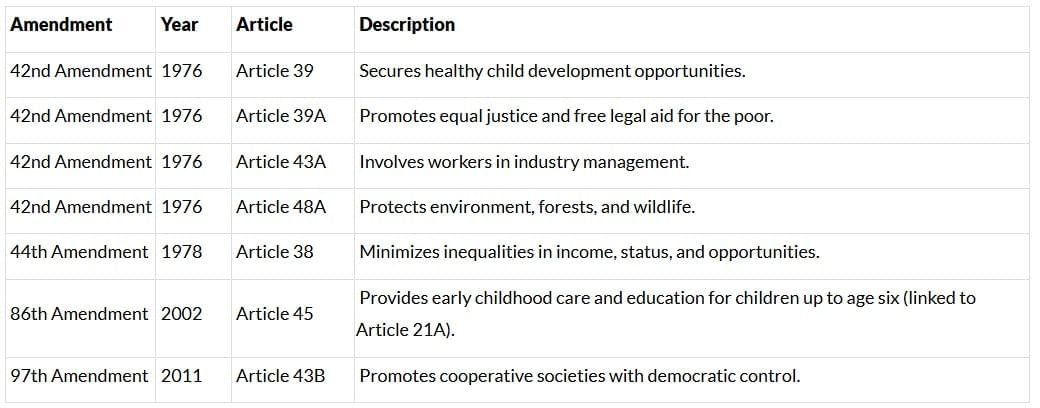
Sanction Behind Directive Principles
The DPSPs carry moral and political weight, guiding the state despite their non-enforceable nature.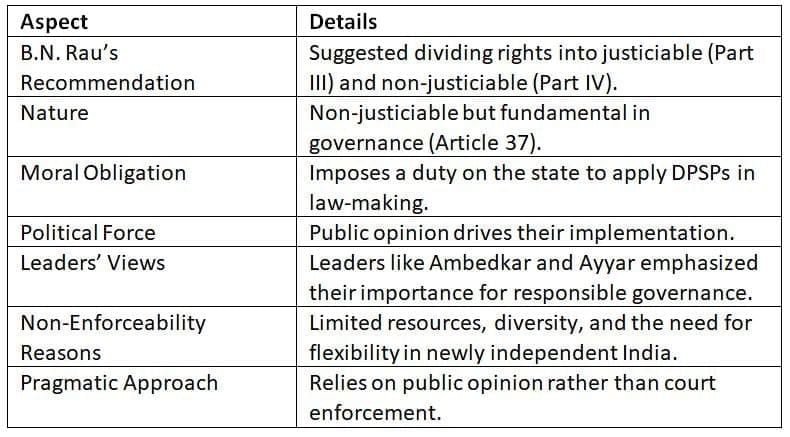
The DPSPs’ strength lies in their moral and political influence, encouraging the state to prioritize public welfare.
Criticism of Directive Principles
Despite their significance, DPSPs have faced criticism for various reasons.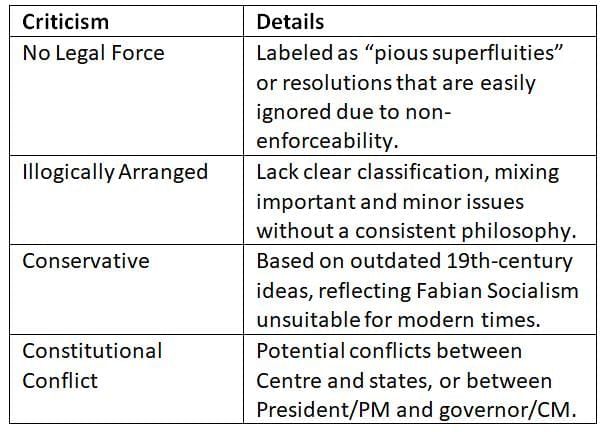
Critics highlight the DPSPs’ lack of enforceability and organization, but their role in guiding governance remains significant.
Conflict Between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles
The relationship between Fundamental Rights (Part III) and DPSPs has been shaped by key judicial decisions.
The judiciary has ensured a balance between Fundamental Rights and DPSPs, maintaining the Constitution’s integrity.
Directives Outside Part IV
Some directives exist outside Part IV, addressing specific social and cultural goals.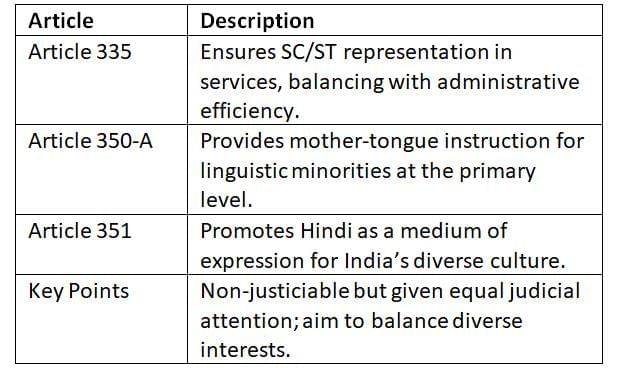
These directives complement Part IV, ensuring inclusivity and cultural harmony in governance.
|
154 videos|981 docs|260 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Directive Principles of State Policy - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the Directive Principles of State Policy in India? |  |
| 2. How are the Directive Principles classified? |  |
| 3. What are the new Directive Principles added by amendments to the Constitution? |  |
| 4. What is the sanction behind the Directive Principles of State Policy? |  |
| 5. How do Directive Principles conflict with Fundamental Rights? |  |
















