Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Science Class 10 > Cheat Sheet: Control and Coordination
Cheat Sheet: Control and Coordination | Science Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Animals – Nervous System |

|
| Reflex Actions |

|
| Human Brain |

|
| Protection of Nervous Tissue |

|
| Nervous Tissue and Muscle Action |

|
| Coordination in Plants |

|
| Hormones in Animals |

|
Introduction
Control and coordination enable living organisms to respond to environmental changes with precise movements. Animals use nervous and muscular tissues, while plants rely on chemical signals and growth. These processes are managed by specialized systems to ensure appropriate responses, such as a cat running from danger or a plant growing toward light.
Animals – Nervous System

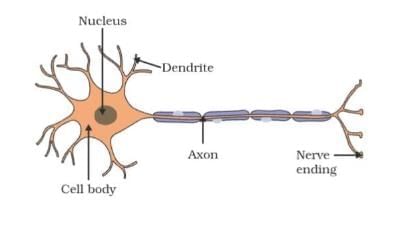
Reflex Actions

Human Brain

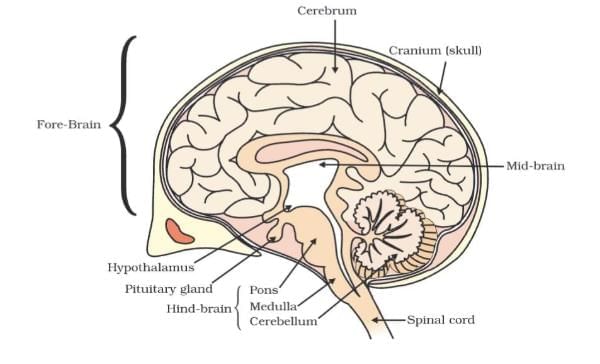
Protection of Nervous Tissue

Nervous Tissue and Muscle Action

Coordination in Plants
Types of Plant Movements
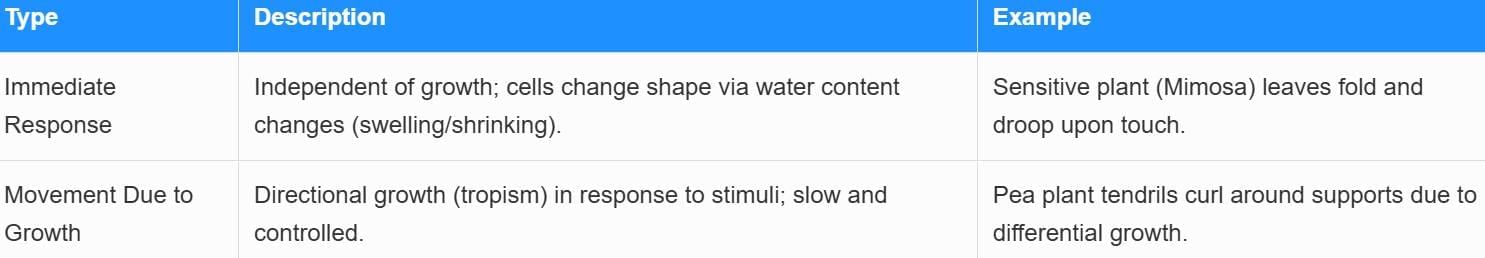
Tropisms

Plant Hormones
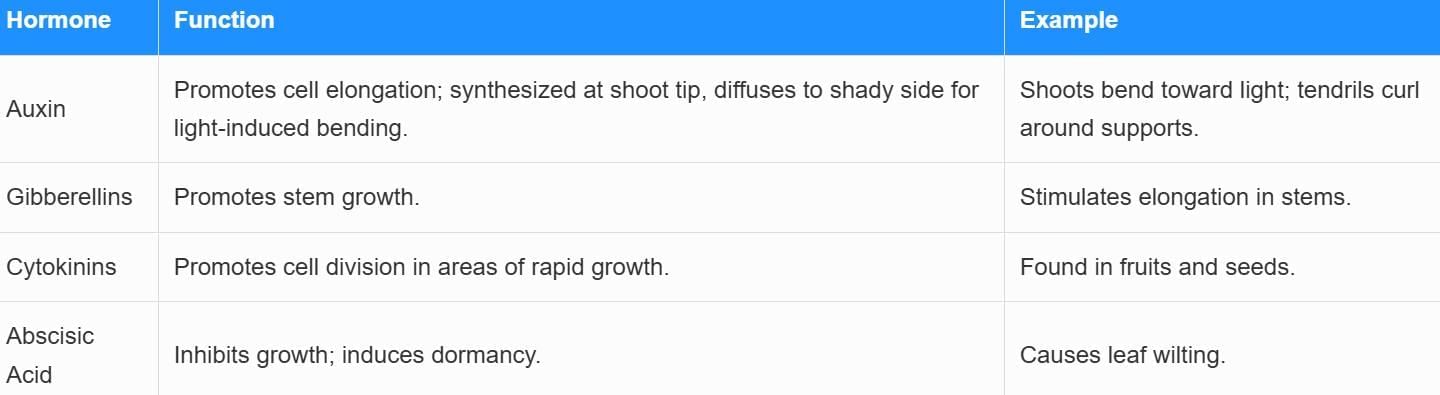
Mechanism
- Plants lack nervous tissue; use electrical-chemical signals to transmit information cell-to-cell.
- Hormones diffuse to target areas, coordinating growth and responses.
Hormones in Animals
Endocrine System
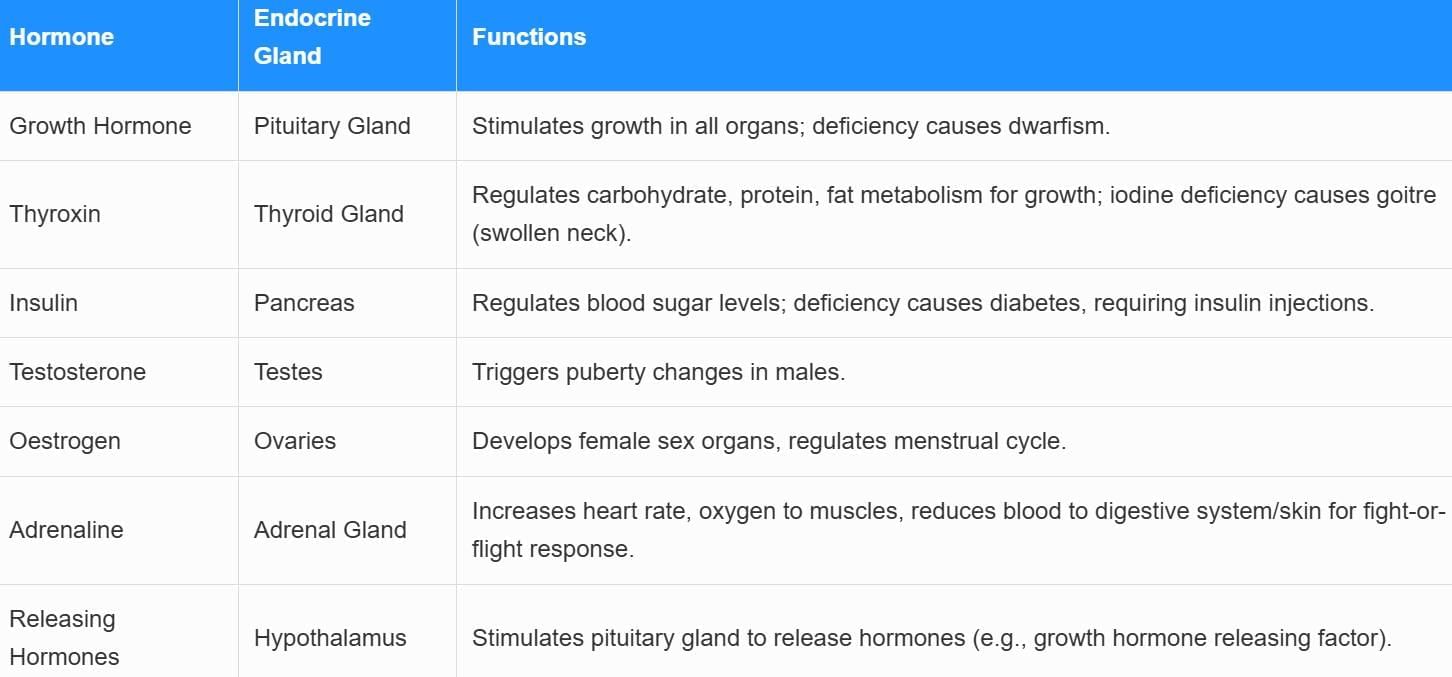
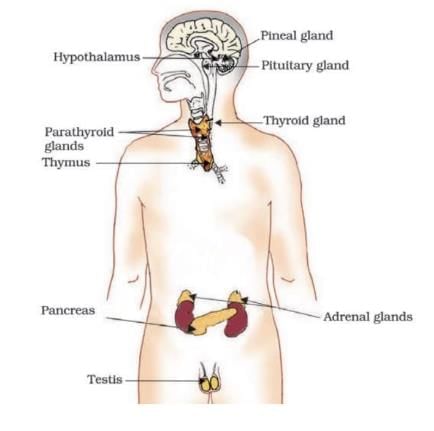
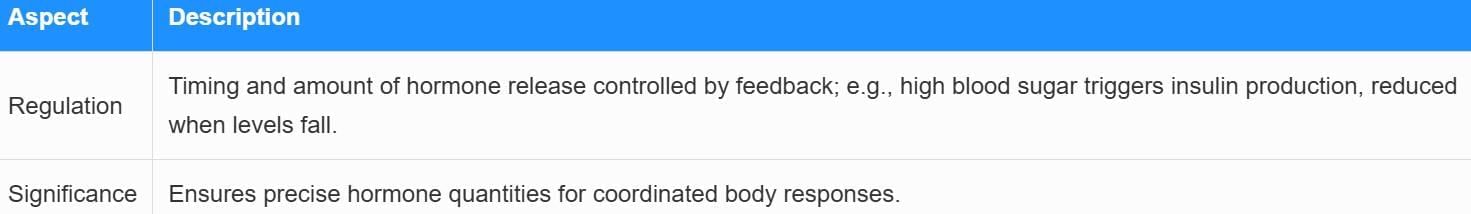
Feedback Mechanism
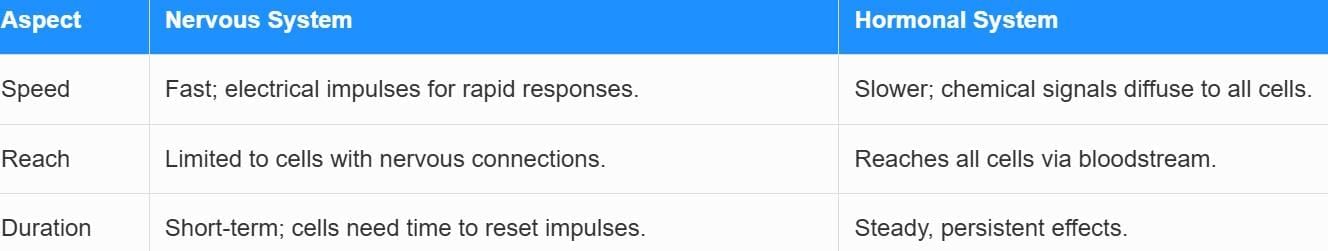
Comparison with Nervous System
The document Cheat Sheet: Control and Coordination | Science Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Science Class 10.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
80 videos|653 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Control and Coordination - Science Class 10
| 1. What are the main components of the nervous system in animals? |  |
Ans. The main components of the nervous system in animals include the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. The brain serves as the control center for processing information and coordinating responses, while the spinal cord transmits signals between the brain and the rest of the body. Peripheral nerves connect the central nervous system to limbs and organs, facilitating communication throughout the body.
| 2. How do plants coordinate their responses to environmental stimuli? |  |
Ans. Plants coordinate their responses to environmental stimuli through a process known as tropism. They utilize growth hormones such as auxins, gibberellins, and cytokinins to regulate growth and movement toward or away from stimuli like light (phototropism) and gravity (gravitropism). This hormonal response allows plants to adapt to their surroundings effectively.
| 3. What role do hormones play in the control and coordination of animal functions? |  |
Ans. Hormones act as chemical messengers in animals, regulating various physiological processes such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction. They are secreted by glands and travel through the bloodstream to target organs, where they bind to specific receptors and trigger a response. This system helps maintain homeostasis and coordinate complex bodily functions.
| 4. Can you explain the difference between the nervous system and the hormonal system in animals? |  |
Ans. The nervous system operates through electrical impulses and neurotransmitters to provide quick and precise control of body functions, often resulting in immediate responses. In contrast, the hormonal system involves slower chemical signaling through hormones, which can have prolonged effects on various body functions. While the nervous system is suited for rapid communication, the hormonal system is better for regulating long-term changes.
| 5. What are some examples of plant hormones and their functions? |  |
Ans. Some examples of plant hormones include auxins, which promote cell elongation and are involved in phototropism; gibberellins, which stimulate seed germination and stem growth; and abscisic acid, which plays a role in stress responses and closing stomata to reduce water loss. Each hormone has specific functions that help plants adapt to their environment and regulate growth.
Related Searches















