Chapter notes: Patterns | Mathematics Class 3 ICSE PDF Download
Introduction
Patterns are sequences or arrangements that follow a specific rule or repeat predictably. They can be seen in everyday objects like clothes, bedsheets, or walls, and can involve designs, shapes, letters, or numbers. Recognising and understanding patterns helps us identify their rules and predict what comes next. This chapter introduces the concept of patterns, focusing on identifying repeating units and the rules that govern them.
Patterns with Unit of Repeat
- A unit of repeat, or core, is the part of the pattern that repeats.
- Examples of units of repeat:
- Colour sequence like red, blue, green, repeating.
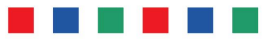
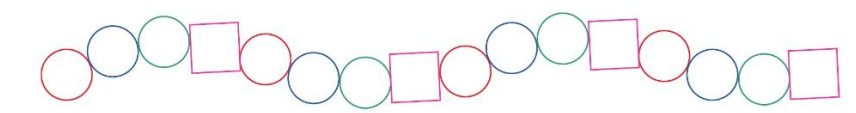
- Shape sequence like three circles followed by a square.
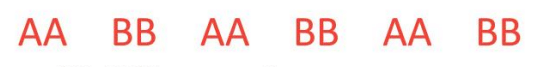
- A letter sequence like AA BB repeating.
- Number sequence like 531 repeating.

- To check if an arrangement is a pattern, identify its unit of repeat.
- Some arrangements may not have a repeating unit and thus do not form a pattern.
Patterns with Rules
Number Patterns
- Number patterns follow a specific rule to generate the next number.
- Rules can involve addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division.
- Identify the rule by observing how numbers change from one to the next.
Examples: In the sequence 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45. Identify the pattern.
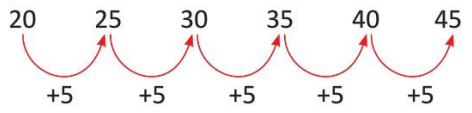
Start at 20 and add 5 each time. Thus, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45 is a pattern.
Examples: In the sequence 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64. Identify the pattern.
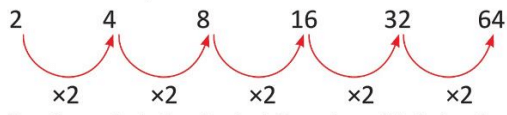
Start at 2 and multiply by 2 each time. Thus, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64 is a pattern.
Letter Patterns
- Letter patterns arrange letters in a sequence that follows a rule.
- The rule can be identified by comparing the first few letters.
Example: In the sequence a, c, e, g, i. Identify the pattern.
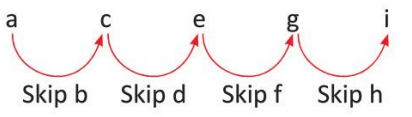
start at 'a' and skip one letter each time to get a, c, e, g and i.
Shape Patterns
- Shape patterns arrange shapes in a sequence that follows a rule.
- The rule can be identified by observing the order of shapes.
Example: Find the missing figures.
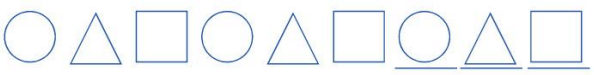
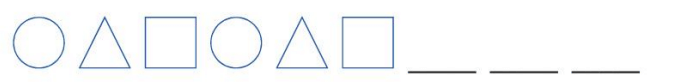 In a pattern with shapes numbered as 1, 2, 3 (e.g., square, triangle, circle), the sequence repeats as 123, 123.
In a pattern with shapes numbered as 1, 2, 3 (e.g., square, triangle, circle), the sequence repeats as 123, 123.
|
78 docs|9 tests
|
FAQs on Chapter notes: Patterns - Mathematics Class 3 ICSE
| 1. What are patterns with a unit of repeat? |  |
| 2. How can I identify patterns with rules? |  |
| 3. Why are patterns important in mathematics for Class 3 students? |  |
| 4. Can you provide an example of a pattern with a unit of repeat in everyday life? |  |
| 5. How can teachers effectively teach patterns to Class 3 students? |  |




















