The Gupta Era: An Age of Tireless Creativity Class 7 Notes Social Science Chapter 7 Free PDF
Introduction
The Gupta Era (3rd to 6th century CE) is known for its progress in art, literature, science, and governance.
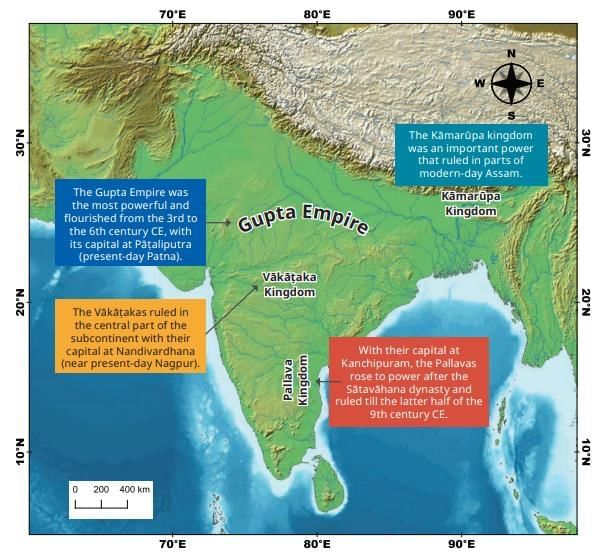
- The Gupta Empire ruled much of north and west India, creating a stable and prosperous society.
- This period is called the Classical Age because of its cultural and intellectual achievements, like beautiful temples, Sanskrit literature, and scientific discoveries.
- Other kingdoms, like the Pallavas in the south and Kamarupa in the northeast, also thrived.
- Great figures like Aryabhata, Varahamihira, and Kalidasa made lasting contributions.
A New Power Emerges
By the 3rd century CE, the Kushana Empire in north and northwest India weakened, allowing new kingdoms to form.
- The Gupta dynasty emerged in present-day Uttar Pradesh as local rulers and grew into a powerful empire.
- The Gupta period is famous for advancements in art, architecture, literature, and science, especially under Chandragupta II.
- The Iron Pillar in Delhi, over 1,600 years old, shows their advanced metallurgy as it resists rust due to a special iron layer.
 Iron Pillar, Mehraulli, Delhi
Iron Pillar, Mehraulli, Delhi
Did You Know?
- Chandragupta II got the ‘II’ in his name because his grandfather was also named Chandragupta.
- Chandragupta I, the grandfather, expanded the Gupta Empire through coins and smart alliances, laying its strong foundation.
The Warrior King
- Samudragupta, father of Chandragupta II, was a great warrior king who expanded the Gupta Empire.
- The Prayāga praśhasti, a pillar inscription in Prayagraj by court poet Harisena, praises Samudragupta’s conquests.
- Samudragupta aimed to unify India, called dharani-bandha, by defeating kings and taking their lands.
- Many defeated kings were allowed to rule again but paid tribute, while others surrendered without fighting.
- Harisena wrote that Samudragupta supported art, learning, and trade, making his kingdom wealthy.
- A coin shows Samudragupta playing the veena, highlighting his love for music.
- The Vishnu Puraṇa lists key Gupta regions: Anuganga, Prayaga, Saketa, and Magadha, but the empire grew larger, covering most of north, west, central, and east India.
 Gold Coin featuring King Chandragupta with his King
Gold Coin featuring King Chandragupta with his King
Did You Know?
Ambitious kings performed the aśvamedha yajña (horse sacrifice) to prove their strength and expand their kingdoms.
It was seen as a way to gain glory and leave behind a lasting legacy.
A Traveller’s Account of Indian Society in the Gupta Age
Faxian, a Chinese traveller, visited India in the early 5th century CE to see Buddhist sites, study with scholars, and collect texts. His travelogue, A Record of Buddhistic Kingdoms, describes Gupta society:
- People were happy, didn’t need to register households, and faced no heavy official duties.
- Farmers paid a portion of their grain as tax on royal land.
- The king’s guards and attendants received salaries.
- Cities in the Gangetic plains were large, with rich and kind inhabitants.
- Vaishya (merchant) families built charity houses for the poor, orphans, and sick, offering food and medicine.
- Cities had wealthy merchants, foreign traders, beautiful homes, and clean lanes.
- Faxian also noted harsh treatment of chandalas (outcastes), who lived outside cities, showing not all parts of society were equal.
- Historians use Faxian’s account but check other sources to understand the full picture, as it reflects only his view.
Glimpses of the Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was characterised by peace and progress, bringing advancements in various fields such as mathematics, astronomy, medicine, and metallurgy. It existed alongside other kingdoms, some of which sought power. The Gupta kings strengthened their control through military campaigns, land grants, and marriages to ensure stability, following the ideas of Kautilya, especially in forming alliances (mitra). Their legacy in art, science, literature, and magnificent temples continues to inspire today.
Governance and Administration
- The Guptas had a well-organised administration system, dividing the empire into provinces.
- They gave land grants to local rulers, priests, and chieftains, recorded on copper plates for accurate tax collection.
- This system allowed local leaders to govern their areas while the Guptas managed the empire efficiently.
- They expanded the empire through military conquests, diplomacy, and matrimonial alliances.
- Prabhavati Gupta, daughter of Chandragupta II, married a Vakataka prince, strengthening ties between the Guptas and Vakatakas.
- After her husband’s early death, Prabhavati became a regent ruler for her sons, ensuring strong Gupta-Vakataka relations.
- She was a devotee of Vishṇu and linked to building seven temples, dedicated to this god and his avatars.
- Some of these temples are in Ramagiri (Ramtek hill) in present-day Maharashtra.
 Kevala Narasimha temple
Kevala Narasimha temple
Did You Know?
- Gupta rulers used grand titles like mahārājadhirāja, samrāṭ, and chakravartin to show their supreme power.
- Earlier kings had simpler titles such as rājan or mahārāja.
- These titles highlighted the Gupta rulers’ authority and superiority over previous dynasties.
Thriving Trade
- The Guptas’ main income came from land tax, along with fines, taxes on mines, irrigation, trade, and crafts.
- This money supported the army, temples, infrastructure, and scholars and artists.
- India traded textiles, spices, ivory, and gemstones with the Mediterranean, Southeast Asia, and China via the Indian Ocean trade network.
- Socotra Island in the Arabian Sea was a key trading stop, with evidence of Indian traders (pottery, Brahmi inscriptions, Buddhist stupa designs) alongside Egyptians, Arabs, Romans, and Greeks.
- Trade promoted rich cultural exchanges across regions.
New Ideas and Wonders: The Classical Age
Gupta rulers followed Vishṇu, as seen in coins and inscriptions, but supported other beliefs, including Buddhism. They funded Nalanda University and Buddhist viharas (monasteries), showing an inclusive approach.
- The long period of peace and stability during the Gupta era led to significant advancements in various fields, prompting many historians to call this time the Classical Age of India.
- Sanskrit literature thrived, highlighted by Kālīdas's works and several important Puranas.
- Aryabhata and Varahamihira made strides in mathematics and astronomy.
- Medical texts improved health practices, and advancements in metallurgy were evident, as seen in the Iron Pillar.
- A strong and stable economy gave rulers the means to support scholars, artists, and scientists, which led to rich cultural growth.
- Chandragupta II surrounded himself with many learned individuals, poets, and artists, greatly enhancing his court through his support of diverse talents.
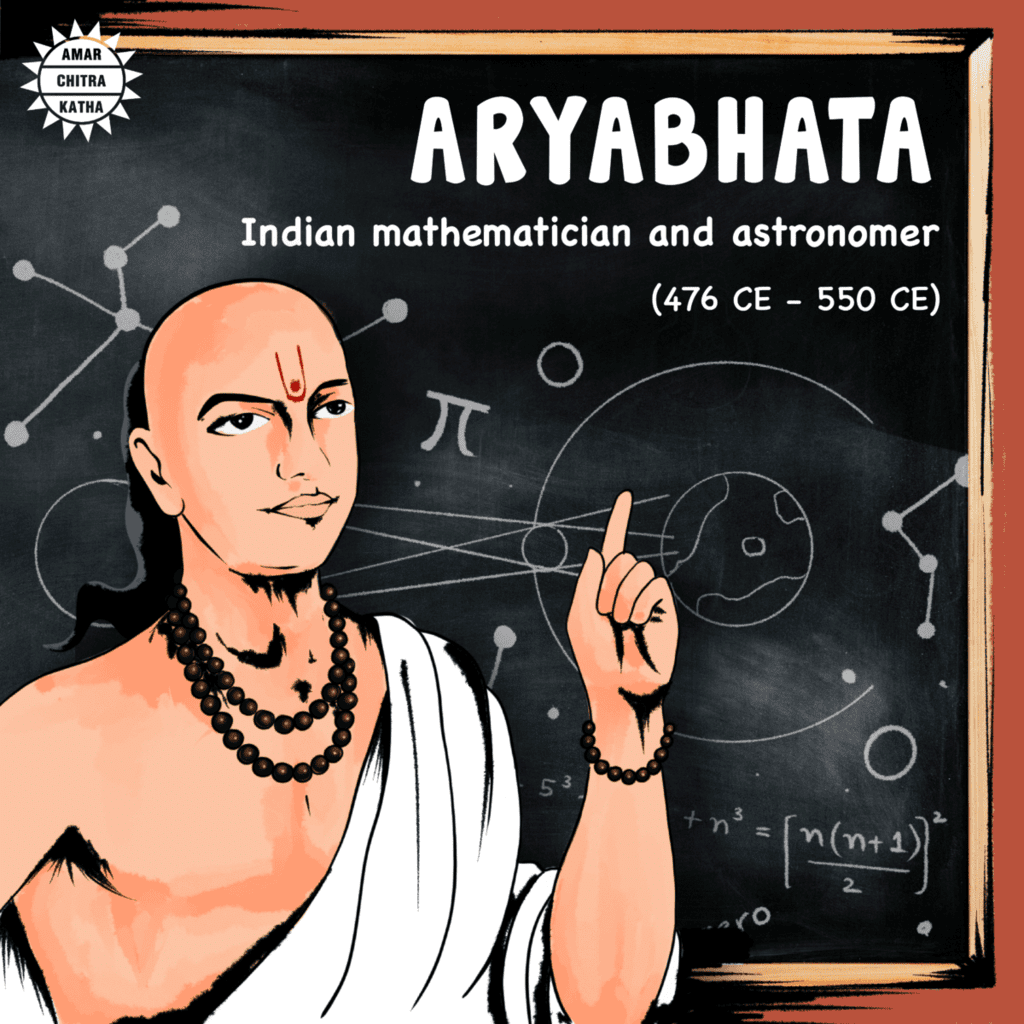
Aryabhata
- Aryabhata lived around 500 CE in Kusumapura (near Patna), a learning center.
- He wrote the Aryabhatiya, a book on mathematics and astronomy.
- He calculated the motions of the Sun, Moon, and planets.
- Aryabhata said the Earth spins on its axis, explaining day and night.
- He estimated a year as 365 days, 6 hours, 12 minutes, and 30 seconds, close to the modern value (365 days, 5 hours, 48 minutes, 45 seconds).
- He gave a good estimate of the Earth’s size and explained solar and lunar eclipses.
- In mathematics, he shared methods for calculations and solving equations, some still taught today.
- His work influenced science in India and beyond.
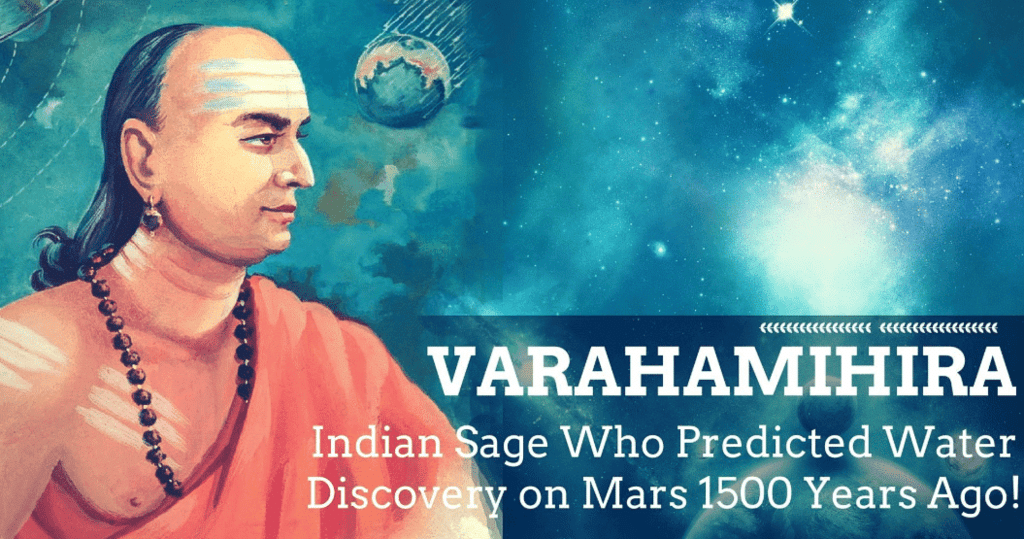
Varahamihira
- Varahamihira, a mathematician, astronomer, and astrologer, lived in Ujjayini, a city known for learning.
- His book, Brihat Samhita, covered astronomy, astrology, weather forecasting, architecture, town planning, and farming.
- He combined observation, logic, and traditional knowledge, making him a pioneer in science.
Kālīdas
- Kālīdas, a famous poet, contributed to Sanskrit literature with his refined poetry.
- Very little is known about Kālidāsa’s real life; legends say he was once ridiculed, which inspired him to improve himself.
- He is celebrated as one of the greatest Sanskrit poets, known for his refined style.
- His poem Meghadutam (The Cloud Messenger) tells of a yaksha sending a message to his beloved via a cloud.
- The poem describes love, north India’s landscapes, and weather in detail.

Did You Know?
- Āyurveda, India’s traditional system of medicine, was codified during the Gupta period.
- Famous texts like the Charaka Saṃhitā and Suśhruta Saṃhitā were compiled then and form the basis of Ayurvedic practices even today.
- These texts cover disease diagnosis, treatments, diet, medicine preparation, and advanced surgical techniques.
- Āyurveda focuses on holistic healing, highlighting the connection between the mind, body, and nature.
The Quest for Beauty
Gupta rulers created an environment where creativity and craftsmanship thrived. Key art centers included Sarnath (near Varanasi) for Buddha sculptures, Ajanta Caves in Maharashtra, and Udayagiri Caves in Madhya Pradesh.
- Gupta art set high standards for beauty, with detailed carvings and paintings.
- Ajanta Caves have cave temples with a seated Buddha and paintings like Bodhisattva Padmapani.
- Udayagiri Caves feature carvings of Hindu deities, like a scene from the Mahabharata showing Arjuna and Karna.
The Decline of the Guptas
By the 6th century CE, the Gupta Empire weakened due to external invasions and internal conflicts.
- The Huna tribe from central Asia attacked repeatedly, reducing Gupta control in north India.
- Powerful regional rulers caused internal challenges.
- This decline marked a turning point in Indian history, leading to new regional powers.
Meanwhile in the South and Northeast ...
While the Guptas ruled the north, the Pallavas grew powerful in the south, ruling parts of Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Telangana, and Andhra Pradesh.
- The Pallavas were once tributaries under the Satavahanas but gained power as the Satavahanas declined.
- They followed Shiva and built magnificent temples and rock-cut caves.
- Their capital, Kanchipuram, was called the “city of a thousand temples” and a learning center with ghatikas (schools).
- In the northeast, the Kamarupa kingdom, ruled by the Varman dynasty, covered Assam, parts of Bengal, and Bangladesh.
- Kamarupa, also called Pragjyotisha, was mentioned in the Ramayana and Mahabharata, with King Bhagadatta linked to the Mahabharata.
- Kamarupa was a cultural and political center with thriving temples and monasteries.
- Samudragupta defeated Pallava and Kamarupa rulers but let them rule as tributaries, maintaining peace.
Various Aspects of Gupta Art
- Gupta art included sculptures, paintings, and carvings known for beauty and detail.
 Aspects of Gupta Art
Aspects of Gupta Art - At Ahichchhatra (Uttar Pradesh), terracotta sculptures show rivers Ganga and Yamuna, with Ganga on a makara (crocodile-like creature) and Yamuna on a tortoise, with water pots symbolizing rivers.
- Deogarh (Uttar Pradesh) has a temple with Vishṇu on Sheshnag from the Dashavatara temple.
- Ajanta Caves feature cave temples and paintings, like Bodhisattva Padmapani, supported by Guptas and Vakatakas.
- Udayagiri Caves and a Gupta-era temple near Sanchi show carvings, like Arjuna and Karna from the Mahabharata.
Points to Remember
- The Gupta kings built a strong empire using military campaigns, land grants, and matrimonial alliances for stability.
- The period had great achievements in art, literature, science, and mathematics.
- Besides the Guptas, dynasties like Vakatakas, Pallavas, and Varmans made the period culturally vibrant.
Difficult Words
- Gupta Era: The period from the 3rd to 6th century CE when the Gupta Empire ruled, known for cultural progress.
- Classical Age: A time of great achievements in art, literature, and science during the Gupta period.
- Metallurgy: The science of working with metals, like making the rust-resistant Iron Pillar.
- Outcastes: People who were excluded from the traditional varṇa system and marginalized in society.
- Prayaga Prashasti: A pillar inscription praising Samudragupta’s achievements.
- Codified: Arranged or written in an organized and systematic way.
- Tribute: Payments or gifts given by smaller kingdoms to a powerful ruler.
- Vaishya: A social group of merchants and traders in ancient India.
- Chandalas: Outcastes who faced harsh treatment and lived outside cities.
- Saptanga: Kautilya’s seven parts of a kingdom, including allies (mitra).
- Maharajadhiraja: A title meaning “king of kings,” used by Gupta rulers.
- Regent Ruler: A person who governs temporarily for a monarch unable to rule.
- Nalanda University: A famous ancient center of learning supported by the Guptas.
- Aryabhatiya: Aryabhata’s book on mathematics and astronomy.
- Brihat Samhita: Varahamihira’s book covering many subjects like astronomy and architecture.
- Meghadutam: Kalidasa’s poem about a yaksha’s message sent via a cloud.
- Huna tribe: Central Asian invaders who weakened the Gupta Empire.
- Ghatikas: Learning centers in south India during the Pallava period.
FAQs on The Gupta Era: An Age of Tireless Creativity Class 7 Notes Social Science Chapter 7 Free PDF
| 1. What were the major contributions of the Gupta Empire to science and mathematics? |  |
| 2. How was the governance and administration structured in the Gupta Empire? |  |
| 3. What role did trade play in the economy of the Gupta Empire? |  |
| 4. Who were some of the notable rulers of the Gupta Empire, and what were their achievements? |  |
| 5. How did the Gupta Empire influence Indian society and culture during its time? |  |





















