Rhythms of Nature Chapter Notes | Our Wondrous World Class 5 - New NCERT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Changes around Us in a Day: Day and Night |

|
| Demonstration: Day and Night |

|
| Changes around Us in a Year (Seasons) |

|
| Classroom Activities: Seasons Chart |

|
| Celebrating Seasons |

|
Saba and Aparna reunite after long time, noticing how they and the world around them have changed! Let’s join them to discover how these changes shape our lives!
- Saba told Aparna that she is now taller than her.
- Both discussed about old classroom and favourite games.
- Saba and Aparna notice changes like growing taller and new trees at school.
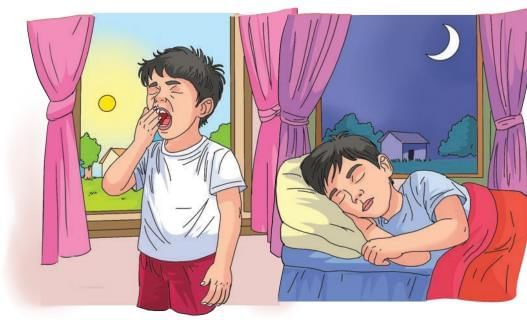
- The world changes daily as day becomes night and night turns to day.
- You grow taller each year.
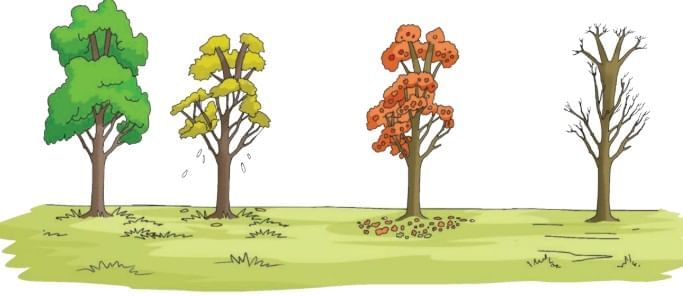
- Leaves fall and grow back again.
- Flowers bloom and then fade.
- The sky changes colour during the day.
- The sun rises in the morning and sets in the evening
Changes around Us in a Day: Day and Night
- Just like we grow and change, the world around us is changing too.
- The day changes into night, and the night becomes day.
- The sun rises in the east and seems to move across the sky.
- Let us see if the sun is moving.
Do you know?
Dong in Arunachal Pradesh is called India’s ‘First Village of the Sunrise’. It’s the very first place in India where the sun’s rays touch the land every morning.
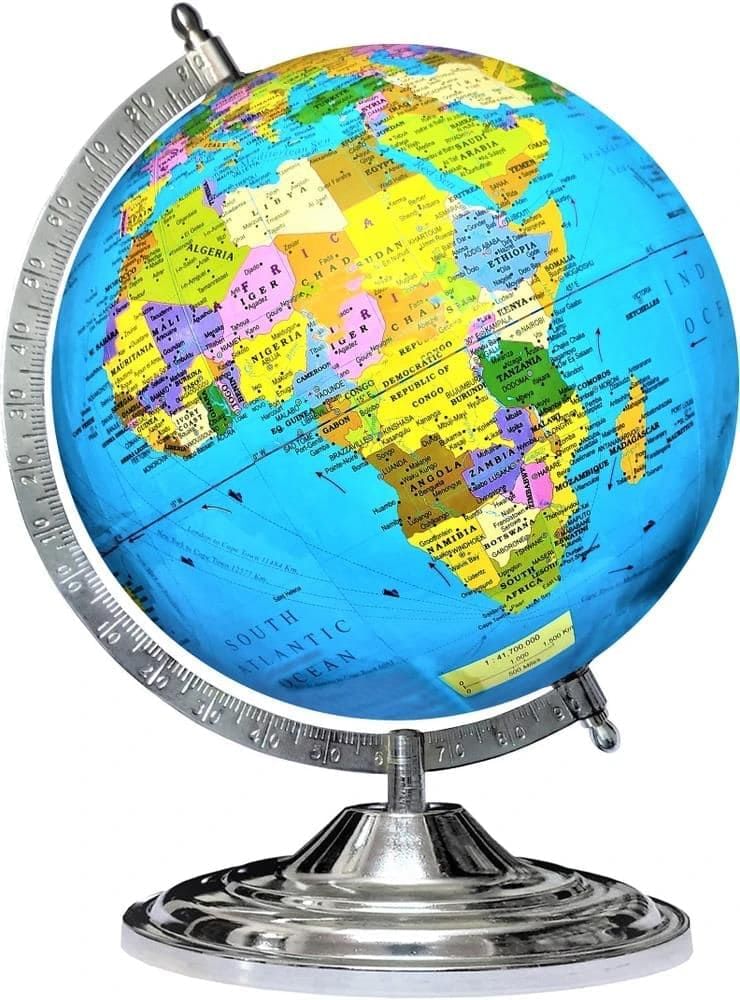
Demonstration: Day and Night
A fun activity shows why day and night happen. Let’s try it!
 Step 1: Place a globe on a table and flash a torch on one side of the globe; the torchlight represents the Sun, with the lit side as day and the dark side as night.
Step 1: Place a globe on a table and flash a torch on one side of the globe; the torchlight represents the Sun, with the lit side as day and the dark side as night.- Step 2: Rotation—Slowly rotate the globe while keeping the torch steady.
- Step 3: Observe how different parts of the globe face the light as it rotates.
You’ll notice that:
- As the globe turns, different parts move into the light (day) while others move out of it (night).
- Only the half facing the torch is lit at any time, just like Earth’s daytime side faces the Sun.
- Areas leaving the light experience sunset, while those coming into the light experience sunrise.
- This rotation explains why day and night happen on Earth.
- The Earth rotates, not the Sun, causing day and night as observed with the torch.
Do you know?
A globe is a ball-shaped model of Earth, with blue areas representing seas and oceans, covering about three-fourths of the planet. Seas are smaller and partly enclosed by land, while oceans are vast open waters. The remaining parts are land masses where all countries are located.
Changes around Us in a Year (Seasons)
Saba and Aparna explore how nature changes over a year. Let’s see what they find!
Seasons' Journal
- Saba and Aparna sit in the school garden, looking at their season’s journal.

- Students can keep a journal to record observations of nature all year.
- They will note changes in plants, animals, air, water, and human activities.
- Like Saba and Aparna, students share their journal observations.

Do you know?
In Odisha, when the koel (cuckoo) bird starts singing, farmers know the rains are coming. That’s when they start planting seeds.
Classroom Activities: Seasons Chart
Students become nature explorers, observing plants, animals, sunlight, water and human activities. Let’s join them in creatinging chart of their findings!
Step 1: Making a Chart for the Classroom
- Make a large wall chart with periods: April–June, July–September, October–December, January–March.
- List themes in rows: plant life, birds and animals, air, heat and light, water and water bodies, human activities.
- The chart helps students see all their journal observations together.
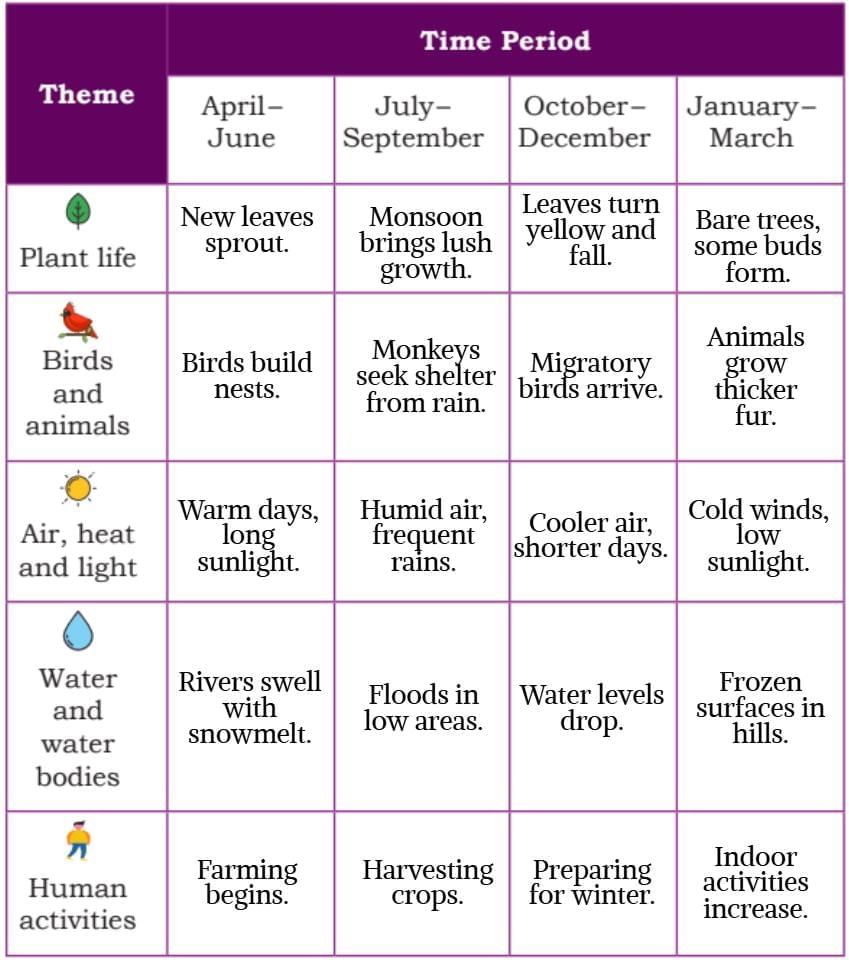
Step 2: Fill the Chart
- Students share journal observations for each theme and period.
- One student asks the class for observations, like plant life in April–June.
- The class discusses and writes the main observations on the chart.
- Each student takes turns filling a box, completing the chart for all to see.
Step 3: Tracking Changes in the Year
- Form five groups, each choosing a theme (e.g., plant life, water and water bodies).
- Each group studies how their theme changed across the year’s time periods.
- Groups create posters showing changes, like leaves blooming or rain in ponds.
Step 4: Looking at the Year Together
- Form four new groups, one for each period (e.g., April–June).
- Each group has one student from each theme to analyse all observations.
- Groups write a short story linking nature and people’s lives for their time period.
During the monsoon, snakes come out of their flooded burrows. This is why the festival Nag Panchami is celebrated — to show respect to nature and reptiles.
When you see ants carrying eggs to higher ground, it is a natural sign that rain will come soon.
Discovering Seasons
- Seasons depend on regional changes in weather, plants, and animals.
- The weather warms up, gets hot and then it rains, and then it gets cooler before warming up again.
- Students learn nature’s changes repeat yearly, forming seasons.
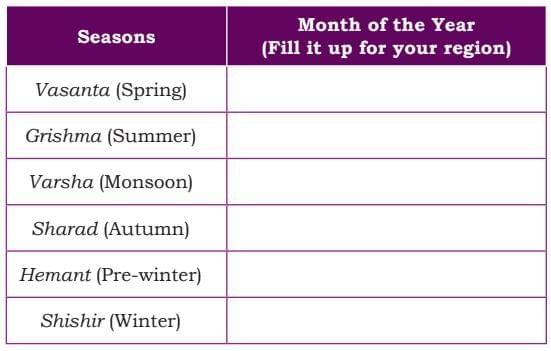
- India has six seasons: Vasanta (Spring), Grishma (Summer), Varsha (Monsoon), Sharad (Autumn), Hemant (Pre-winter), and Shishir (Winter).
- Students can find out the names of seasons in their region.

- Students are advised to do the following with their parents.
 e.g. In Punjabi, Gujarati and Marathi:
e.g. In Punjabi, Gujarati and Marathi: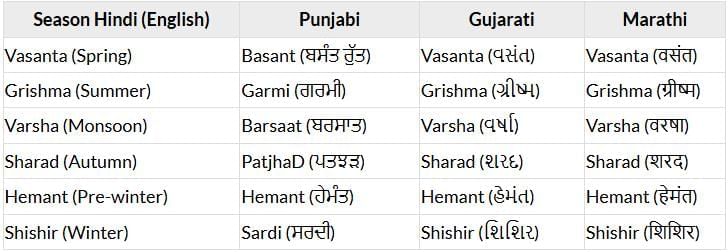
India has the wettest place on Earth — Mawsynram in Meghalaya.
It also has one of the driest places — the Thar Desert
Celebrating Seasons
Seasons bring special traditions to life. Let’s see how India celebrates them!
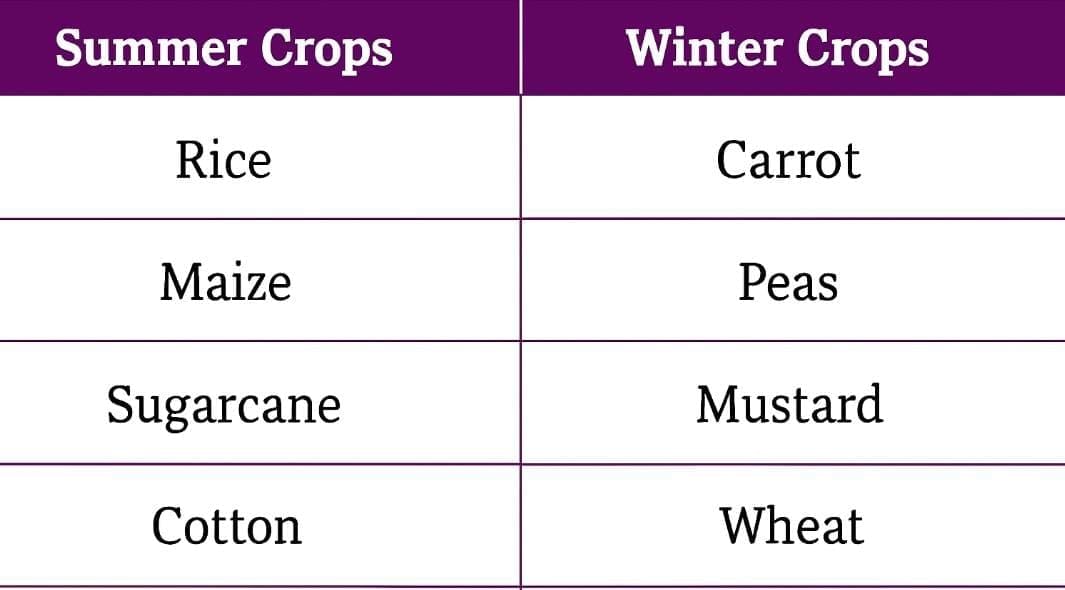
- Farmers grow different crops in each season, like some in winter and others in summer.
- Some crops grow best in summer, while others grow in winter.
- Some are planted in the rainy season because they need more water.
- With help from teachers and elders, students learn about local summer and winter crops.
- Many songs in India are connected to seasons, adding joy to these changes.

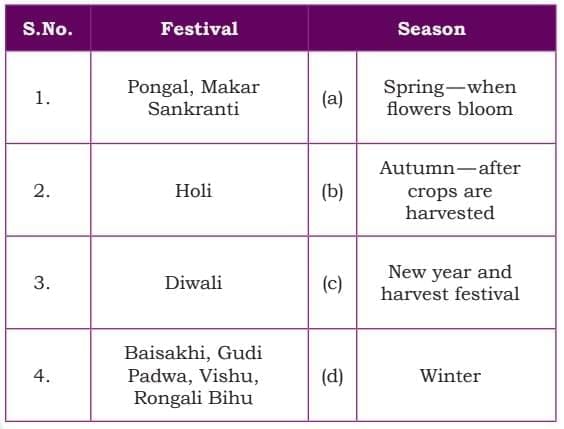
- Festivals like Pongal and Makar Sankranti celebrate spring and harvests.
- Holi is linked to spring, when flowers bloom, and Diwali to autumn, after crops are harvested.
- Baisakhi, Gudi Padwa, Vishu, and Rongali Bihu mark the new year and harvest in winter.
- Every season brings something special and has its own magic, shaping everything around us beyond just weather changes.
- Seasons help us know how plants grow, how animals live, and what people eat, wear, and do, from harvested crops to celebrated festivals.
- They give rhythm to our lives, reminding us that change is natural and necessary, while teaching us about life’s cycles.
- As you step out each day, you are witnessing nature’s rhythm unfolding, one season at a time
|
11 videos|212 docs|10 tests
|
FAQs on Rhythms of Nature Chapter Notes - Our Wondrous World Class 5 - New NCERT
| 1. What causes day and night? |  |
| 2. How do the seasons change throughout the year? |  |
| 3. What are some key characteristics of each season? |  |
| 4. How can we create a seasons chart in the classroom? |  |
| 5. Why is understanding day, night, and seasons important for students? |  |
















