Class 5 Exam > Class 5 Notes > Mathematics Class 5 ICSE > Chapter Notes: Numbers
Numbers Chapter Notes | Mathematics Class 5 ICSE PDF Download
Introduction
Numbers are the building blocks of mathematics, and in this exciting chapter, we dive into the world of large numbers, exploring how they are written, read, and used in different systems. Imagine counting stars in the sky or grains of sand on a beach—numbers help us make sense of such huge quantities! This chapter takes you on a journey to understand numbers up to crores, learn the Indian and International number systems, and discover how to compare, arrange, and round off these numbers. Get ready to unlock the magic of numbers and see how they work in our daily lives!
Numbers up to Crores
- Numbers larger than 6 digits are explored, building on previous knowledge.
- The smallest 6-digit number is 1,00,000, and the largest is 9,99,999.
- Adding 1 to the largest 6-digit number (9,99,999) gives the smallest 7-digit number: 10,00,000 (ten lakhs).
- The largest 7-digit number is 99,99,999 (ninety-nine lakh ninety-nine thousand nine hundred ninety-nine).
- Adding 1 to the largest 7-digit number gives the smallest 8-digit number: 1,00,00,000 (one crore).
- The largest 8-digit number is 9,99,99,999 (nine crore ninety-nine lakh ninety-nine thousand nine hundred ninety-nine).
- Adding 1 to the largest 8-digit number gives the smallest 9-digit number: 10,00,00,000 (ten crores).
- The largest 9-digit number is 99,99,99,999 (ninety-nine crore ninety-nine lakh ninety-nine thousand nine hundred ninety-nine).
- The crores period includes crores and ten crores, following the lakhs period.
Example: Adding 1 to the largest 8-digit number, 9,99,99,999, results in 10,00,00,000, which is read as ten crores.
Indian and International Number Systems
- Two systems are used to read and write large numbers: Indian and International number systems.
- Each system groups digits into periods to make numbers easier to read and understand.
Indian Number System
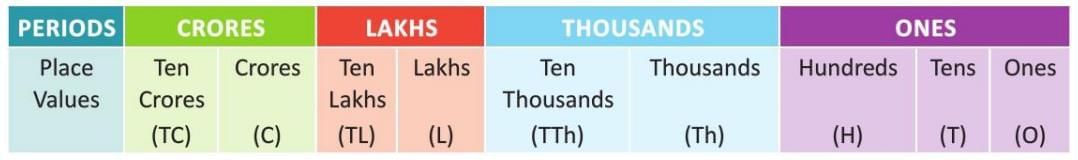
- Divides large numbers into periods: ones, thousands, lakhs, and crores.
- Ones period includes ones, tens, and hundreds (3 places).
- Thousands period includes thousands and ten thousands (2 places).
- Lakhs period includes lakhs and ten lakhs (2 places).
- Crores period includes crores and ten crores (2 places).
- Commas are placed starting from the right: first after 3 digits, then after every 2 digits.
- This helps identify place values and read numbers easily.
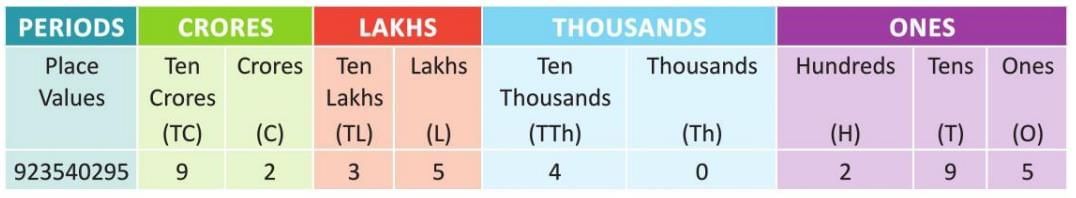
- Example: For the number 92,35,40,295, commas are placed as 92,35,40,295. It is read as ninety-two crore thirty-five lakh forty thousand two hundred ninety-five.
International Number System
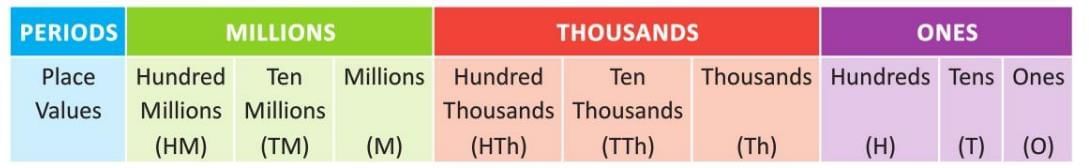
- Divides large numbers into periods: ones, thousands, and millions.
- Each period has 3 places: ones (ones, tens, hundreds), thousands (thousands, ten thousands, hundred thousands), and millions (millions, ten millions, hundred millions).
- Commas are placed after every 3 digits from the right.
- This system is used worldwide for reading and writing large numbers.
- Example: The number 618,345,215 is written with commas as 618,345,215 and read as six hundred eighteen million three hundred forty-five thousand two hundred fifteen.
Comparison of Indian and International Number Systems
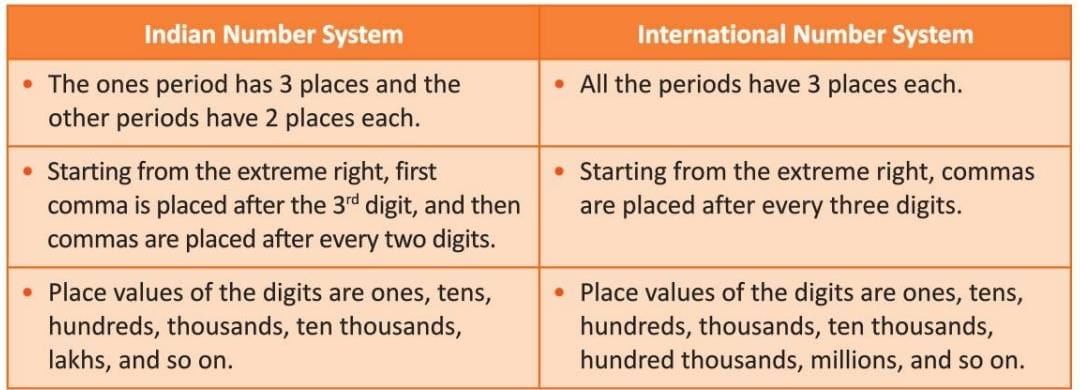

- Example: The number 795,432,651 in Indian system is 79,54,32,651 (seventy-nine crore fifty-four lakh thirty-two thousand six hundred fifty-one). In International system, it is 795,432,651 (seven hundred ninety-five million four hundred thirty-two thousand six hundred fifty-one).
Place Value and Face Value
- Face value is the value of the digit itself, regardless of its position.
- Place value depends on the digit’s position in the number.
- Place value is calculated by multiplying the digit by its place (e.g., ones, tens, lakhs).
- Example: In 62,14,36,754, the face value of 2 is 2, and its place value is 2 crores (2,00,00,000). The face value of 1 is 1, and its place value is 1 ten lakh (10,00,000).
Expanded Form and Standard (Short) Form
- Expanded form shows a number as the sum of the place values of its digits.
- Standard form is the usual way of writing a number using digits in their correct places.
- To write in expanded form, break the number into its place values (e.g., crores, lakhs).
- To write in standard form, combine the digits in their correct place value positions.
- Example: The number 23,40,28,762 in expanded form is 20,00,00,000 + 3,00,00,000 + 40,00,000 + 20,000 + 8,000 + 700 + 60 + 2.
Predecessor and Successor
- The predecessor of a number is found by subtracting 1 from it.
- The successor of a number is found by adding 1 to it.
- Example: For 3,42,13,211, the predecessor is 3,42,13,211 - 1 = 3,42,13,210, and the successor is 3,42,13,211 + 1 = 3,42,13,212.
Comparison of Numbers
- A number with more digits is always larger than a number with fewer digits.
- For numbers with the same number of digits, compare digits from left to right (highest place value to lowest).
- If digits in the highest place are the same, move to the next place and continue comparing.
- Shortcut method: Write numbers one below the other, mark same digits with a tick (✓) and different digits with a cross (✗), then compare the first different digits.
Example: To compare 8,06,13,408 and 7,8921,036, align them:

Ordering of Numbers
- Ascending order arranges numbers from smallest to largest.
- Descending order arranges numbers from largest to smallest.
- First, compare the number of digits to identify the smallest and largest numbers.
- For numbers with the same number of digits, compare digits step-by-step from left to right.
- Example: For numbers 8,06,13,408; 83,43,999; 13,00,55,444; 7,89,21,036:
Ascending order: 83,43,999 < 7,89,21,036 < 8,06,13,408 < 13,00,55,444
Descending order: 13,00,55,444 > 8,06,13,408 > 7,89,21,036 > 83,43,999
Formation of Numbers
- Different numbers can be formed by arranging given digits in various orders.
- Arranging digits in ascending order (smallest to largest) gives the smallest number.
- Arranging digits in descending order (largest to smallest) gives the largest number.
- Example: Using digits 2, 3, 5, 6, 1, 4, 7, the smallest 7-digit number is 12,34,567, and the largest is 76,54,321.
Rounding Off Numbers
- Rounding off gives an approximate value of a number to the nearest 10, 100, or 1,000.
Rounding Off to the Nearest 10
- Look at the ones place digit.
- If the ones digit is 4 or less, keep the tens digit the same and make the ones digit zero.
- If the ones digit is 5 or more, increase the tens digit by 1 and make the ones digit zero.
- Example: For 69,33,89,427, the ones digit is 7 (more than 5), so it rounds to 69,33,89,430.
Rounding Off to the Nearest 100
- Look at the tens place digit.
- If the tens digit is 4 or less, keep the hundreds digit the same and make tens and ones digits zero.
- If the tens digit is 5 or more, increase the hundreds digit by 1 and make tens and ones digits zero.
- Example: For 64,34,76,586, the tens digit is 8, so it rounds to 64,34,76,600.
Rounding Off to the Nearest 1,000
- Look at the hundreds place digit.
- If the hundreds digit is 4 or less, keep the thousands digit the same and make hundreds, tens, and ones digits zero.
- If the hundreds digit is 5 or more, increase the thousands digit by 1 and make hundreds, tens, and ones digits zero.
- Example: For 1,85,63,901, the hundreds digit is 9, so it rounds to 1,85,64,000.
The document Numbers Chapter Notes | Mathematics Class 5 ICSE is a part of the Class 5 Course Mathematics Class 5 ICSE.
All you need of Class 5 at this link: Class 5
|
138 docs|15 tests
|
FAQs on Numbers Chapter Notes - Mathematics Class 5 ICSE
| 1. What are the main differences between the Indian and International number systems? |  |
Ans. The Indian number system groups digits in pairs after the first three digits, using terms like lakh and crore. In contrast, the International system groups digits in threes, using terms like thousand and million. For example, 1,00,000 in the Indian system is written as 100,000 in the International system.
| 2. How do you find the place value and face value of a digit in a number? |  |
Ans. The place value of a digit is determined by its position in the number. For example, in the number 5,678, the place value of 6 is 600 (as it is in the hundreds place). The face value is simply the digit itself, which is 6 in this case.
| 3. What is the expanded form of a number and how is it written? |  |
Ans. The expanded form of a number breaks it down to show the value of each digit. For example, the expanded form of 4,325 is 4,000 + 300 + 20 + 5. It shows each digit's contribution to the overall number.
| 4. How do you round off numbers and why is it important? |  |
Ans. Rounding off a number means adjusting it to the nearest specified place value, making calculations easier. For example, rounding 67 to the nearest ten results in 70. It is important for simplifying numbers in calculations and estimating values.
| 5. What methods can be used to compare and order numbers? |  |
Ans. To compare and order numbers, you can look at the number of digits first; more digits typically mean a larger number. If the digits are the same length, compare them one digit at a time from left to right. Arrange the numbers from smallest to largest or vice versa based on this comparison.
Related Searches





















