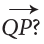Geometry Class 3 Notes Maths

What is Geometry?
Look around you! You will see different shapes everywhere—a ball, a book, or a table. But how do we know which shape is which?
Geometry is the study of shapes and how they work. It helps us understand how big or small things are, how they fit together, and how they move. We learn about points, lines, angles, and solid objects like cubes and spheres.
Simply put, geometry is all about the shapes we see in the world around us!
What are the Basic Elements of Geometry?
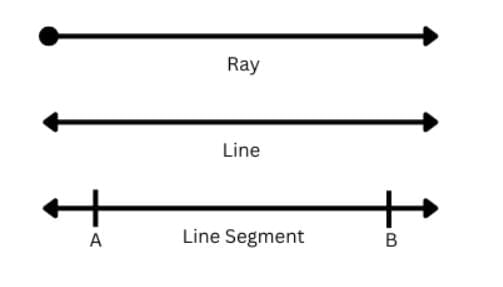
Let us now, learn about few basic elements of geometry which are:1. Point
2. Line Segment
3. Line
4. Ray
1. Point
A tiny dot ‘·’ represents a point. We name points by a capital letter such as A, B, C, D, ... which we write near the dot.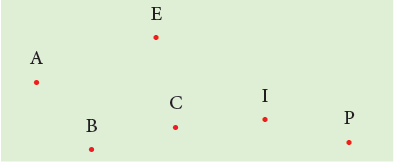
A point shows an exact location or position. It has no length, breadth or depth.
2. Line Segment
A line segment is the shortest path between two points. It has two endpoints and a fixed length.
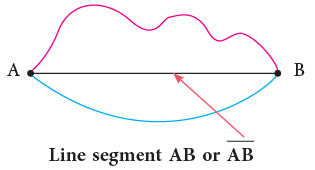
- The figure shows three paths from a fixed point A to another fixed point B. Two paths are curved and one path is straight. The straight path is the shortest path.
- We call the straight path between the fixed points A as B a line segment.
- A line segment AB has two end points, A and B and is denoted by drawing a bar over AB, i.e.,
 You can draw a line segment through two points A and B with the help of a ruler.
You can draw a line segment through two points A and B with the help of a ruler.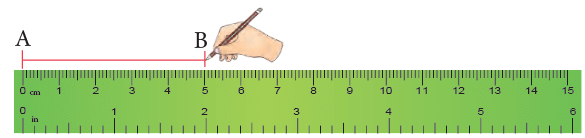
- Put a ruler in such a way that one of its straight edges touches both the points. Now, move the pencil from A to B along the edge of the ruler.
- Whenever two line segments meet, they meet at a point.
A line segment has a fixed length.
Observe the following figures: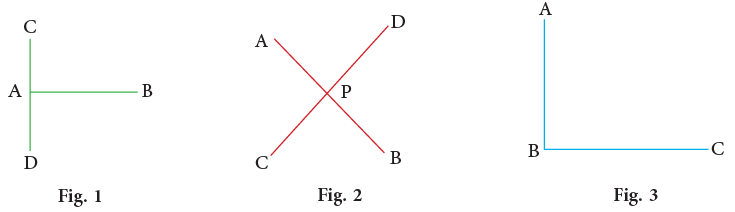 In the first figure, line segments CD and AB are meeting at the point A. In the second figure, line segments CD and AB are meeting at the point P. In the third figure, line segments AB and BC are meeting at the point B.
In the first figure, line segments CD and AB are meeting at the point A. In the second figure, line segments CD and AB are meeting at the point P. In the third figure, line segments AB and BC are meeting at the point B.
We use line segments to build figures as given below: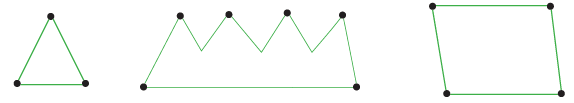
3. Line
A line is different from a line segment. It goes on forever in both directions. The picture of a line is drawn by putting arrowheads at both ends. The arrowheads at ends tell us that it goes on and on in both directions.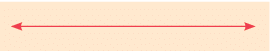 The figure given below shows the line AB. It is denoted as
The figure given below shows the line AB. It is denoted as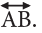

- A line segment is a part of a line.
- A line has no end points and it has no fixed length.
4. Ray
A ray is a part of a line which can be extended endlessly in one direction only.
 Think of the rays of the Sun. Do they have a starting place and then go on and on in one direction?
Think of the rays of the Sun. Do they have a starting place and then go on and on in one direction?
- A ray has only one end-point which is its tailpoint.
- To name a ray, first name its end-point. Then, name any other point on the ray.
- Thus, the ray having end point P and Q as any other point on it is denoted by
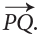
Look at the following figures:
What is the end point of ray PQ?
Ans: P
And of ray QP?
Ans: Q
Why isnot the same as
Ans: Their directions and end-points are different.
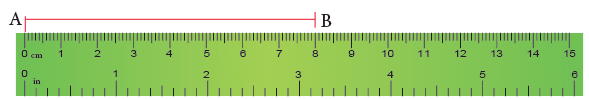
Measuring and Drawing Line Segments
To measure the length of a line segment, a ruler is used.
To measure a line segment:
Place a ruler so that its edge lines up with the segment.
Align the 0 mark with one endpoint.
Read the mark where the other endpoint falls.
Example: If one endpoint is at 0 cm and the other is at 8 cm, the length of the segment is 8 cm.
To Draw a Line Segment of Given Length
Method
Suppose, we have to draw a line segment of length 6 cm.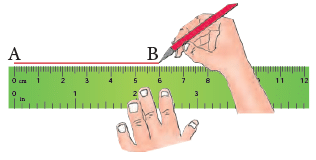
Step 1: Place the ruler on the plane paper and hold it as shown in the figure.
Step 2: Mark two points A and B against the marks 0 and 6 on the ruler.
Step 3: Pressing the ruler evenly, join these two points A and B with a pencil. The line segment AB thus drawn is the required line segment 6 cm long.
If instead of joining the points against the marks 0 and 6, you had joined them against the marks 1 and 7, or 2 and 8 or 5 and 11 etc., you would have still drawn a line segment 6 cm long.
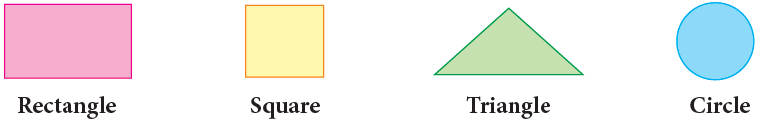
Flat (Plane - 2D) Shapes
Plane shapes are flat and can be drawn on paper. Some common plane shapes are:
Let us learn about 2D shapes in detail:
1. Rectangle
The figure given on the right is a rectangle. It has four corners (vertices) and four sides.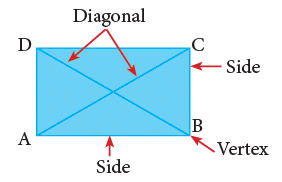
- Has 4 sides and 4 corners (vertices).
- Opposite sides are equal.
- Has 2 diagonals that are equal in length.
2. Square
A square is a closed figure. It has four sides and four vertices. If you measure its sides, you will find that:
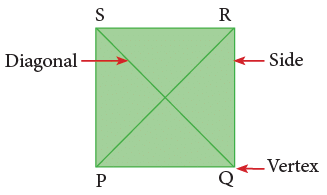
All the sides of a square are equal.
In the square PQRS, we have:
Vertices (Corner): P, Q, R, S;
Sides: PQ, QR, RS, SP;
Diagonals: PR and SQ
A square also has two diagonals, which are of equal length
Thus, in a square PQRS, we have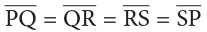 and diagonal
and diagonal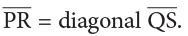
3. Triangle
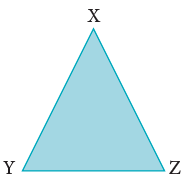 The figure shown alongside is of a triangle. It has three vertices and three sides. In the triangle XYZ, we have:
The figure shown alongside is of a triangle. It has three vertices and three sides. In the triangle XYZ, we have:
Vertices (Corner): X, Y, Z;
Sides: XY, YZ, ZX
The sides of a triangle may or may not be equal.
4. Circle
A circle is a simple closed curve. It does not have any corner or side. Look at the figure given alongside:
Look at the figure given alongside: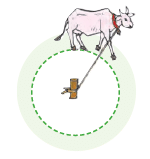 Will the bullock move along a circular path, if the rope is tight?
Will the bullock move along a circular path, if the rope is tight?
Ans: Yes
If several stones are placed along the path, will the distance from the stake to each of these points be the same?
Ans: Yes
5. Parts of a Circle
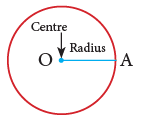 A circle has a centre. A line segment from the centre to the circle is called radius.
A circle has a centre. A line segment from the centre to the circle is called radius.
Point O is the centre. OA is a radius.
Drawing a circle
Compasses are used to draw circles. The pictures given below show how to do it.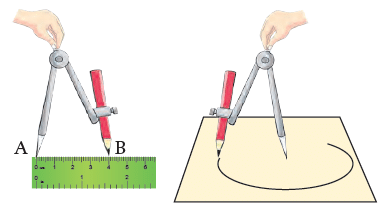
- Mark some point to be the centre of the circle.
- Name this point A. Use a ruler to locate a point that is 4 cm from point A in any direction you choose. Call this point B.
- Put the steel tip of the compasses as on A. Open or close the compasses so that the pencil tip is on B. Press down on the steel tip and turn the compasses to draw a circle. This circle has a 4 cm radius.
Idea of Space
1. The football rolls on the ground. Where does it go after rising off from the ground when it is kicked up? It moves up in space.
2. Have you heard or seen a pilot bailing out from his aeroplane in an emergency? He does so with the help of a parachute.
The aeroplane moves in space. The paratrooper moves in space after having bailed out.
3. Have you ever seen a satellite? It moves in space. The moon also moves in space. All the stars move in space. Our earth also moves in space.
4. You walk on the ground. You swim along the length and breadth of a swimming pool. When you jump from the diving board, you move in space.
Solid (3D) Shapes
Some things around us, like a ball, a box, or an ice cream cone, cannot be drawn exactly on paper because they are not flat. We can only draw their flat shape, like a circle for a football.
These objects are called solid shapes because they have three dimensions – length, width, and height. Solid shapes take up space and are different from flat shapes.
Examples of Solid Shapes
- Sphere – Looks like a football or tennis ball
- Cube – Looks like a dice
- Cuboid – Looks like a matchbox
- Cylinder – Looks like a drum
- Cone – Looks like an ice cream cone
Solid shapes are everywhere around us!
Some common solid shapes are shown below: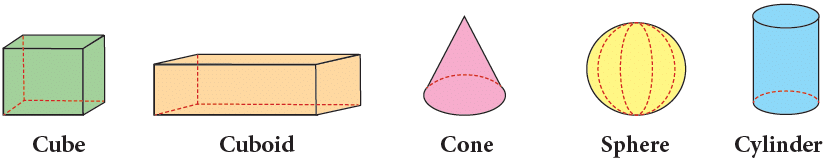
Surfaces of Solid Shapes: Plane vs. Curved
A solid occupies space. The part of a solid which we usually see and touch is called the surface of the solid. Solids have different types of surfaces.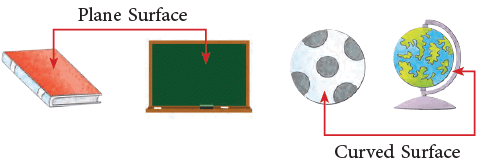 The notebook and the blackboard have plane surfaces. The ball and the globe have curved surfaces.
The notebook and the blackboard have plane surfaces. The ball and the globe have curved surfaces.
Some objects like an unsharpened pencil (cylinder) have both types of surfaces.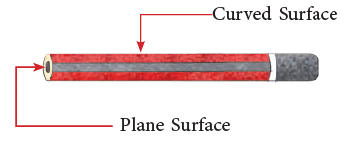
Faces, Edges and Vertices
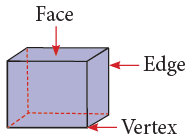
- A face is a flat surface of a solid figure.
- An edge is formed where two or more two faces meet.
- A corner of a solid is called a vertex. It is a point where the two or more edges meet.
Types of Solids
1. Cube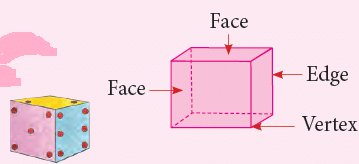
- A cube has 6 plane faces, 12 edges and 8 vertices.
- All the six faces are identical. They are squares.
- Common examples of a cube are: Ice cube, Playing die, Rubik’s cube, etc.
2. Cuboid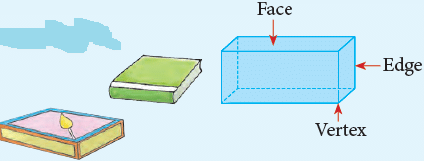
- A cuboid has 6 plane faces, which are rectangles, 12 edges and 8 vertices. Its opposite faces are identical.
- Common examples of a cuboid are: Matchbox, Book, Gift box, etc.
3. Cylinder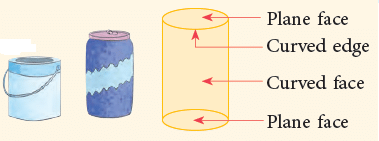
- A cylinder has 2 plane faces and 1 curved face.
- It has 2 edges and no vertices.
- Common examples of a cylinders are: Paint can, Post box, Soft drink can, etc.
4. Cone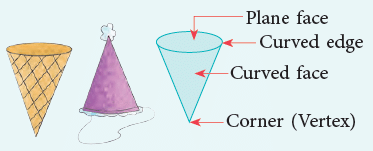
- A cone has 1 plane face and 1 curved face.
- It has 1 edge and 1 vertex.
- Common examples of a cone are: Icecream cone, Joker’s cap, Traffic cone, etc.
5. Sphere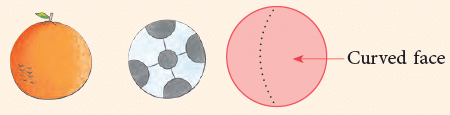
- A sphere has only 1 curved face.
- It has no vertices and no edges.
- Common examples of a sphere are: Orange, Football, Earth, etc.
What is Symmetry?
If one part of a figure matches the other part exactly, when it is folded, the figure is said to be symmetrical.- Line of Symmetry: The line of symmetry is where the fold is.
The dotted lines in the figures given below show the line of symmetry: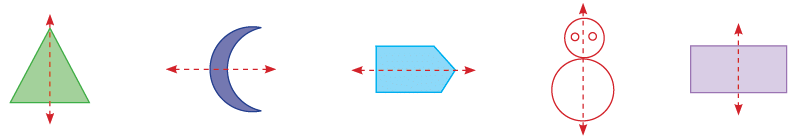
- Mirror Images: A shape is said to be symmetrical, when on placing one-half of the shape in front of a mirror, you see the other half in the mirror. Each half is called a mirror image of the other.
Study the following images: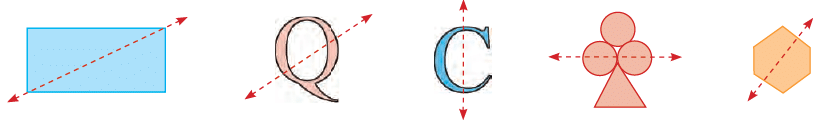 The dotted lines in the figures given above are not lines of symmetry. If the figure is cut along the dotted line, then both the parts when folded along the dotted line do not fit exactly into each other.
The dotted lines in the figures given above are not lines of symmetry. If the figure is cut along the dotted line, then both the parts when folded along the dotted line do not fit exactly into each other.
Some Practice Questions for you!
1. Identify the Shape:
Look at the objects around you. Which of these is a solid shape and which is a plane shape?
- A book
- A football
- A handkerchief
- A dice
 (Write "Solid" or "Plane" next to each object.)
(Write "Solid" or "Plane" next to each object.)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer:
- A book → Solid
- A football → Solid
- A handkerchief → Plane
- A dice → Solid
2. Find the Missing Word:
- A cube has __ faces, __ edges, and __ vertices.
- A sphere has __ faces, __ edges, and __ vertices.
- A cone has __ face(s), __ edge(s), and __ vertex/vertices.
(Fill in the blanks with the correct numbers!)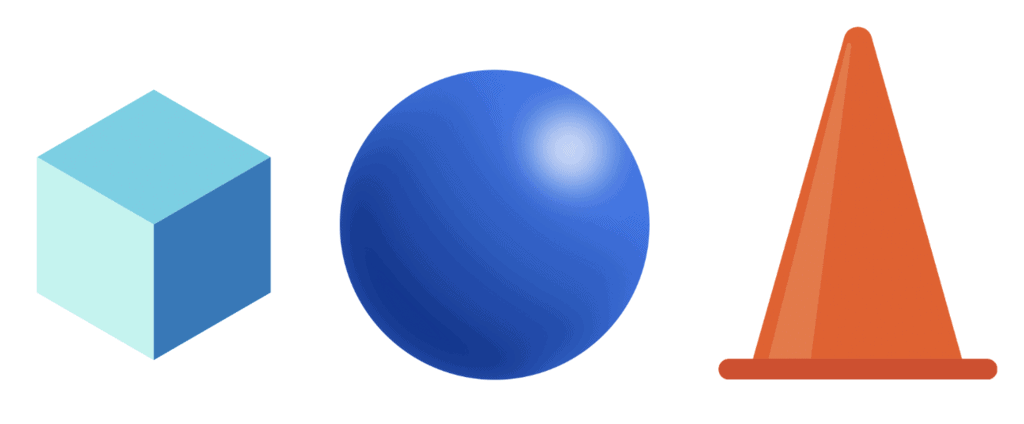
 View Answer
View Answer 
Answer:
- A cube has 6 faces, 12 edges, and 8 vertices.
- A sphere has 1 face, 0 edges, and 0 vertices.
- A cone has 2 faces, 1 edge, and 1 vertex.
|
45 videos|88 docs|61 tests
|
FAQs on Geometry Class 3 Notes Maths
| 1. What is the definition of geometry? |  |
| 2. What are the basic elements of geometry? |  |
| 3. What are some common plane shapes in geometry? |  |
| 4. How do we define the idea of space in geometry? |  |
| 5. What is symmetry in geometry? |  |