Contemporary Western Democracies Chapter Notes | AP European History - Grade 9 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Economic Growth and the Welfare State |

|
| Economic Stagnation and Public Debate |

|
| Timeline: Key Economic Developments in Western Democracies |

|
Introduction
Following World War II, Western Europe embraced democracy and rebuilt through robust economic growth and expansive welfare states. The triumph over fascism contrasted with communism’s rise in the East, shaping ideological divides. This chapter notes explores the "economic miracle," the development of welfare systems, and the challenges they faced by the late 20th century, highlighting debates over their sustainability that continue to influence policy today.
Economic Growth and the Welfare State
Postwar Prosperity and the "Economic Miracle"
In the decades after World War II, Western European economies experienced remarkable growth, often termed the "economic miracle." This rapid expansion was driven by:
- The Marshall Plan: Over $13 billion in U.S. aid supplied capital to reconstruct infrastructure and industries. Increased industrial production and growing consumer demand. Export-oriented economies, particularly in West Germany and France.
This prosperity enabled governments to expand social welfare programs, leading to the establishment of comprehensive "cradle-to-grave" welfare states.
The Role of the Welfare State
As economies flourished, Western European governments adopted welfare policies based on Keynesian economics, using public spending to stabilize demand and support unemployed citizens.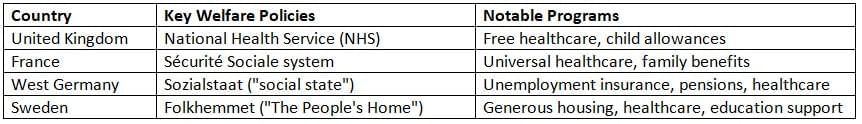
Economic Stagnation and Public Debate
The Crisis of the Welfare State
- By the 1970s, the global economy faced stagnation and inflation, known as stagflation, caused by:
- The 1973 oil crisis.
- Declining productivity rates.
- Increasing global competition, particularly from Asian economies.
- These challenges made it increasingly difficult to sustain expansive welfare systems.
Criticism and Retrenchment
The once-celebrated welfare systems faced growing criticism:
- High taxation levels, required to finance benefits, led to resistance from middle and upper classes.
- Budget deficits placed significant pressure on national economies.
- Conservative leaders, such as Margaret Thatcher in the United Kingdom and Helmut Kohl in West Germany, advocated for welfare reforms to address inefficiencies.
Timeline: Key Economic Developments in Western Democracies

Conclusion
Post-war Western democracies capitalized on their economic growth to establish some of the most comprehensive welfare systems in history. These programs became central to European identity and lifted millions out of poverty. However, economic challenges in the 1970s and 1980s sparked intense debates over taxation, government spending, and the role of the state, discussions that continue to influence public policy today.
Key Terms
- Childcare: The provision of care for children by parents, guardians, or professionals, gaining prominence post-war as women joined the workforce, driving demand for formal childcare services.
- Communism: An ideology advocating for a classless society with collective ownership, significantly influencing global politics and ideological conflicts with capitalism during the 20th century.
- Cradle-to-Grave Social Welfare Programs: Comprehensive social support systems providing benefits from birth to death, including healthcare, education, and pensions, prominent in post-war Western Europe to promote equity and stability.
- Democracy: A government system where power lies with the people, exercised directly or through elected representatives, fostering participation and accountability, foundational to post-war Western Europe.
- Economic Miracle: The rapid economic growth in Western Europe during the 1950s and 1960s, driven by industrial expansion, technological advancements, and foreign aid, transforming war-torn economies.
- Education Programs: Structured initiatives to enhance education quality and skills, critical post-war for addressing labor needs, boosting economic growth, and adapting to technological changes.
- Fascism: A far-right ideology emphasizing authoritarian nationalism and state control, opposing democracy and communism, defeated in World War II but shaping post-war ideological divides.
- Great Depression: A severe global economic crisis (1929–1930s) marked by unemployment and poverty, influencing pre-war policies and post-war economic recovery efforts.
- Housing Assistance: Programs providing support for affordable housing, such as subsidies and public housing, vital post-war for social stability and economic growth in Western Europe.
- Marshall Plan: A 1948 U.S. initiative providing over $13 billion to rebuild Western European economies, countering communism and promoting political stability.
- Public Welfare: Government programs to support citizens’ basic needs, expanded post-war to prevent poverty and enhance quality of life in Western Europe.
- Social Security: A government program providing financial support for retirement, disability, or survivors, influential post-war in Europe for economic stability and social safety.
- Universal Healthcare: A system ensuring healthcare access for all citizens, funded through taxation, widely adopted in post-war Western Europe to promote public health.
- Welfare Debate: Discussions over the role, impact, and efficiency of welfare programs, intensified post-war by economic challenges, reflecting ideological divides on state intervention.
- World War II: A global conflict (1939–1945) between the Allies and Axis powers, reshaping political, social, and economic structures, and setting the stage for post-war recovery.
FAQs on Contemporary Western Democracies Chapter Notes - AP European History - Grade 9
| 1. What is the relationship between economic growth and the welfare state in contemporary Western democracies? |  |
| 2. How has economic stagnation influenced public debate in Western democracies? |  |
| 3. What are some key economic developments that have shaped Western democracies in recent decades? |  |
| 4. Why is understanding the timeline of economic developments important for analyzing contemporary issues in Western democracies? |  |
| 5. What role do citizens play in shaping the welfare state during times of economic change? |  |














